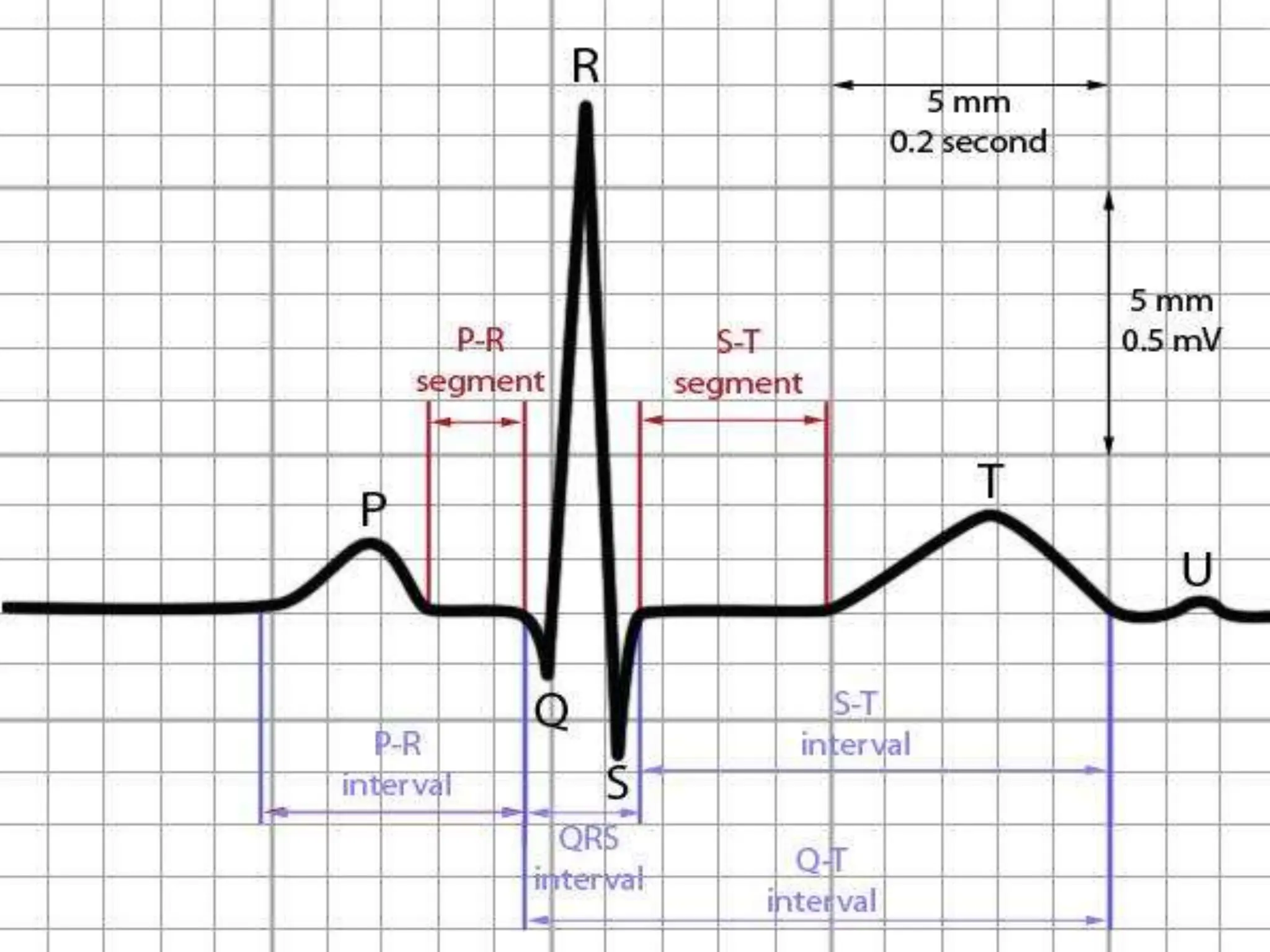
