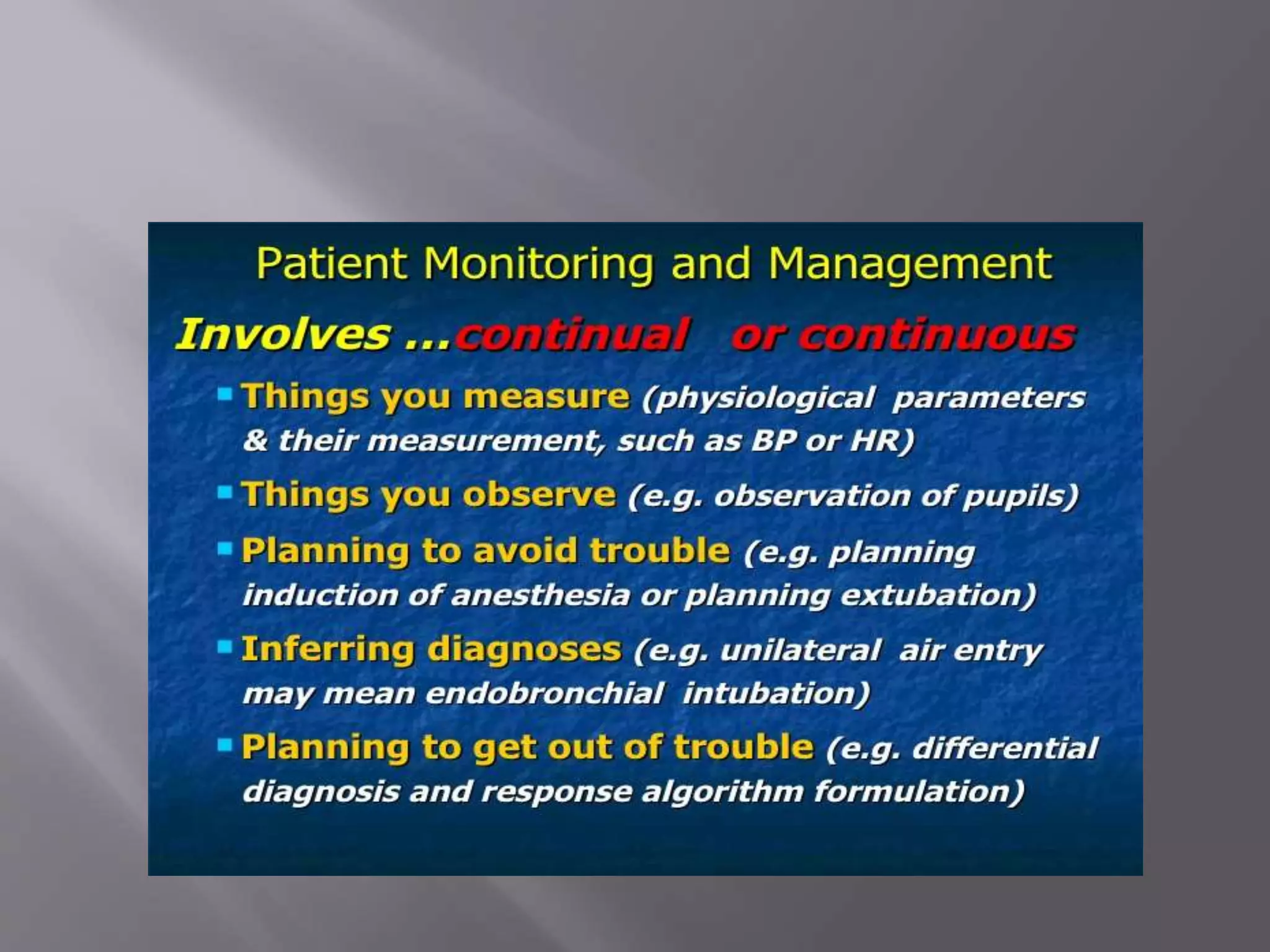
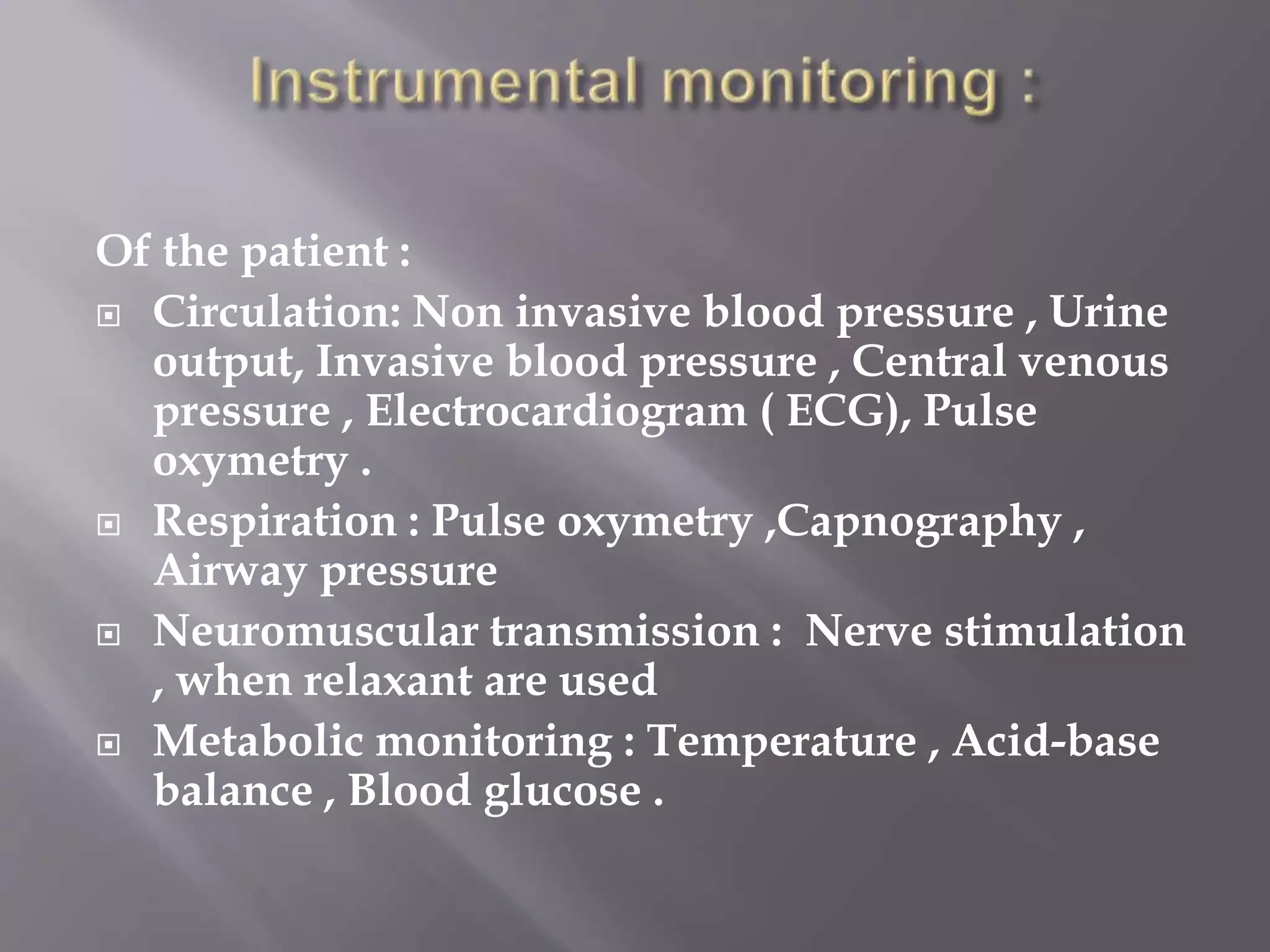
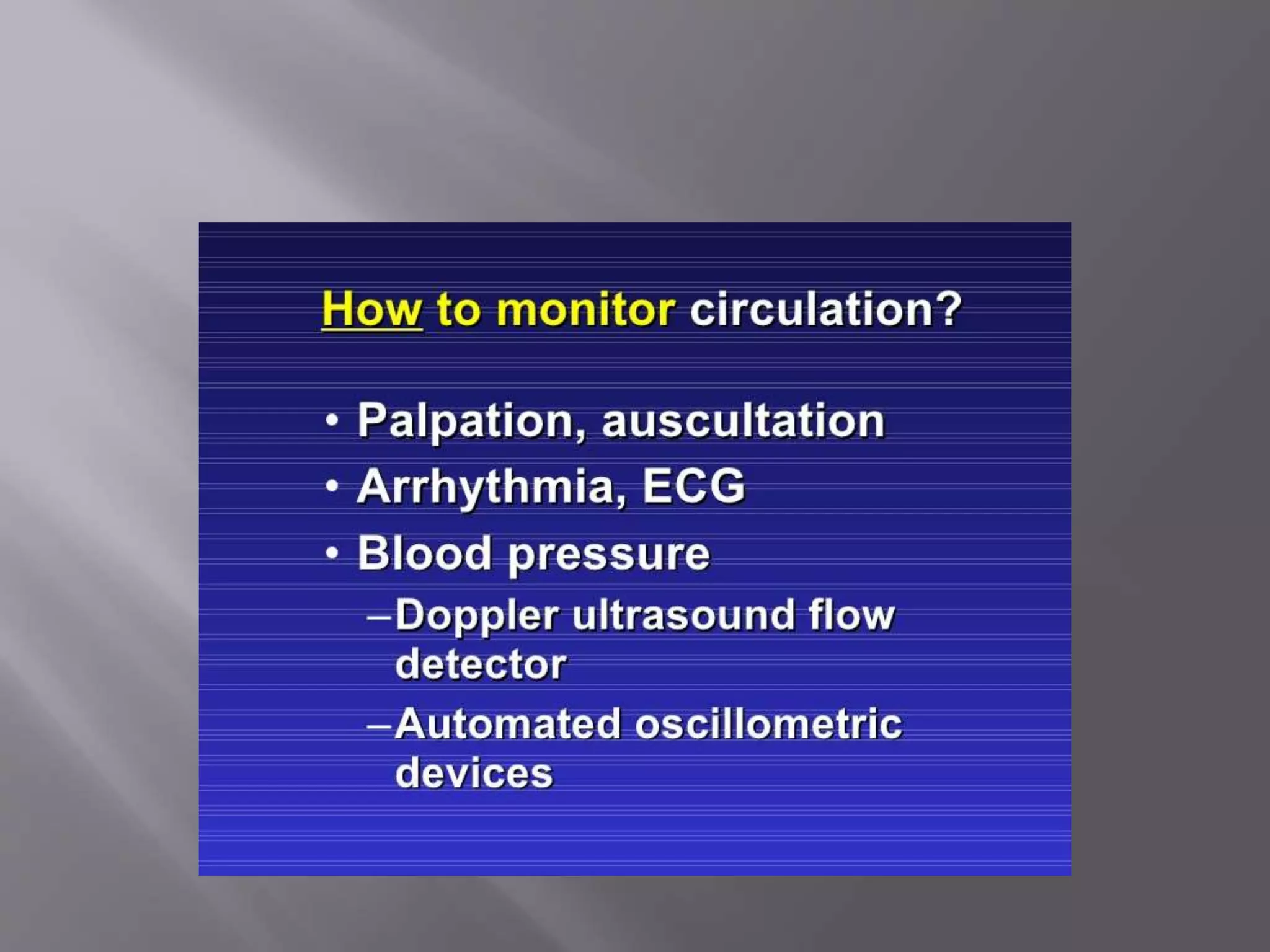
