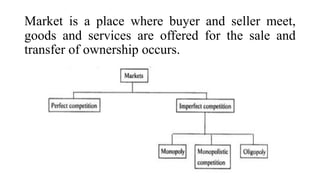
- Market structure refers to the level of competition within a market. The main types are perfect competition, monopoly, monopolistic competition, and oligopoly.
- Under perfect competition, there are many small producers and consumers of a standardized product, while a monopoly has a single producer and no close substitutes. Monopolistic competition features product differentiation and free entry/exit of many firms. Oligopoly has a small number of interdependent producers controlling the market.
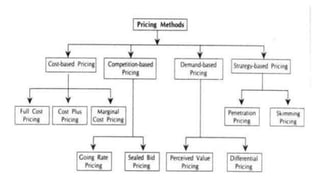
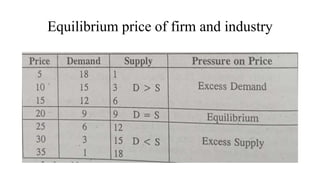
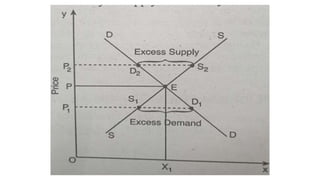
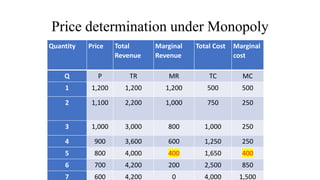
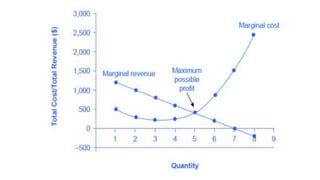
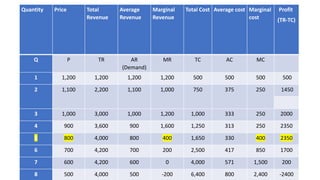
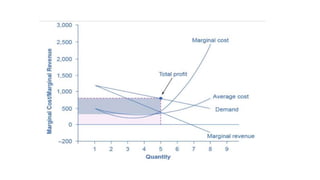
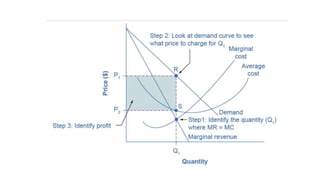
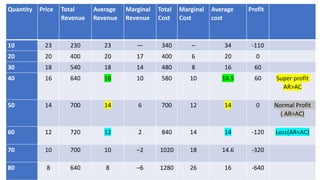
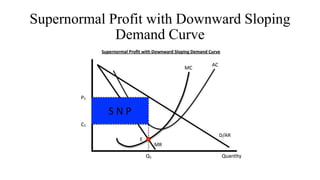
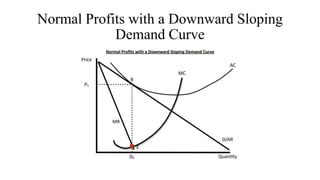
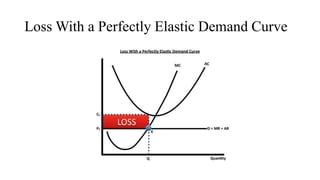
- Profit maximization occurs where marginal revenue equals marginal cost under perfect competition and monopolistic competition. A monopoly chooses output where marginal revenue is zero. Pricing strategies depend on market structure and include cost-plus, penetration, skimming, and prestige pricing.