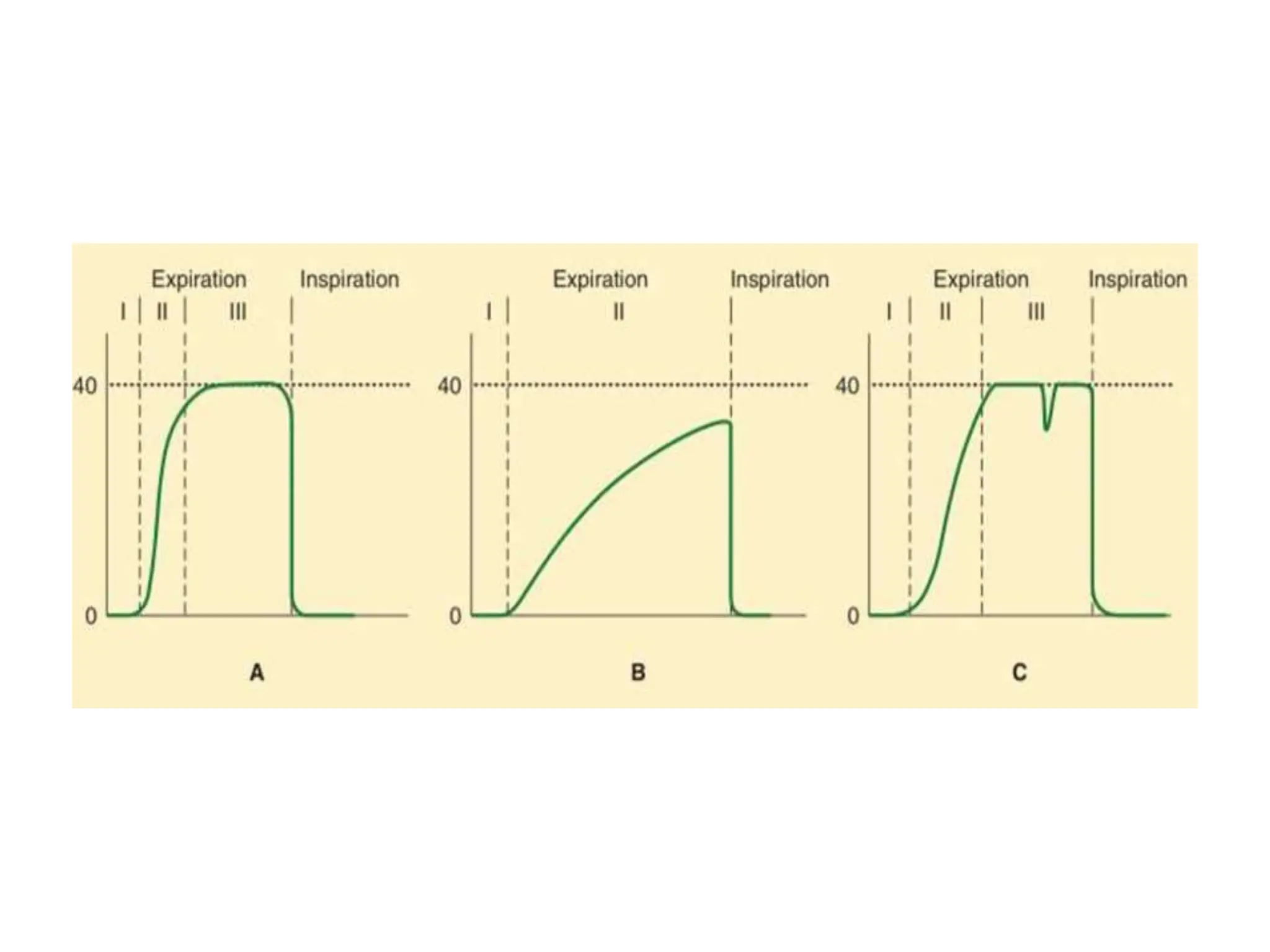