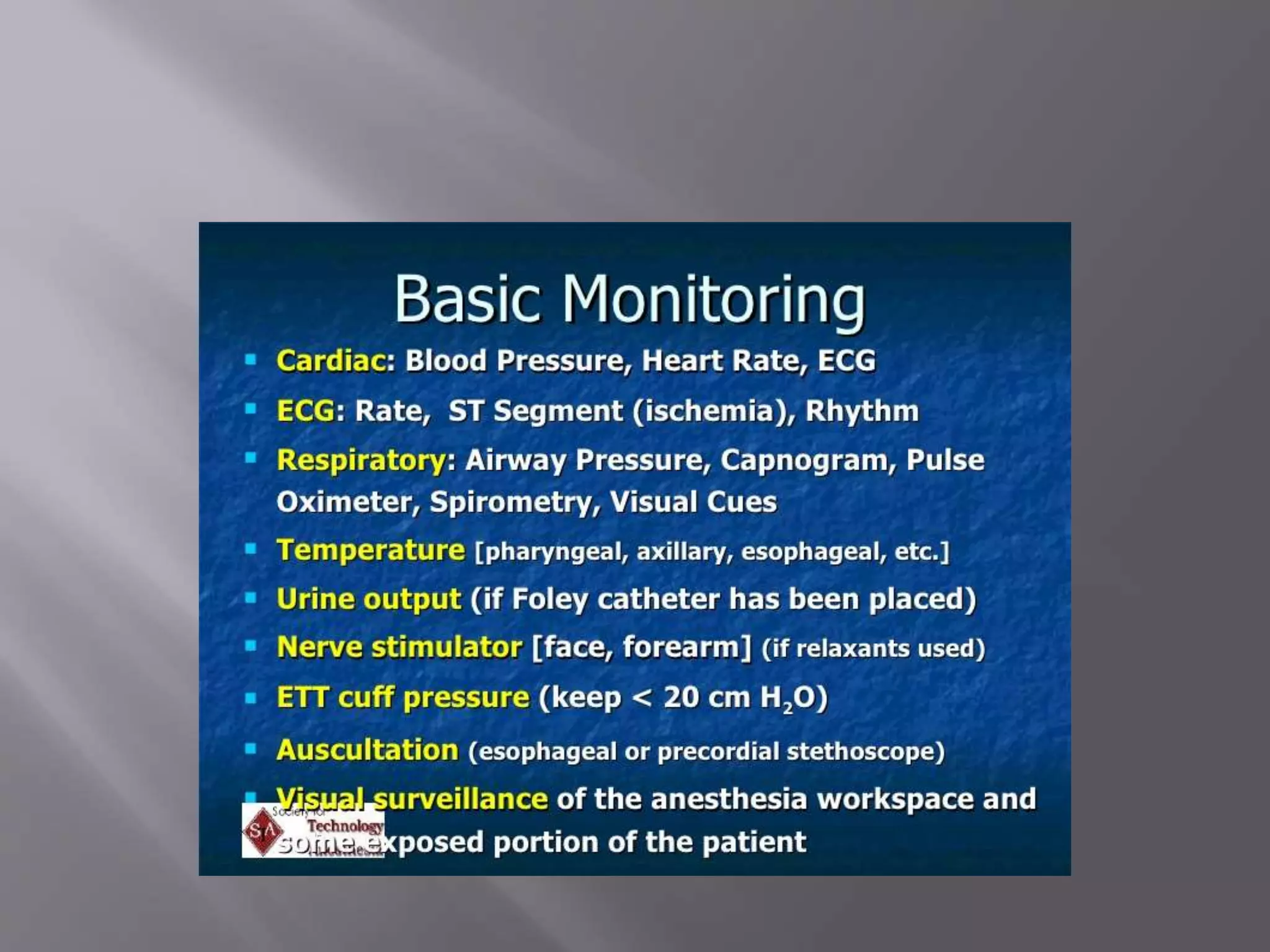
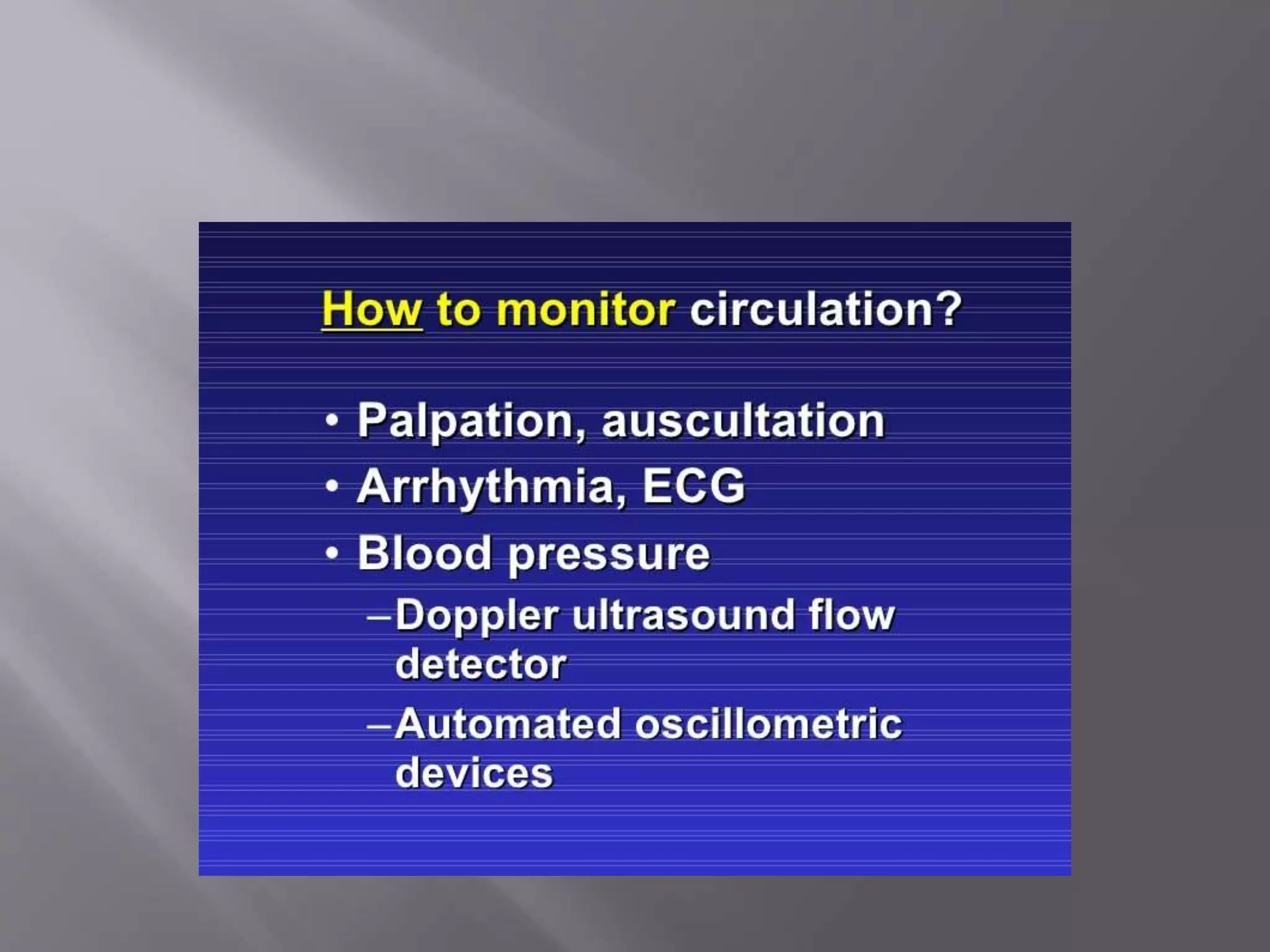
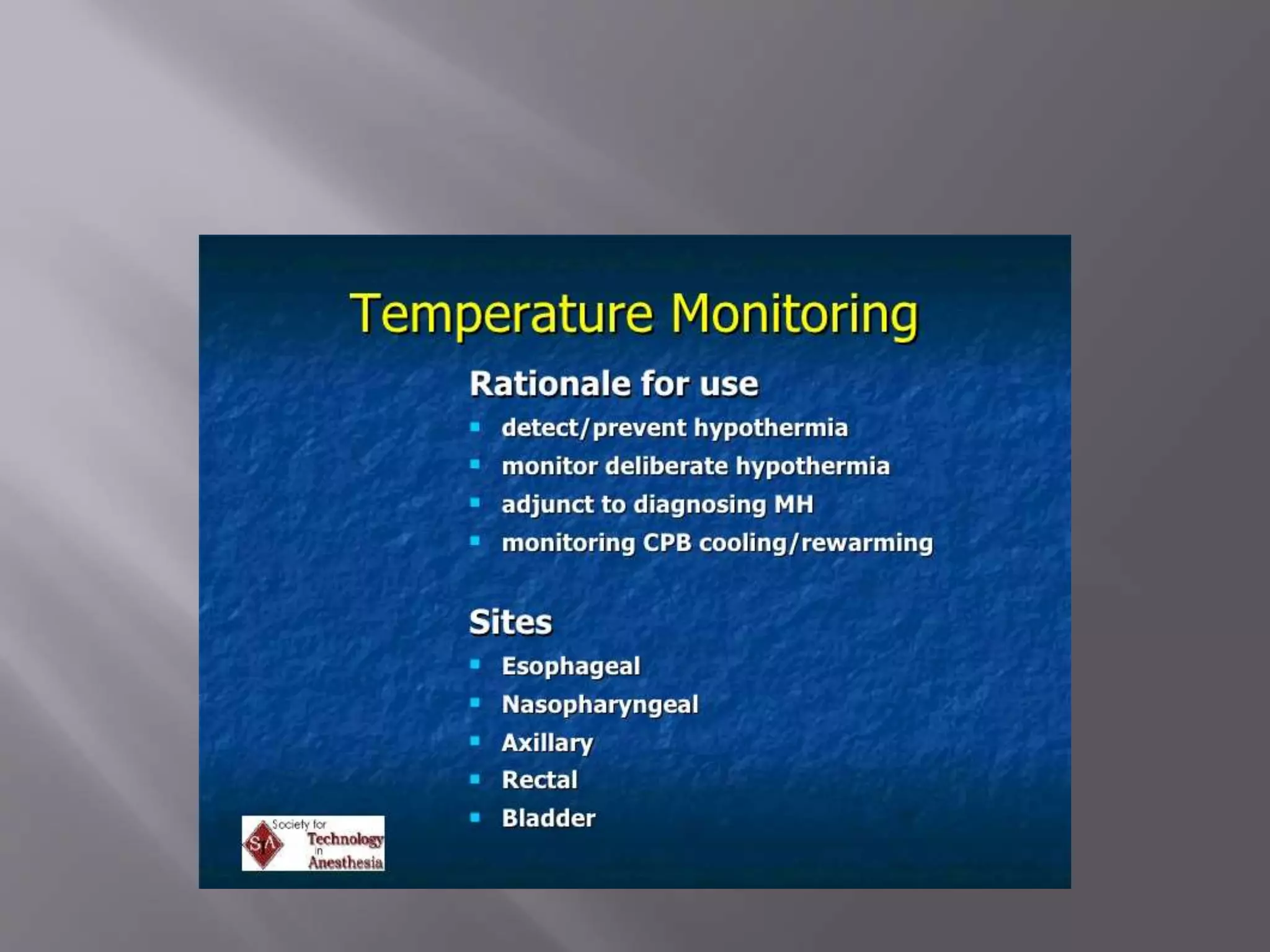
