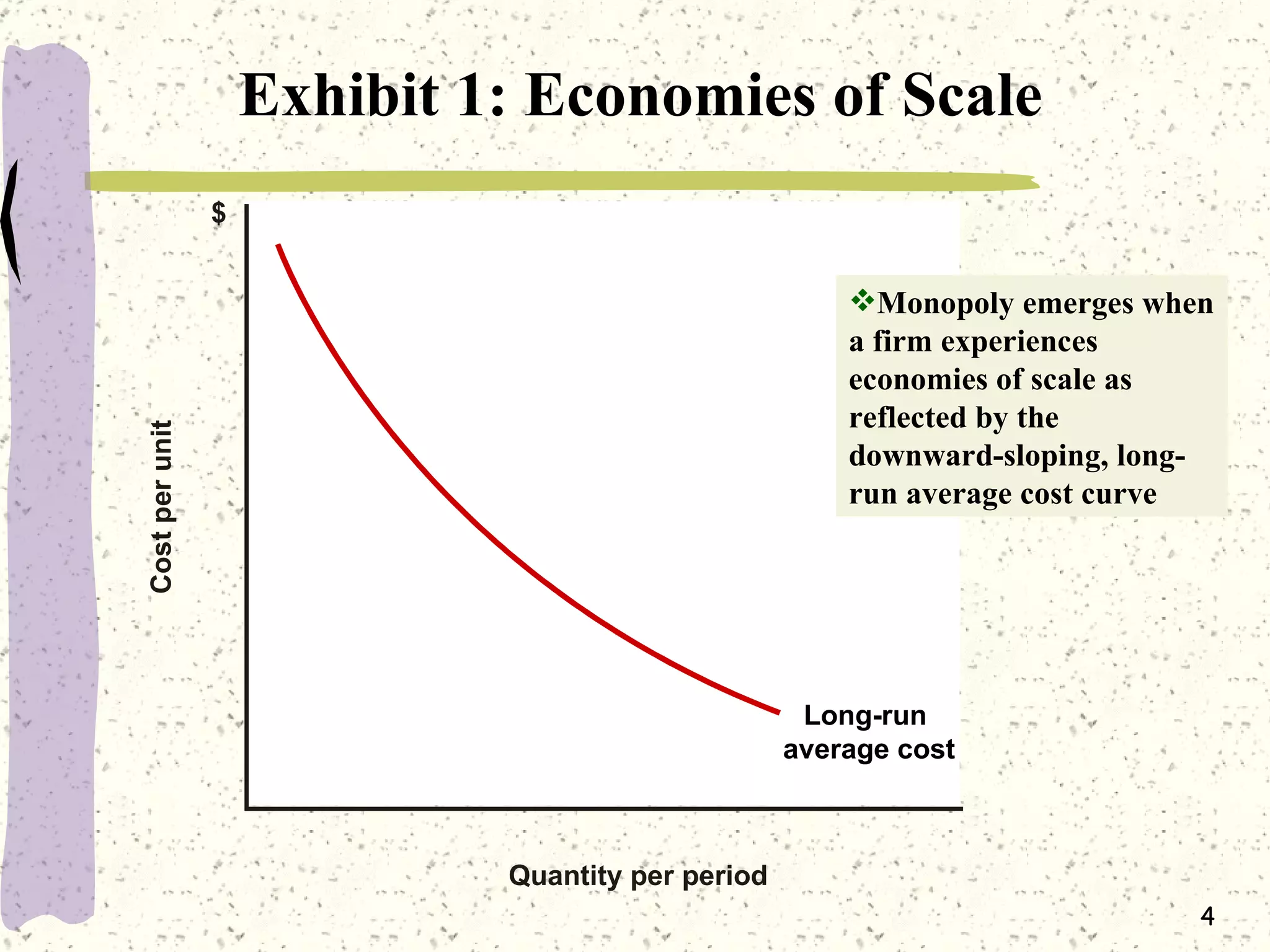
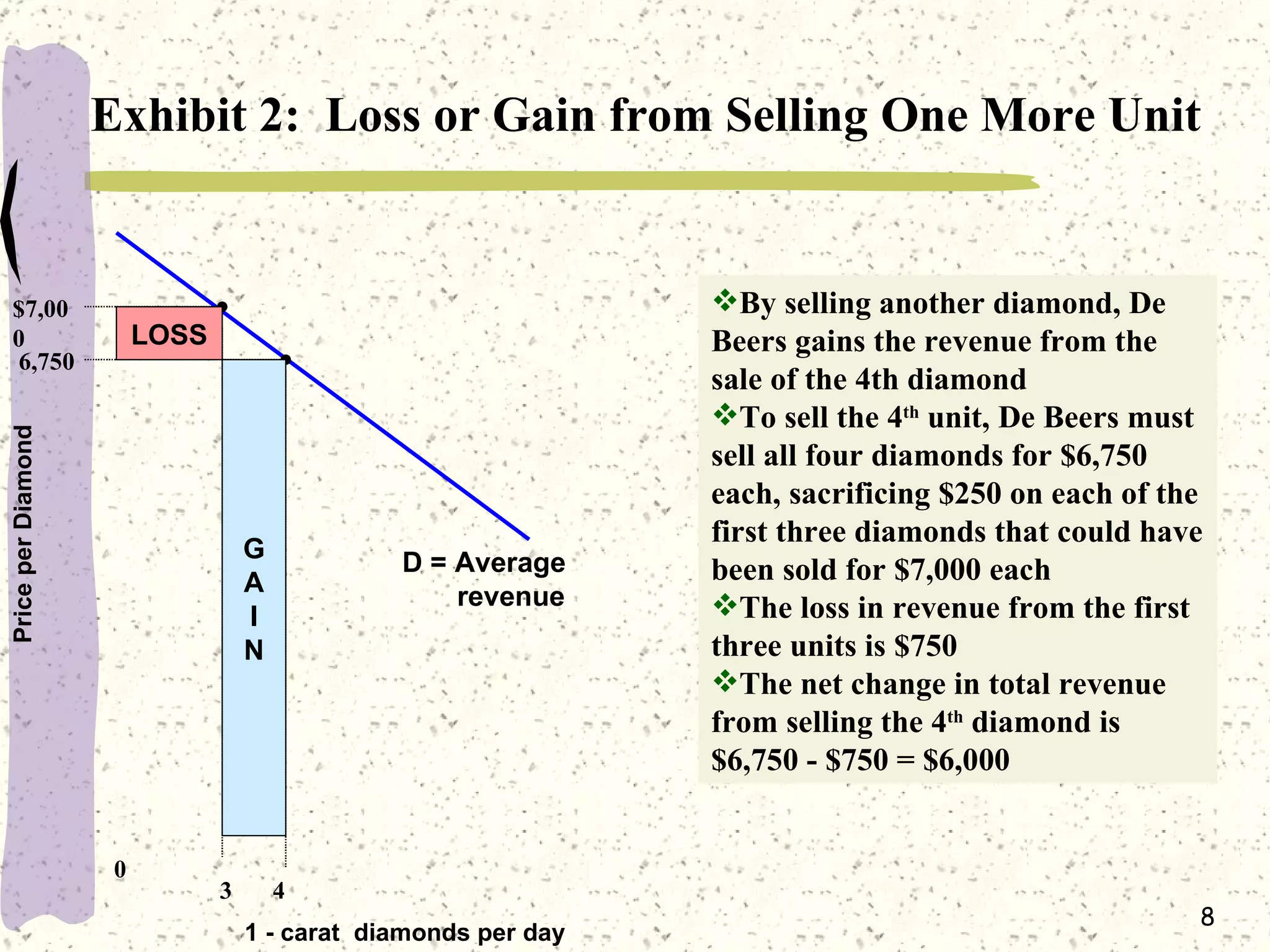
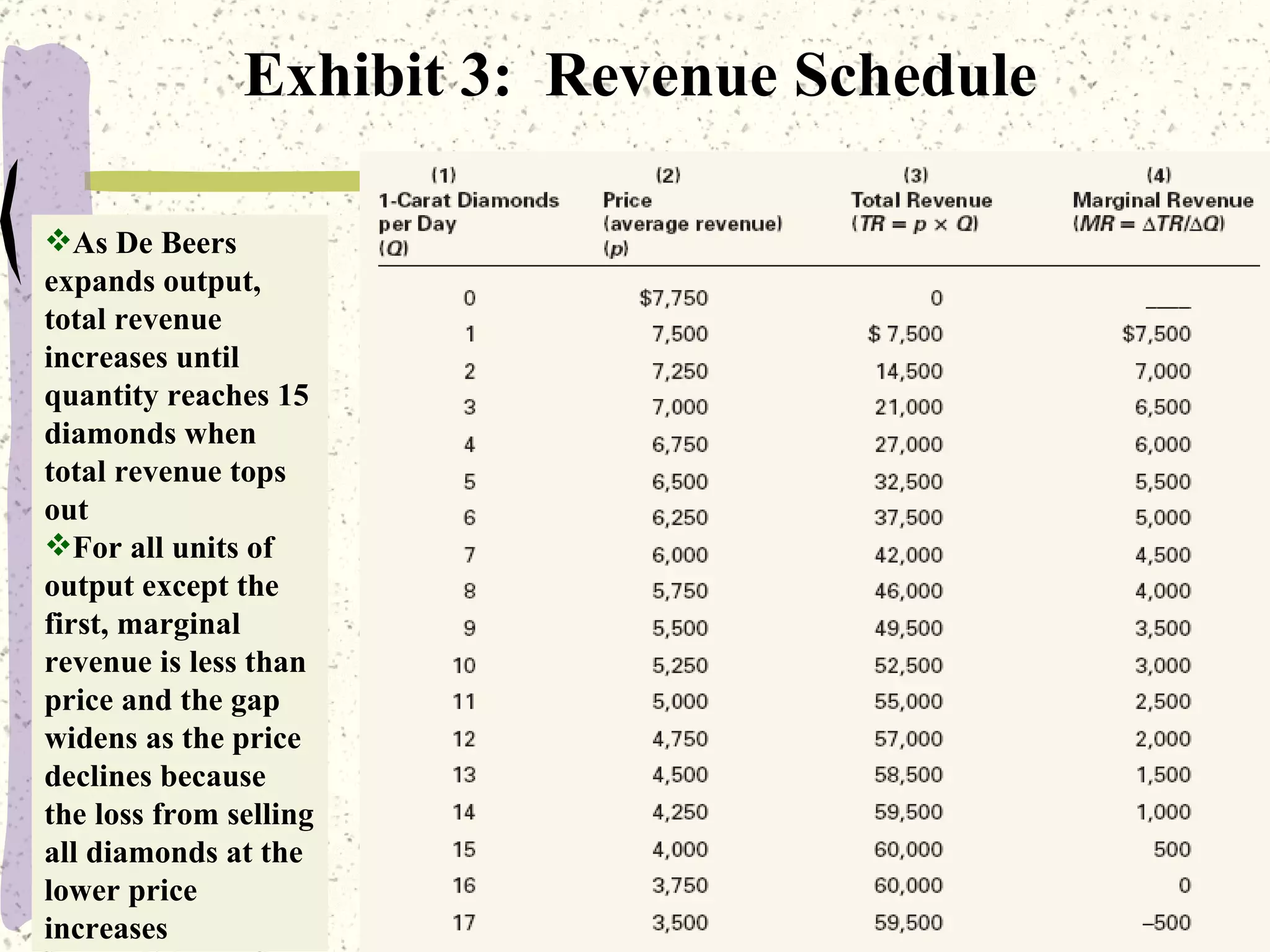
