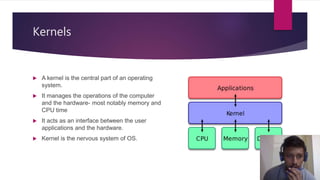
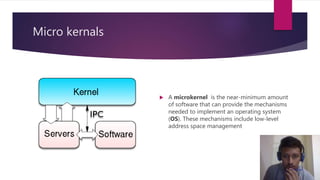
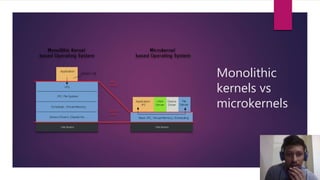
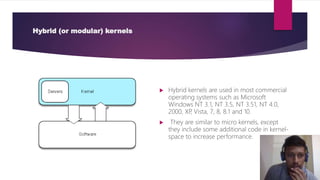
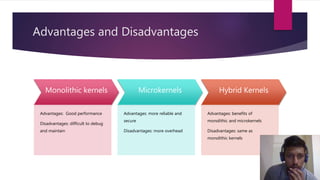
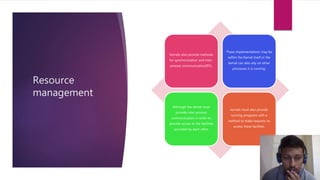
This document discusses different types of computer operating system kernels. It begins by defining a kernel as the central part of an OS that manages hardware resources and acts as an interface between applications and hardware. The main types discussed are monolithic, micro, and hybrid kernels. Monolithic kernels have all OS components in the kernel space, while microkernels minimize kernel space. Hybrid kernels combine aspects of monolithic and microkernels. The document also briefly outlines nano and exokernels, and compares advantages and disadvantages of the different kernel types. Key kernel functions discussed are resource management, memory management, device management, and system calls.