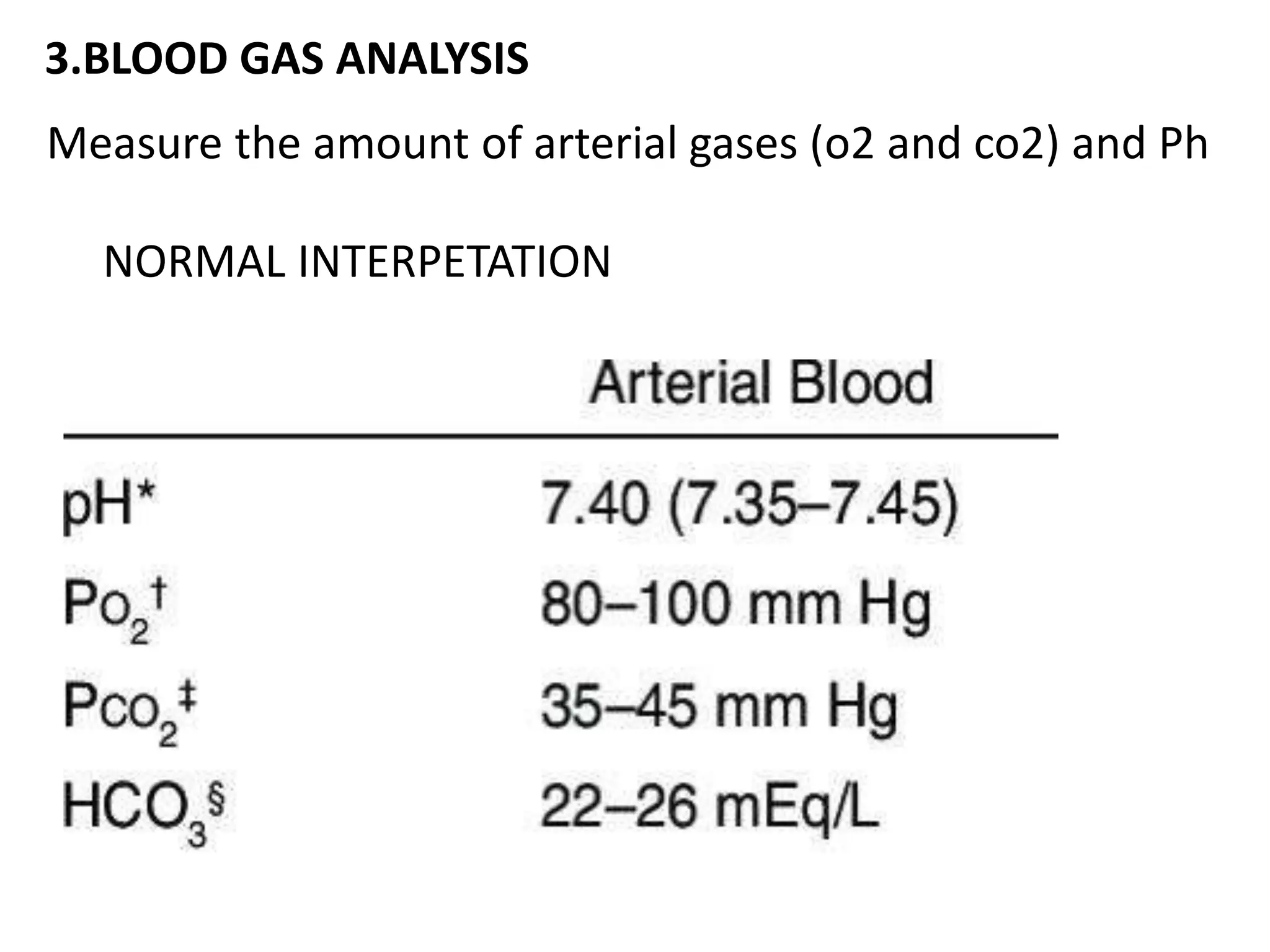
