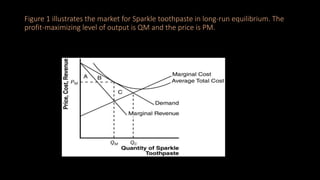
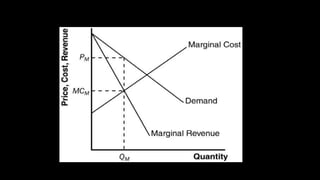
The document discusses markets for various goods and classifies them as perfectly competitive, monopolistically competitive, or monopolistic. It then analyzes the characteristics of firms in these different market structures and how they determine profit maximizing price and output. The document also provides examples of how individual firms might behave in these market contexts.