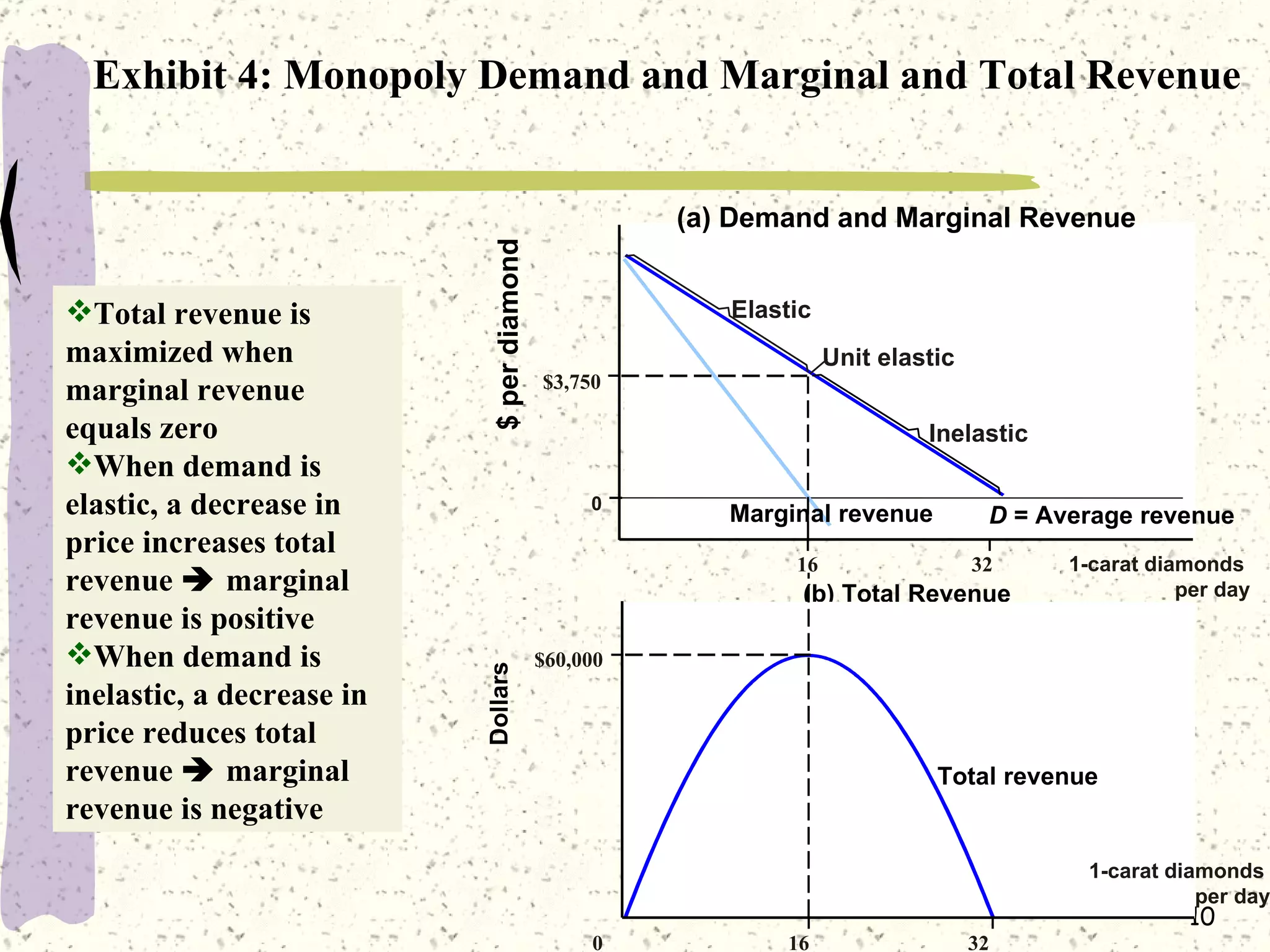
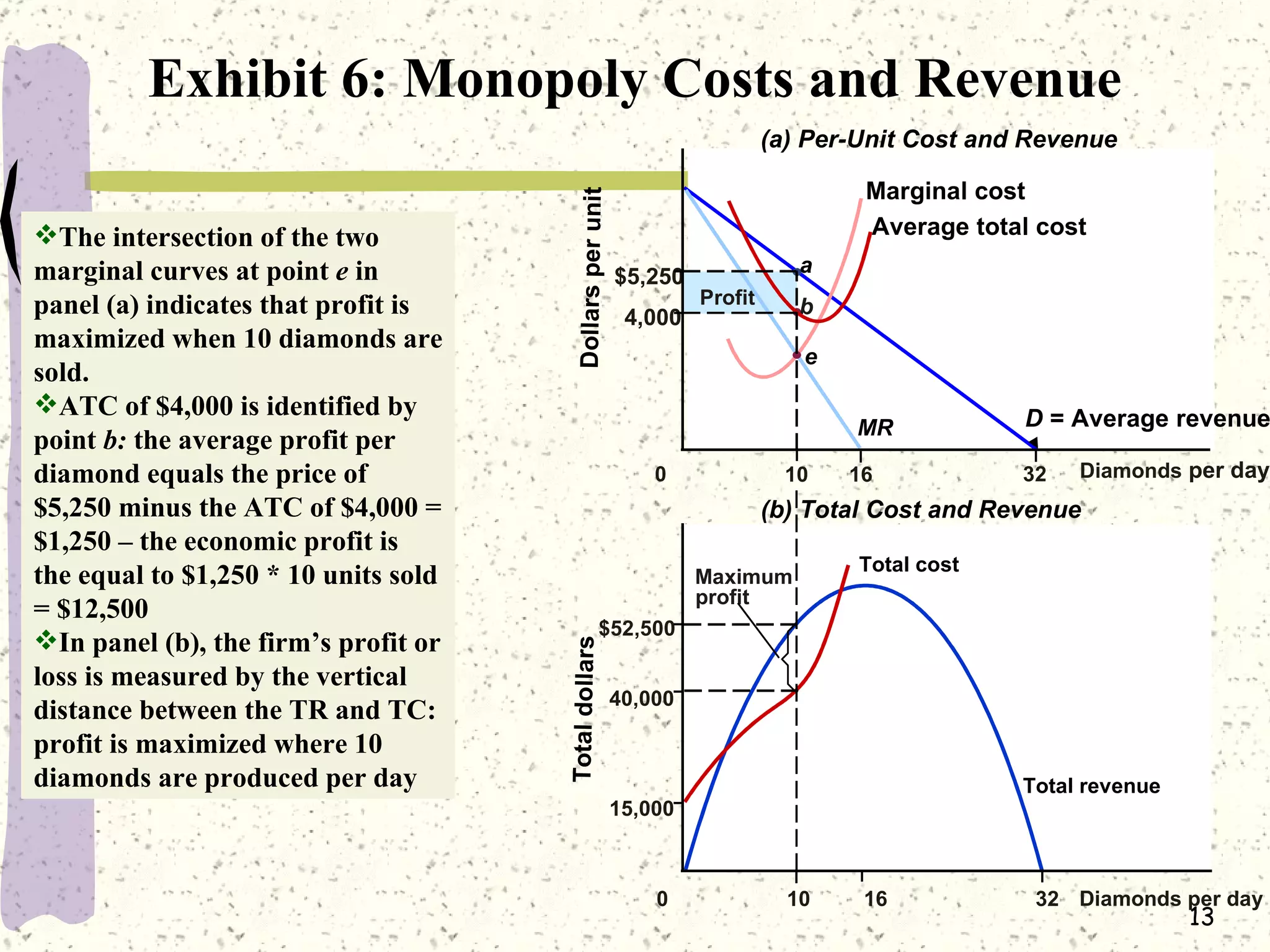