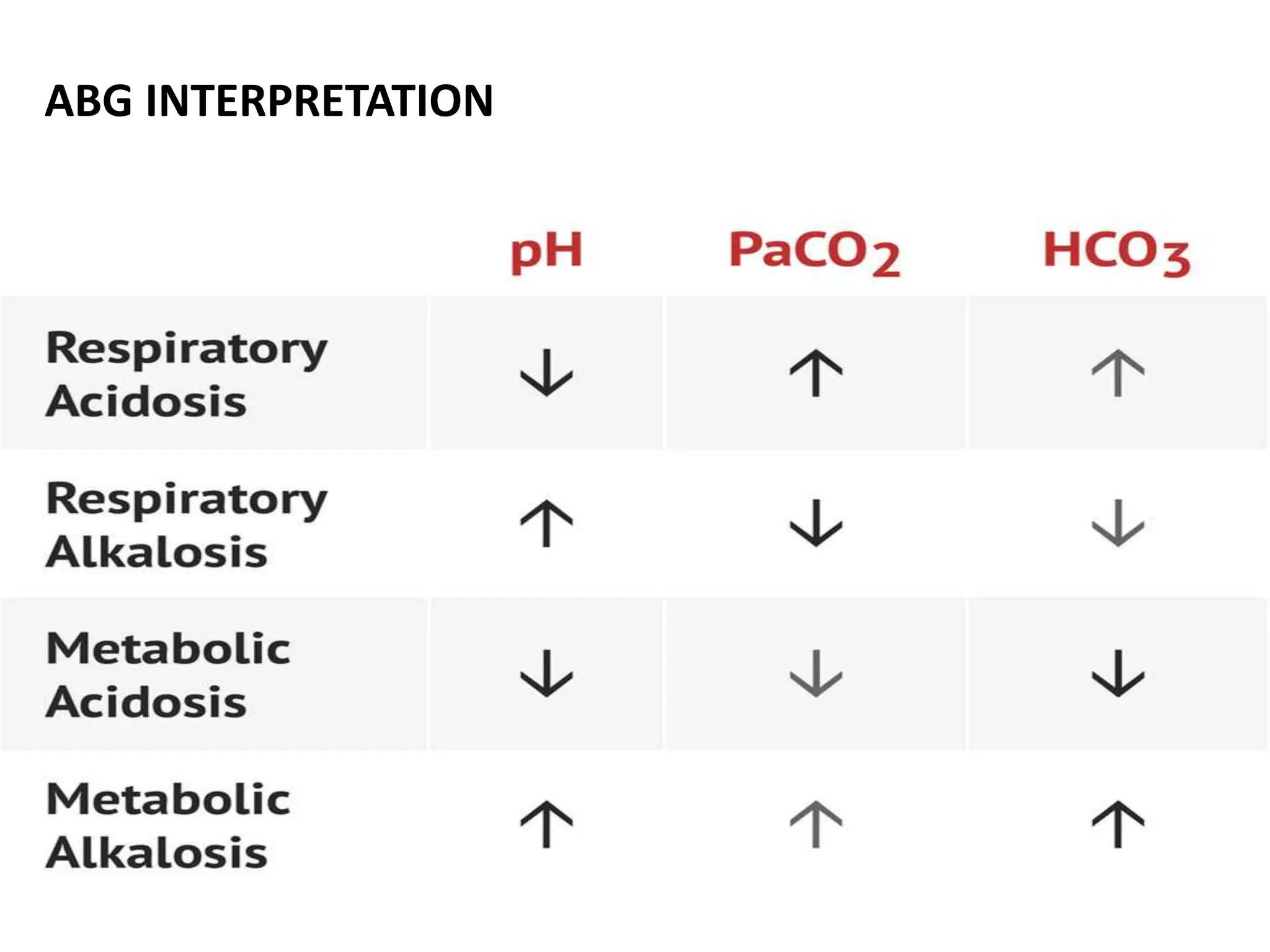