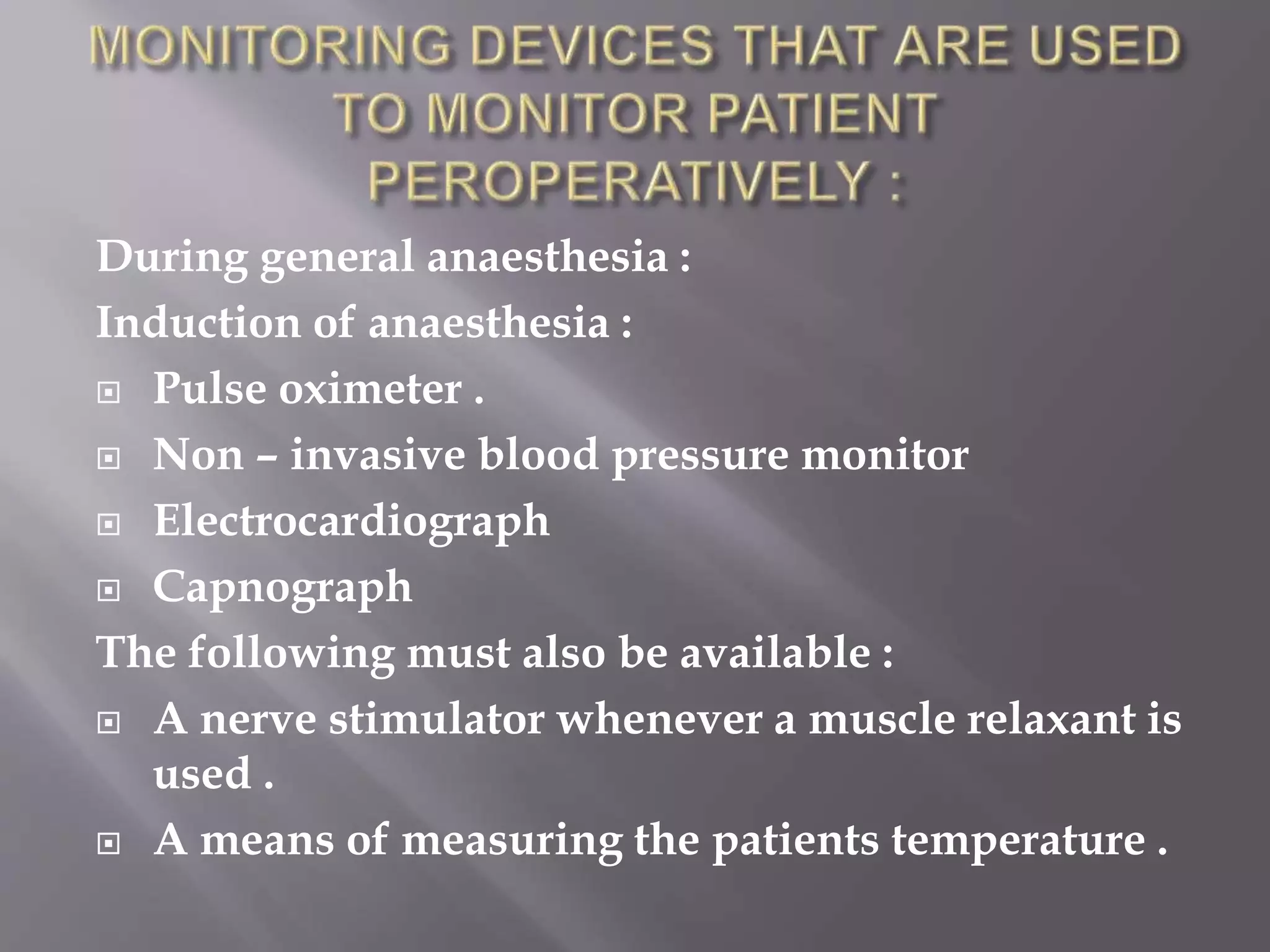
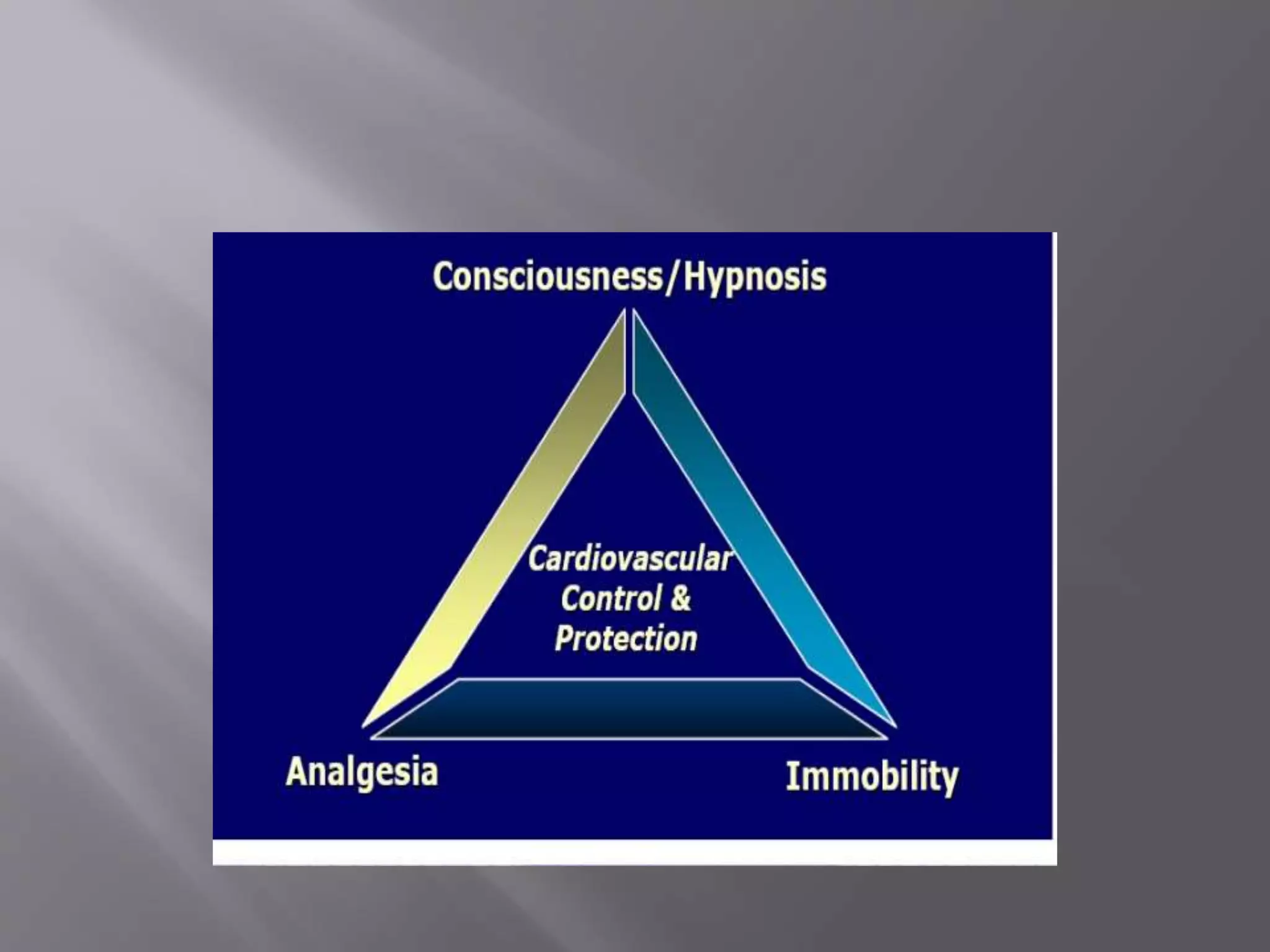
This document discusses monitoring during anesthesia. It defines monitoring as the continuous recording of particular data to observe and regulate a process. There are two main types of monitoring - clinical monitoring done by an experienced anesthesiologist observing vital signs, and instrumental monitoring using medical devices. Standards require qualified medical staff to monitor oxygenation, ventilation, circulation, temperature, and depth of anesthesia throughout all general and regional anesthetics and recovery. A variety of devices are recommended for monitoring at different stages of anesthesia.