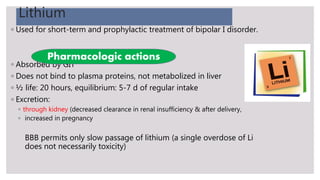
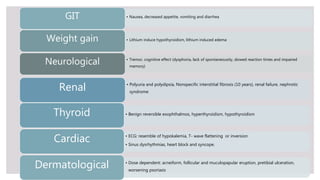
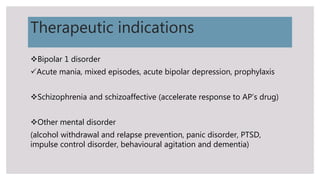
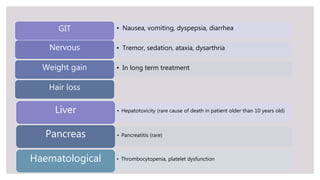
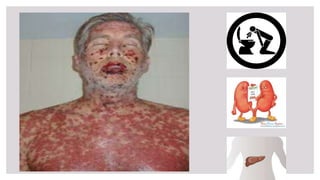
This document outlines mood stabilizers, including lithium, valproate, carbamazepine, and antipsychotic agents. It discusses their pharmacologic actions, therapeutic indications, dosages, guidelines, and precautions. Mood stabilizers are used to treat bipolar disorder and other conditions by decreasing the frequency and severity of manic and depressive episodes. Key precautions include risks during pregnancy, adverse effects like weight gain and liver toxicity, and the need for monitoring. Mood stabilizers are an important treatment option for bipolar disorder but require awareness of safety considerations.