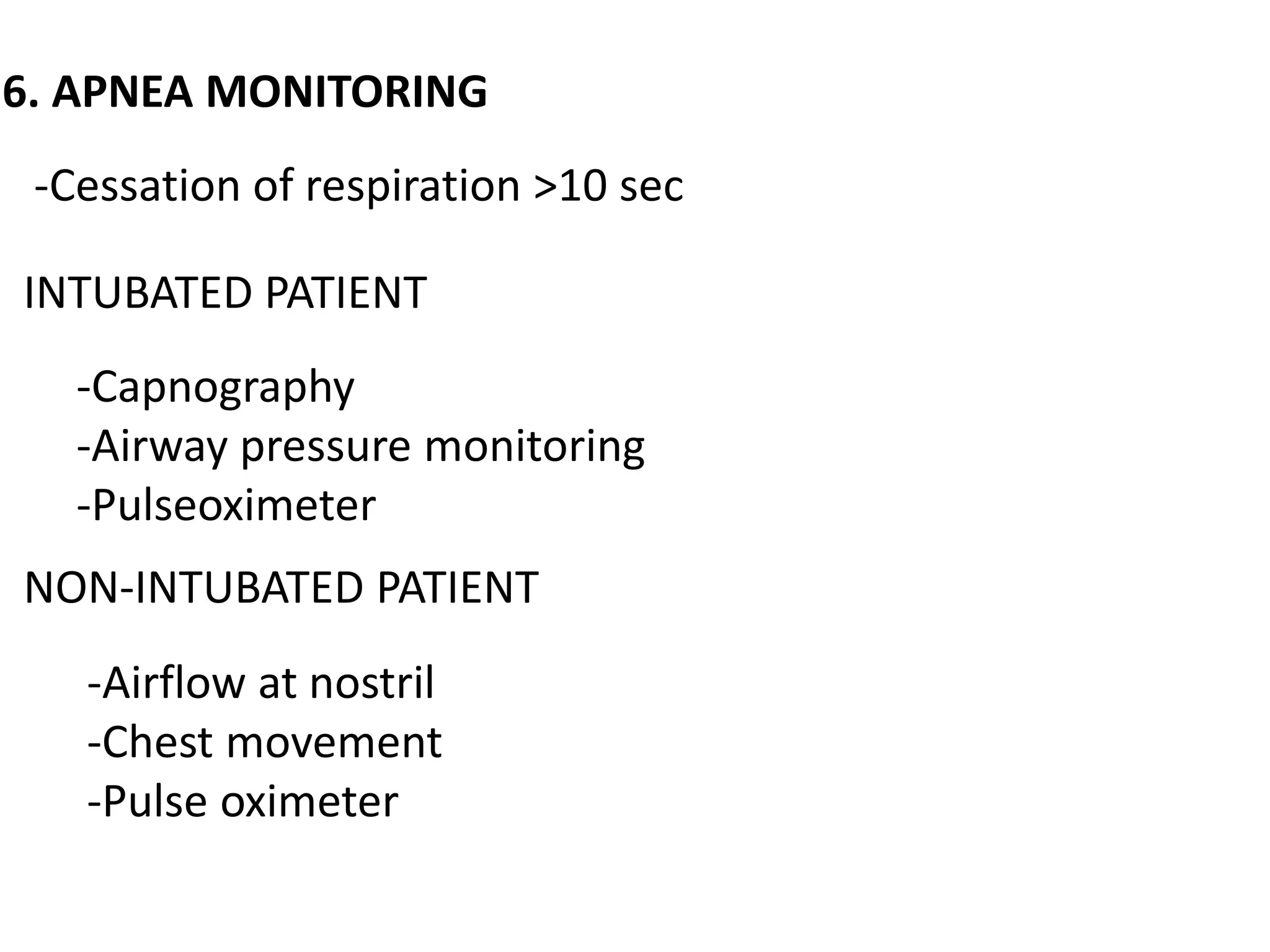
