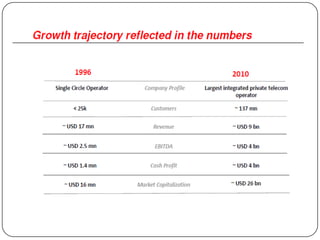
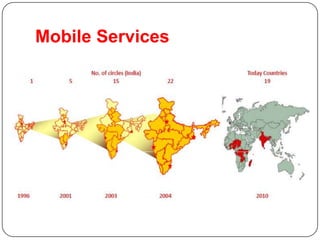
1. Bharti Airtel was incorporated in 1995 as a subsidiary of Bharti Telecom and has since acquired other mobile and telecom companies to expand its operations and reach.
2. The company's vision is to provide global telecom services and delight customers, while its mission includes error-free service, innovative products, cost efficiency, and unified messaging solutions.
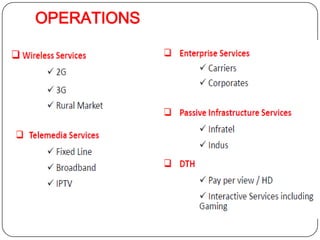
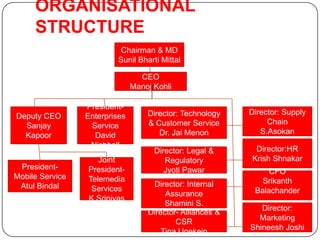
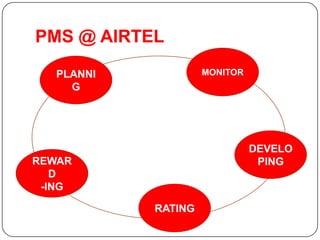
3. The organizational structure outlines the roles and responsibilities of key leadership positions like the Chairman & MD, CEO, and various directors overseeing functions like technology, marketing, and operations.