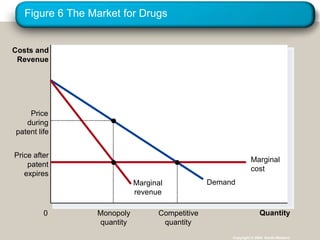
A monopoly is a sole seller that is a price maker and faces a downward sloping demand curve. Monopolies can arise from barriers to entry such as government protections like patents. Unlike competitive firms, monopolies produce less than the efficient quantity and charge a price above marginal cost, resulting in deadweight loss. Governments address monopolies through regulation, antitrust laws, or public ownership.