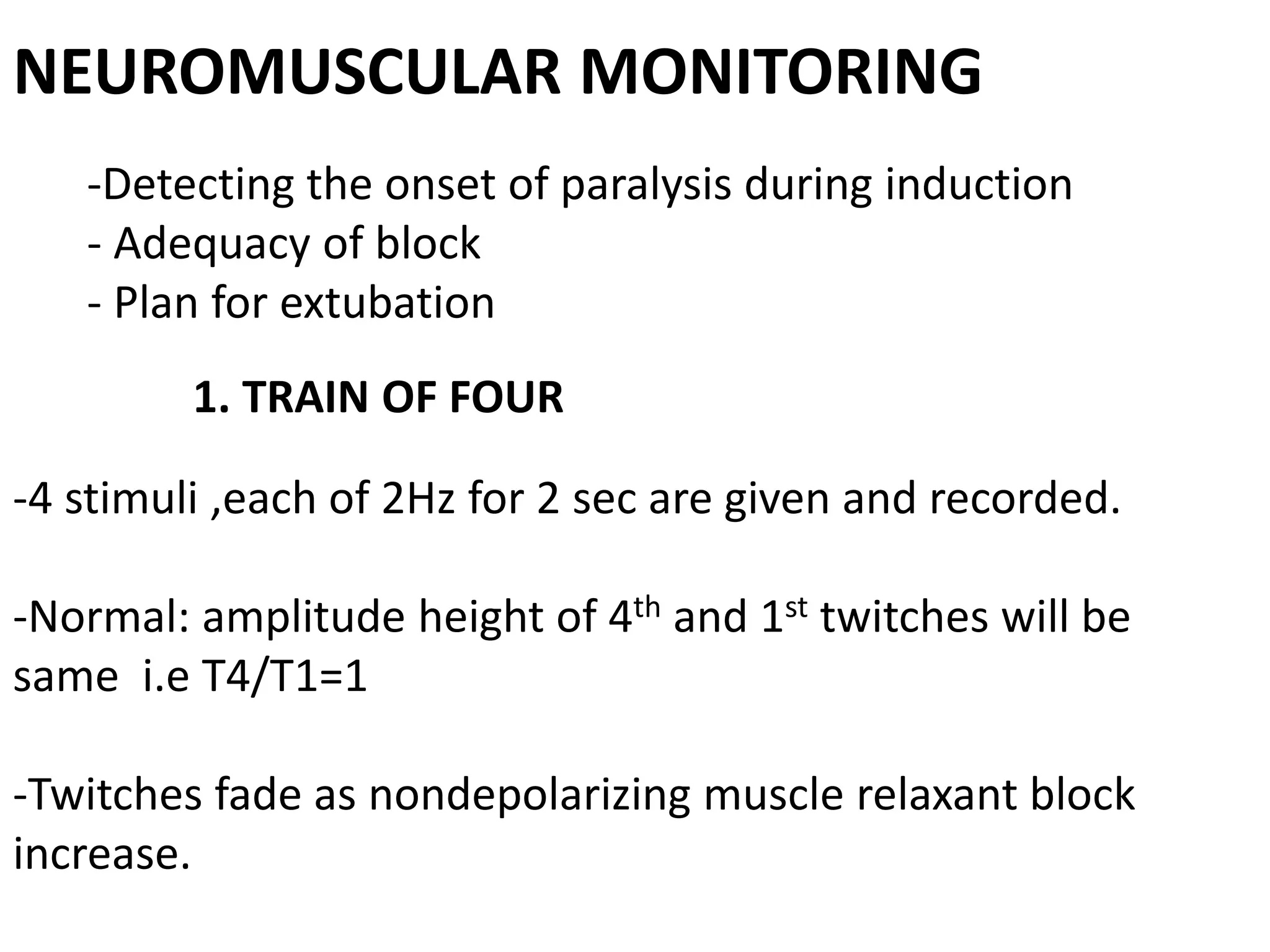
