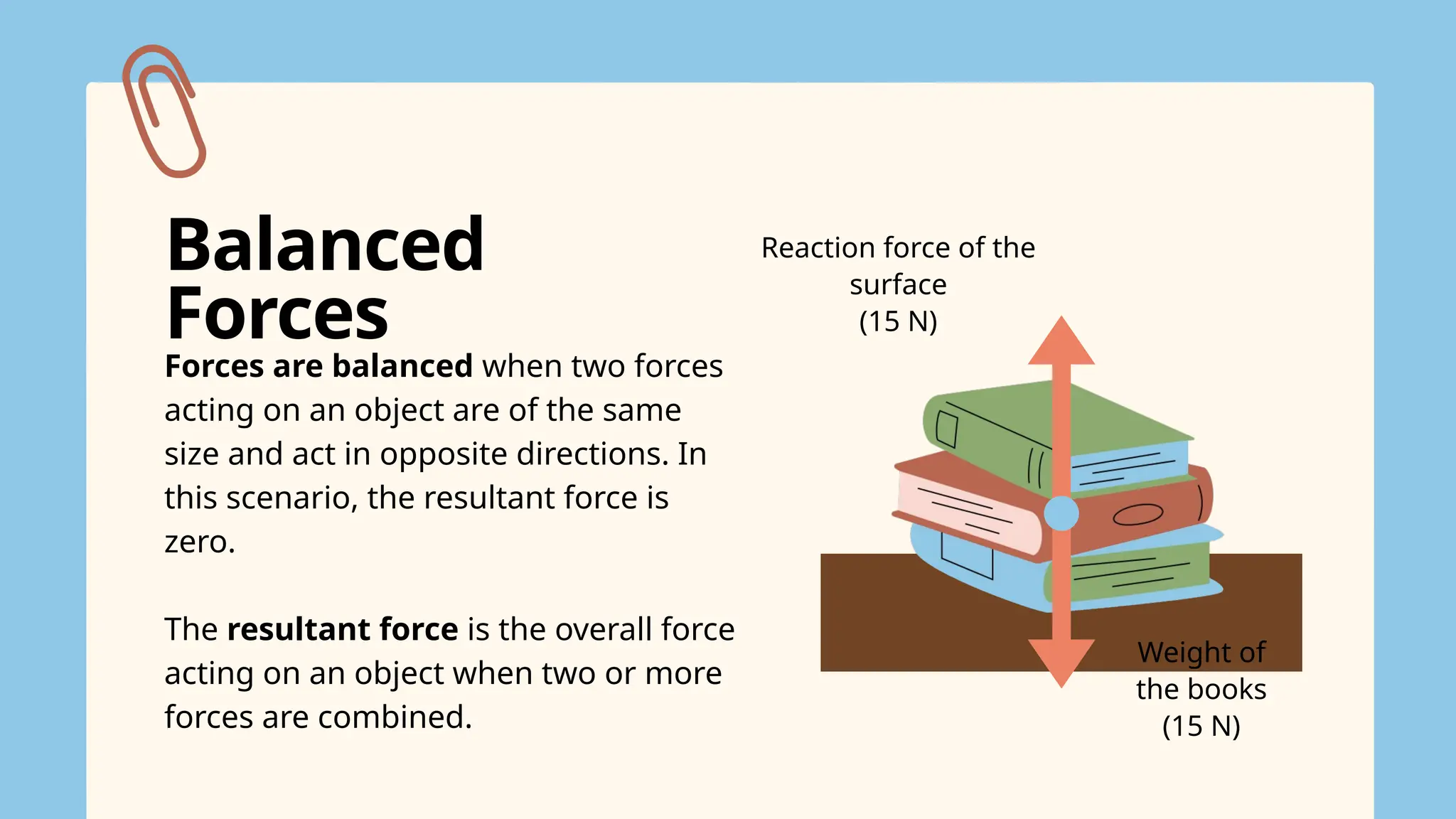
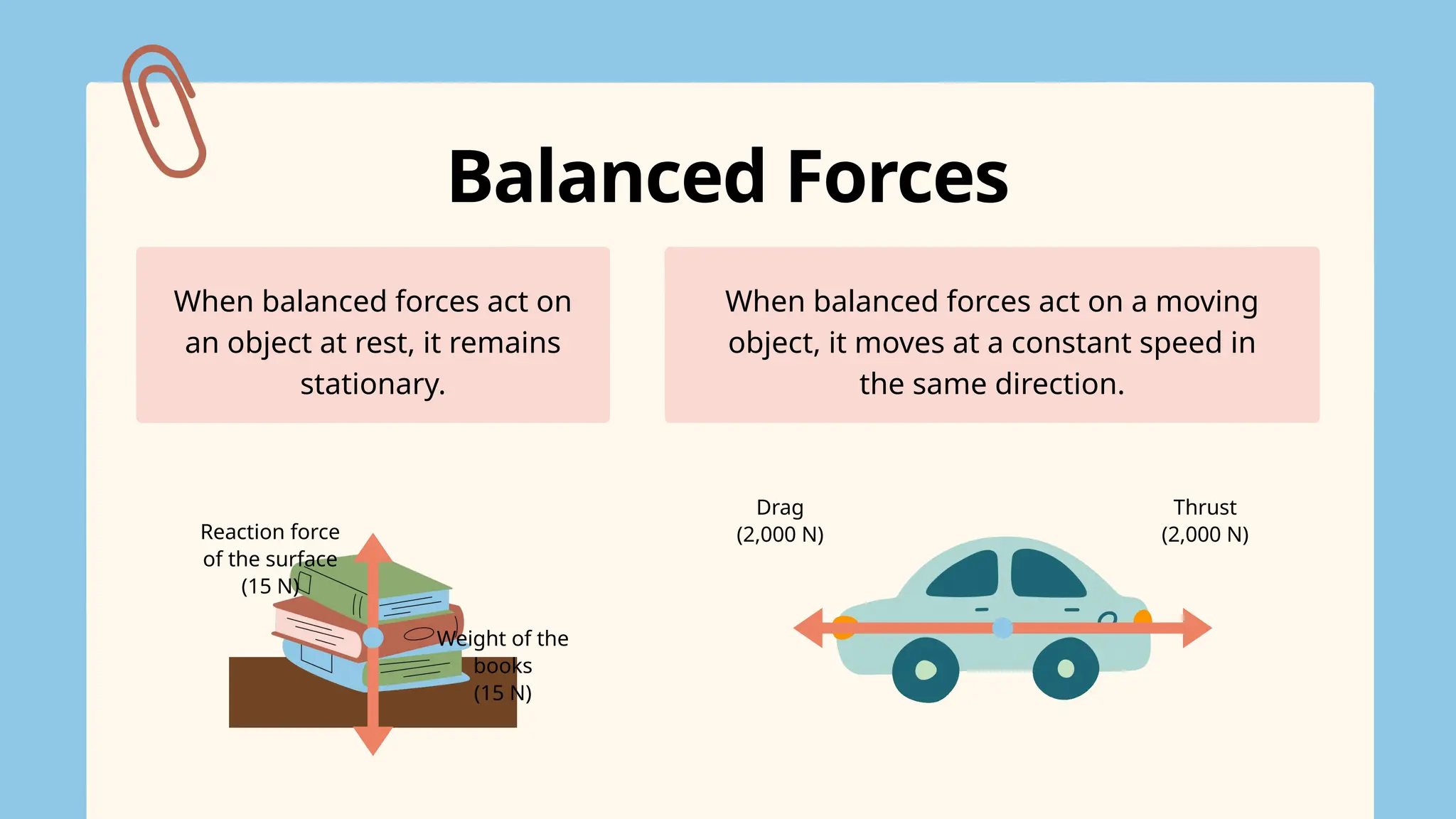
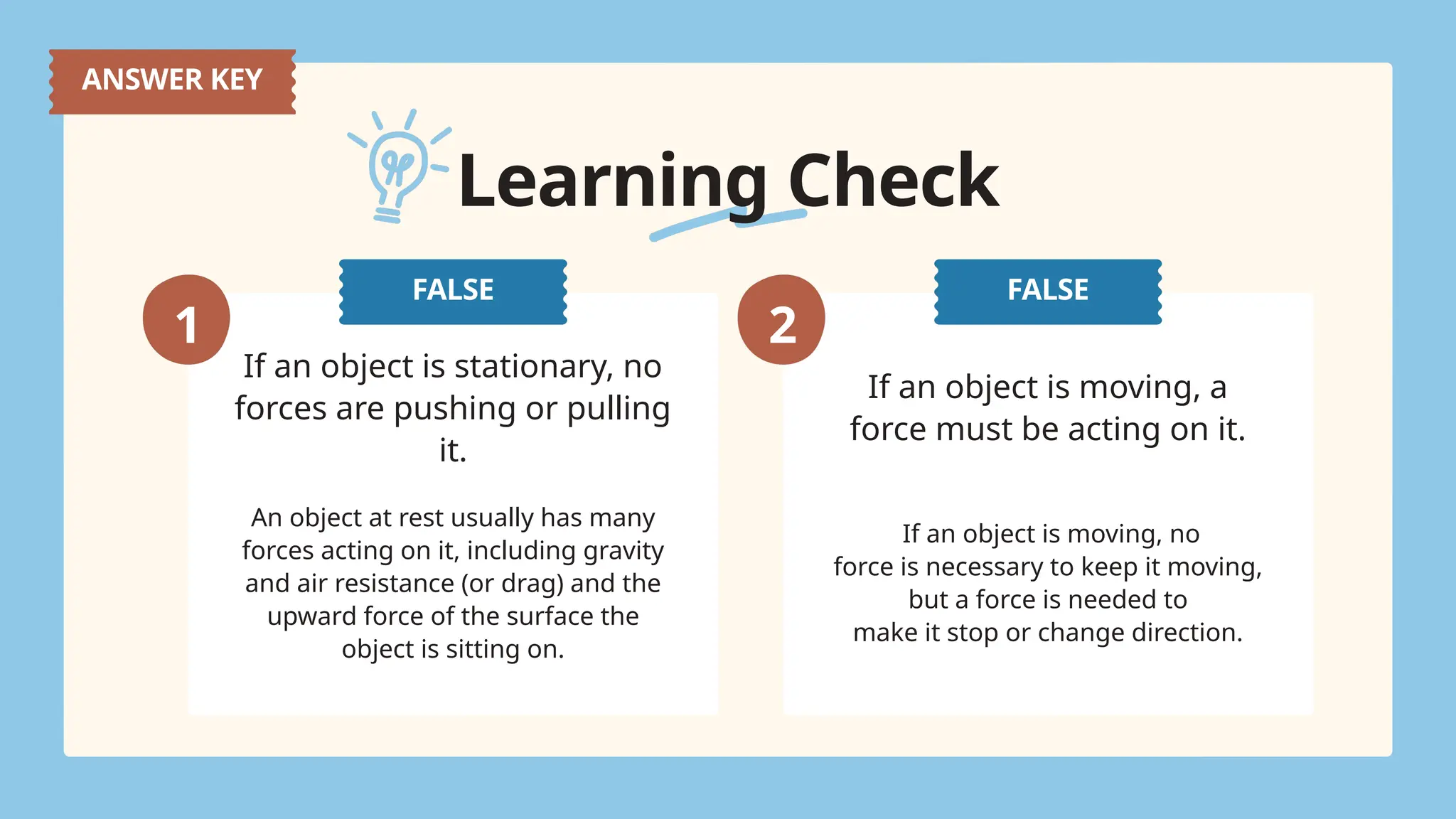
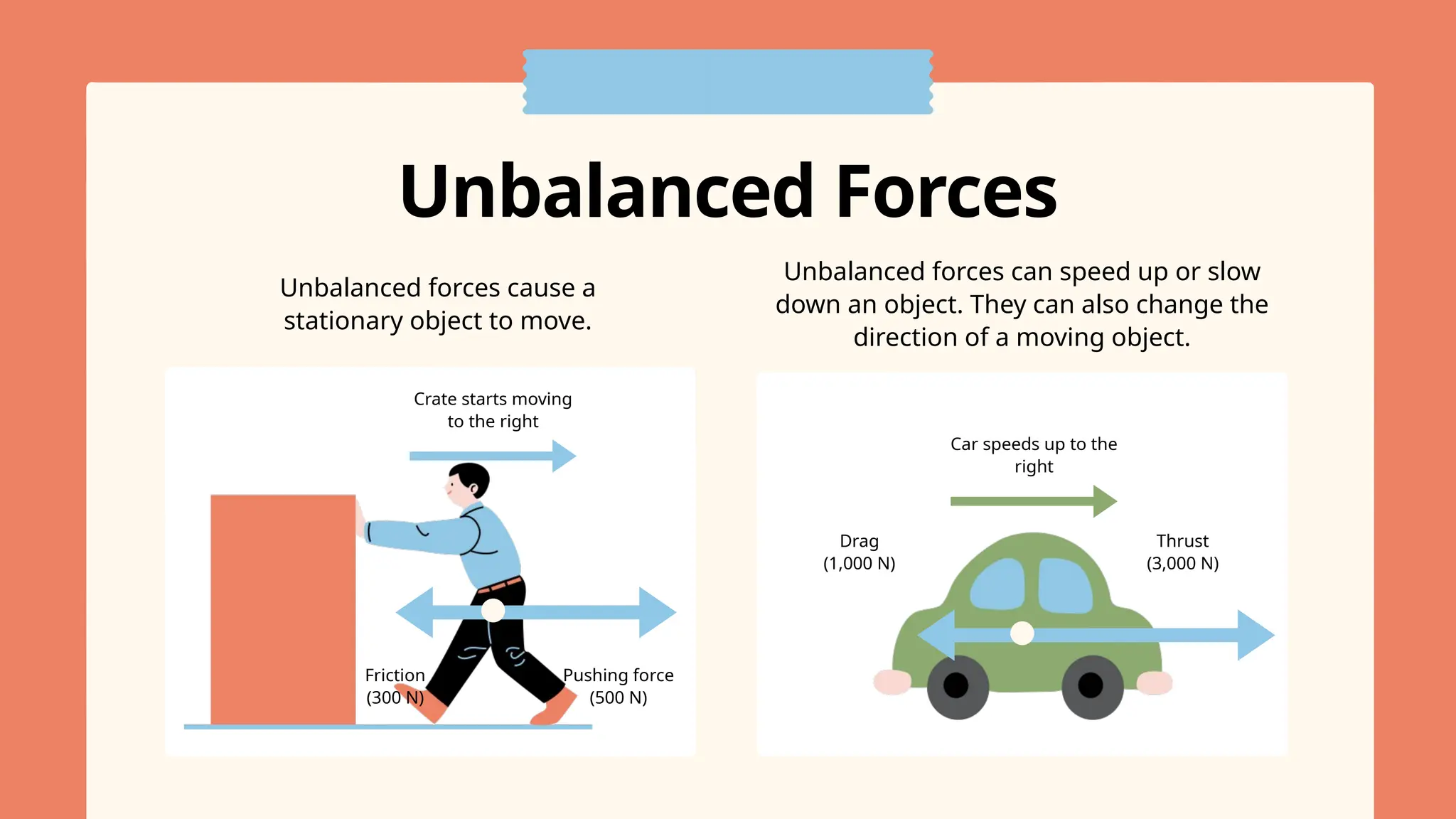
The document explains the concepts of forces, specifically focusing on balanced and unbalanced forces, which can cause changes in an object's motion. It details how forces are represented through force diagrams with arrows indicating size and direction, as well as the significance of the resultant force. The text also highlights that balanced forces keep an object stationary or moving at a constant speed, while unbalanced forces lead to acceleration or a change in motion.