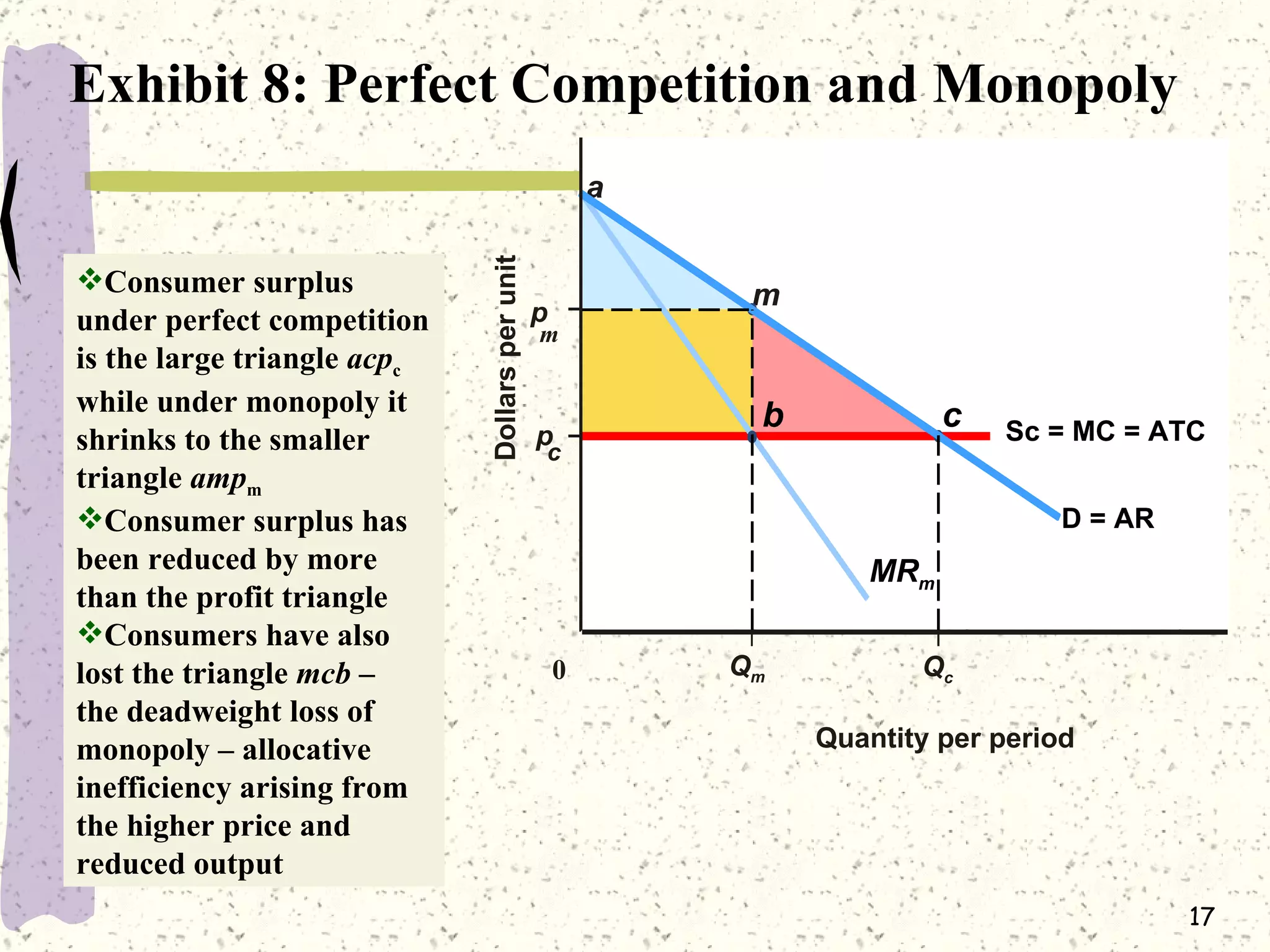
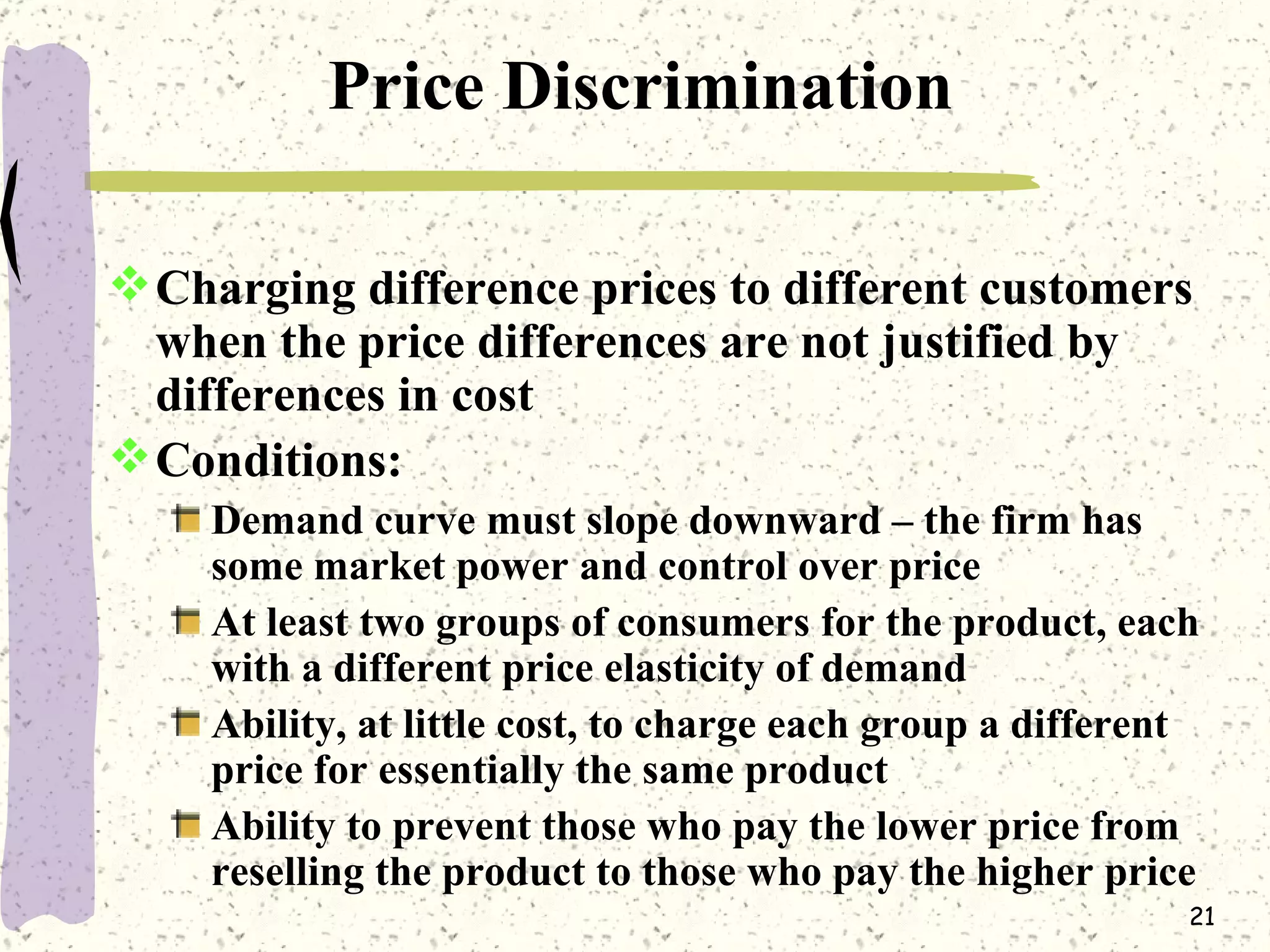
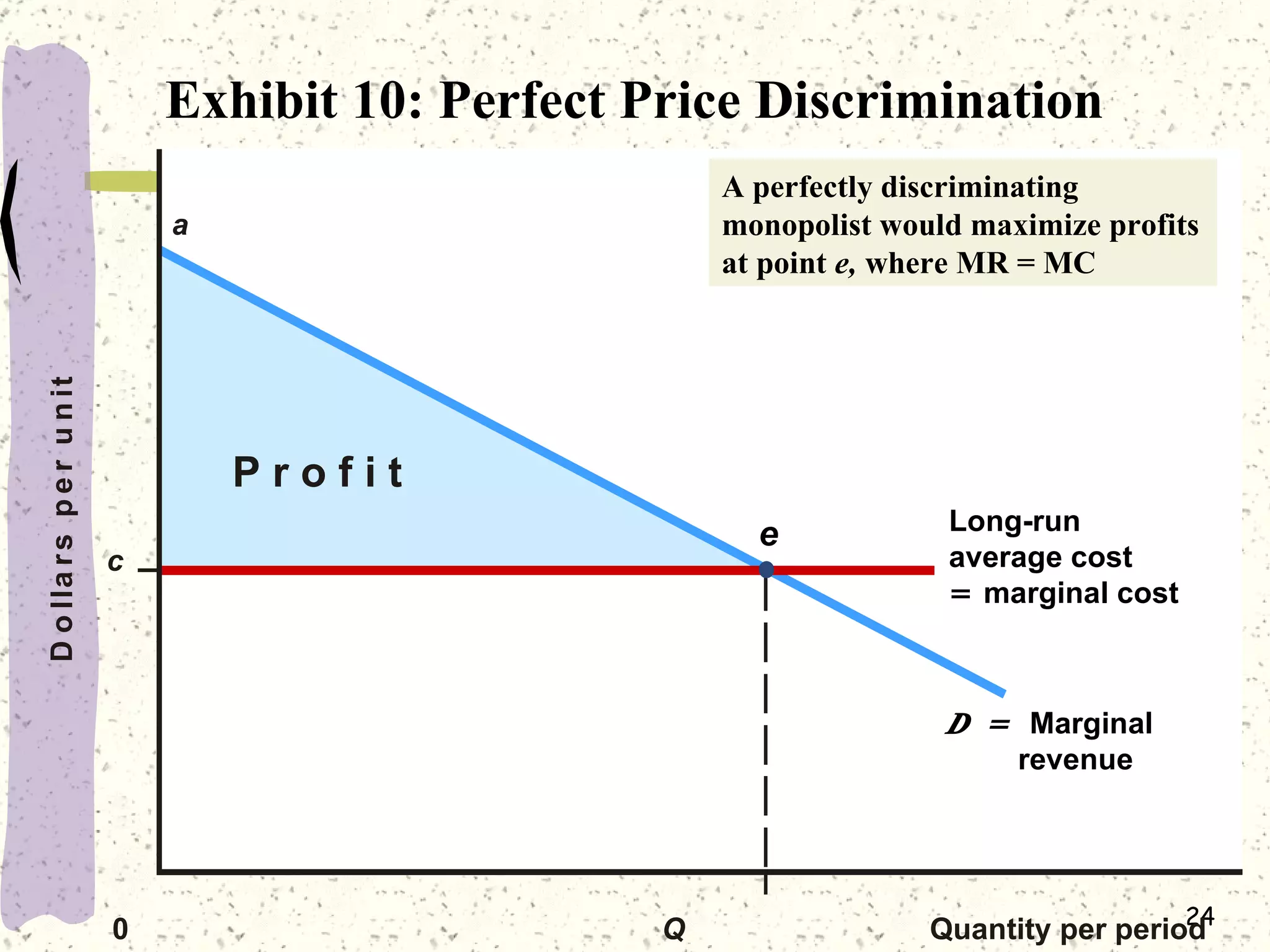
This document discusses various barriers to entry that allow monopolies to form and persist, including legal restrictions like patents, economies of scale, and control of essential resources. It provides examples of monopolies in different industries. The document also examines how a monopoly determines the profit-maximizing price and quantity to produce by equating marginal revenue and marginal cost, and outlines how this differs from perfect competition. Consumer surplus is lower under monopoly compared to perfect competition due to the deadweight loss.