Embed presentation
Downloaded 175 times



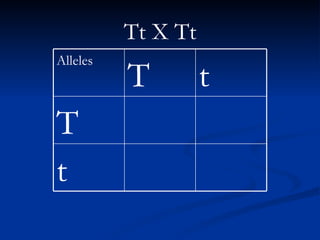
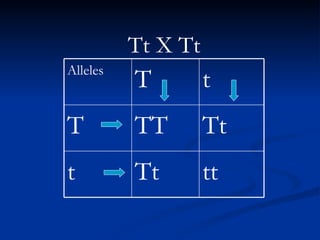



Complete dominance is a type of genetic dominance where the dominant gene fully masks the expression of the recessive gene in heterozygous individuals. In a monohybrid cross exhibiting complete dominance, such as tail length in cats, the dominant gene for long tails (T) will be represented by capital letters while the recessive gene for short tails (t) uses lowercase. Crossing two heterozygous individuals (Tt x Tt) will result in a genotypic ratio of 1 TT : 2 Tt : 1 tt and a phenotypic ratio of 3 long tails : 1 short tail.







