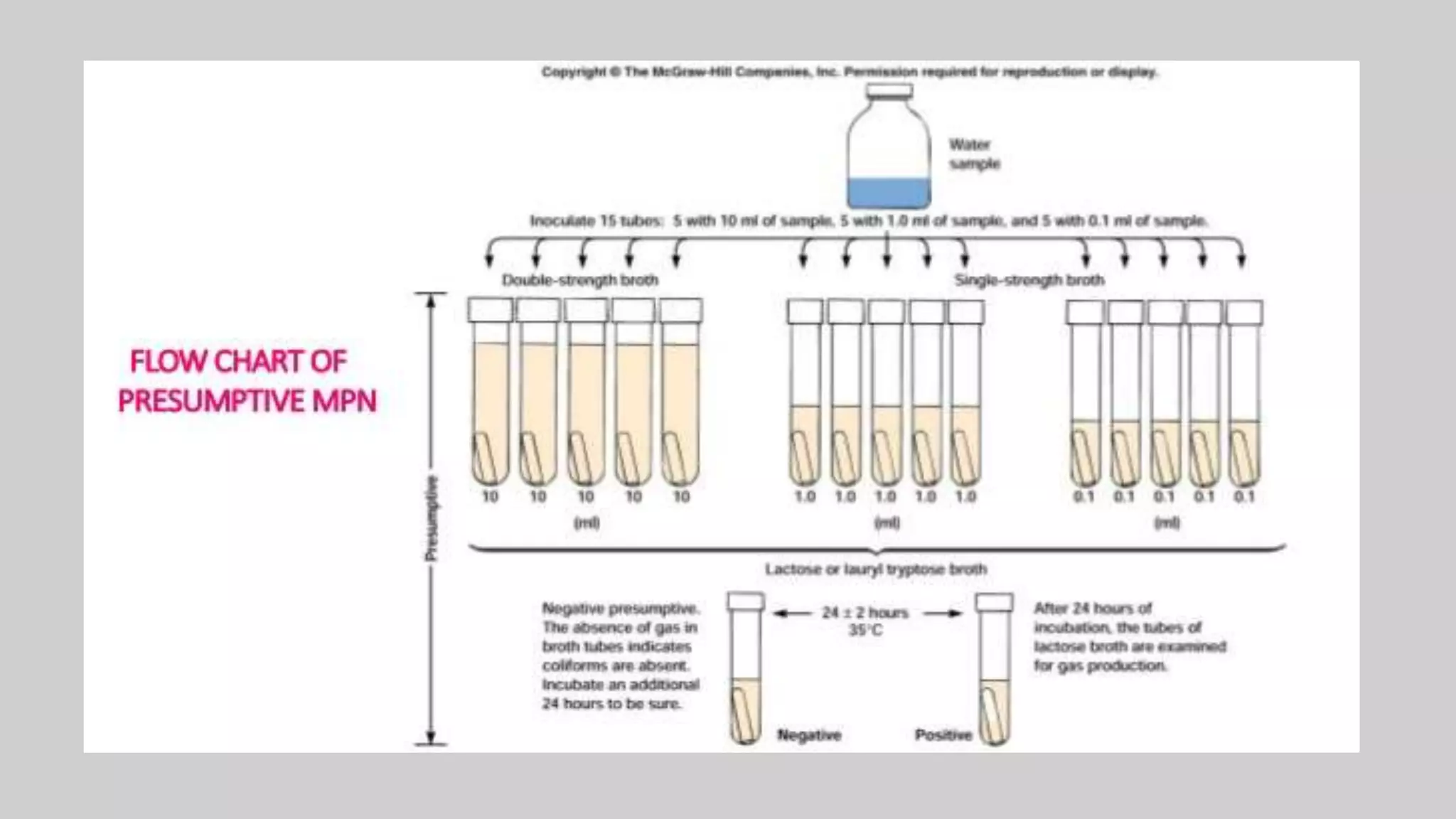
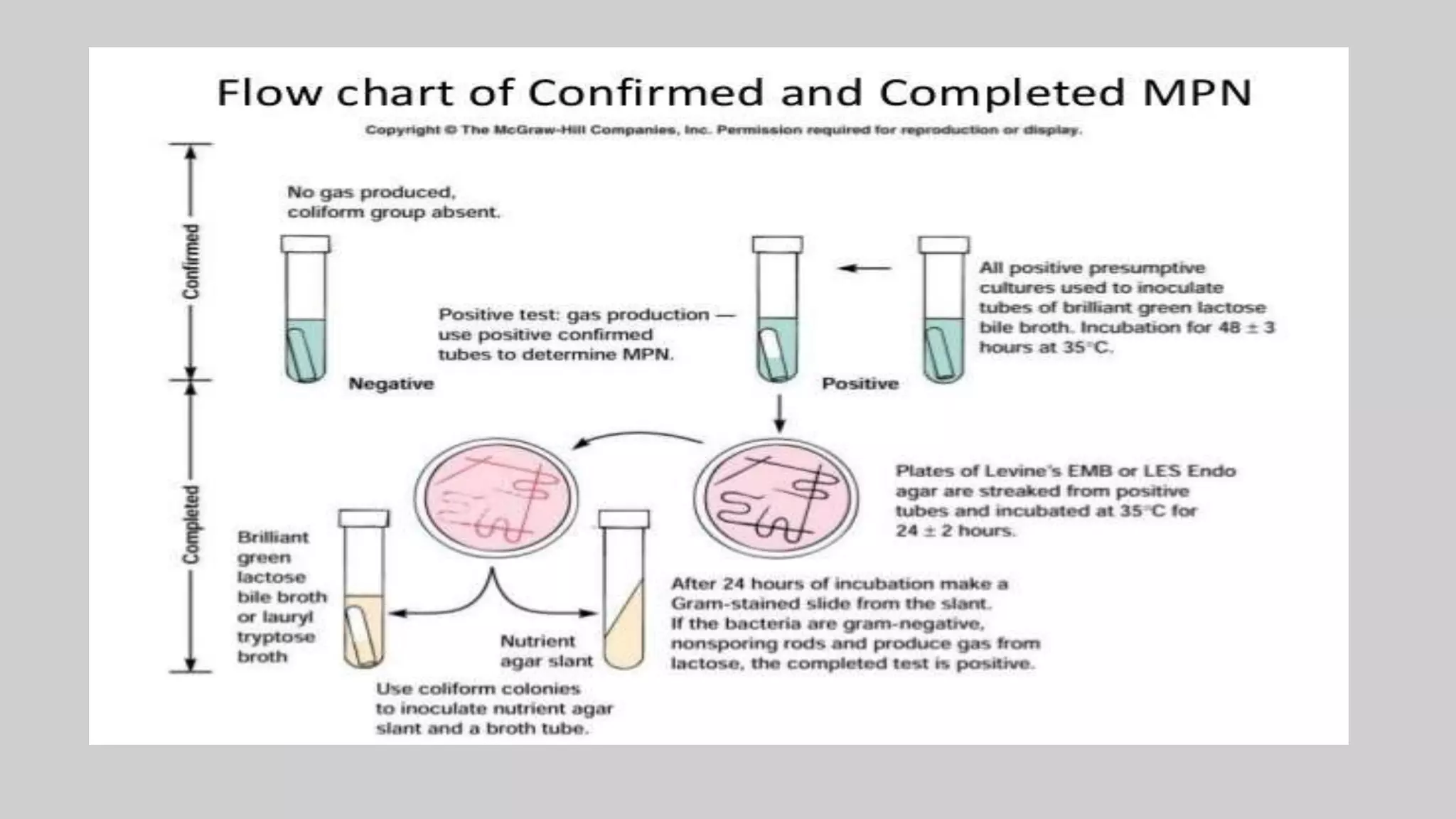
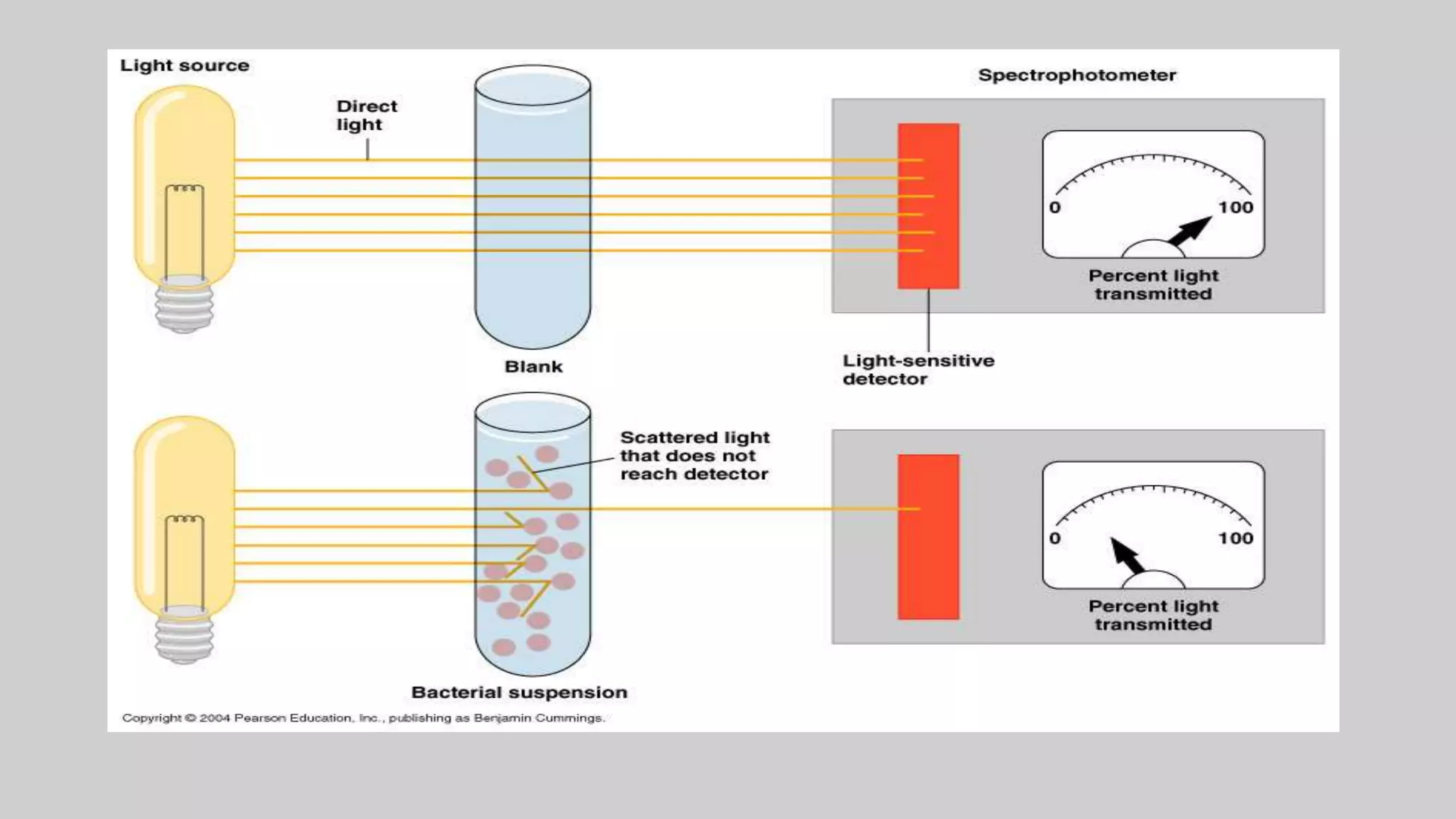
This document discusses methods for measuring microbial growth, including the most probable number (MPN) method and indirect turbidity measurements. The MPN method involves inoculating water samples into multiple tubes containing growth media and observing results to statistically estimate microbial concentrations. It involves presumptive, confirmed, and completed tests to identify coliforms and E. coli. Turbidity measurements use a spectrophotometer to measure light passage through cultures, where increased microbial growth causes higher turbidity and lower light transmission. Both methods provide ways to quantify microbes in samples without direct microscopic counting.