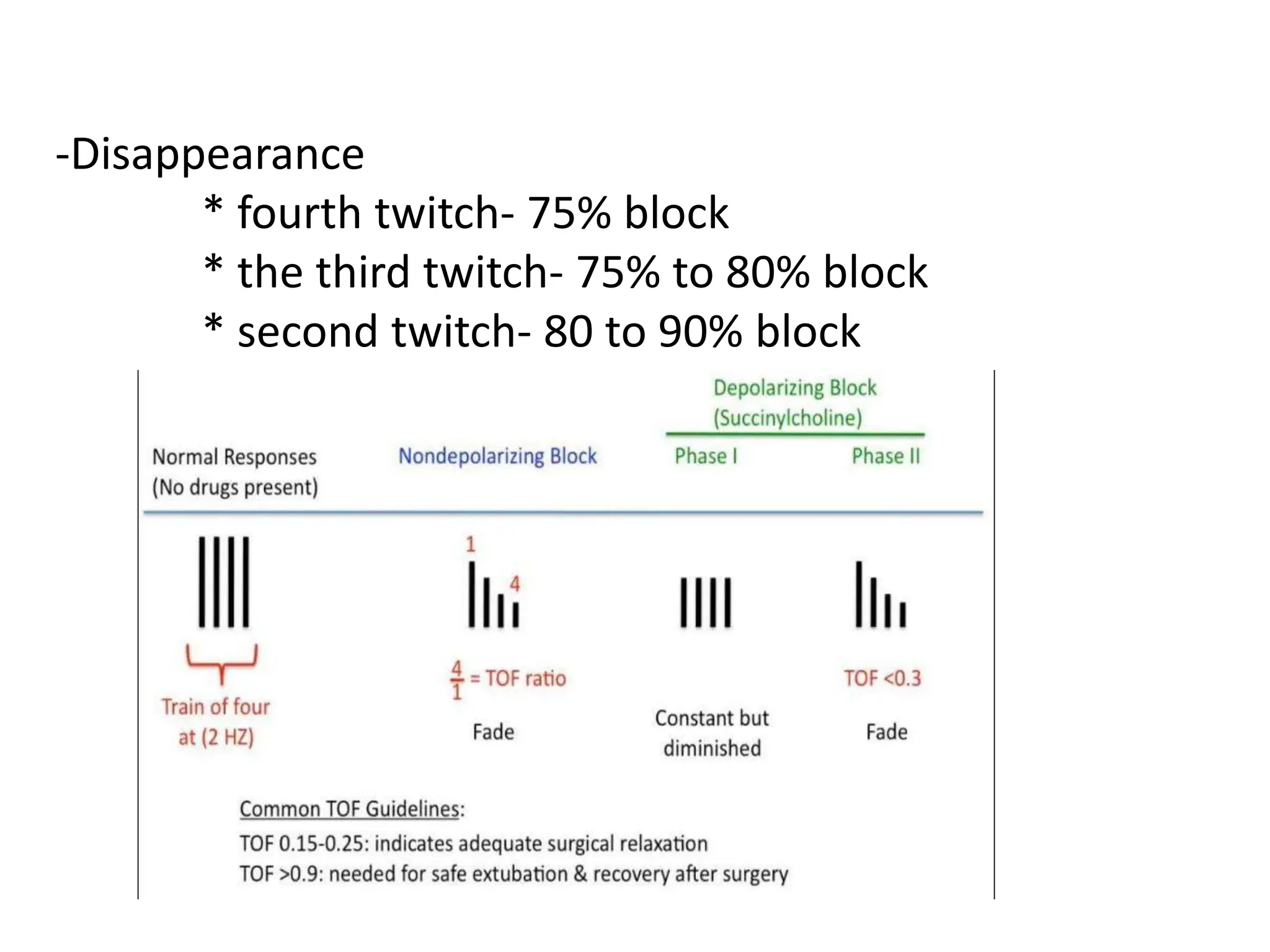
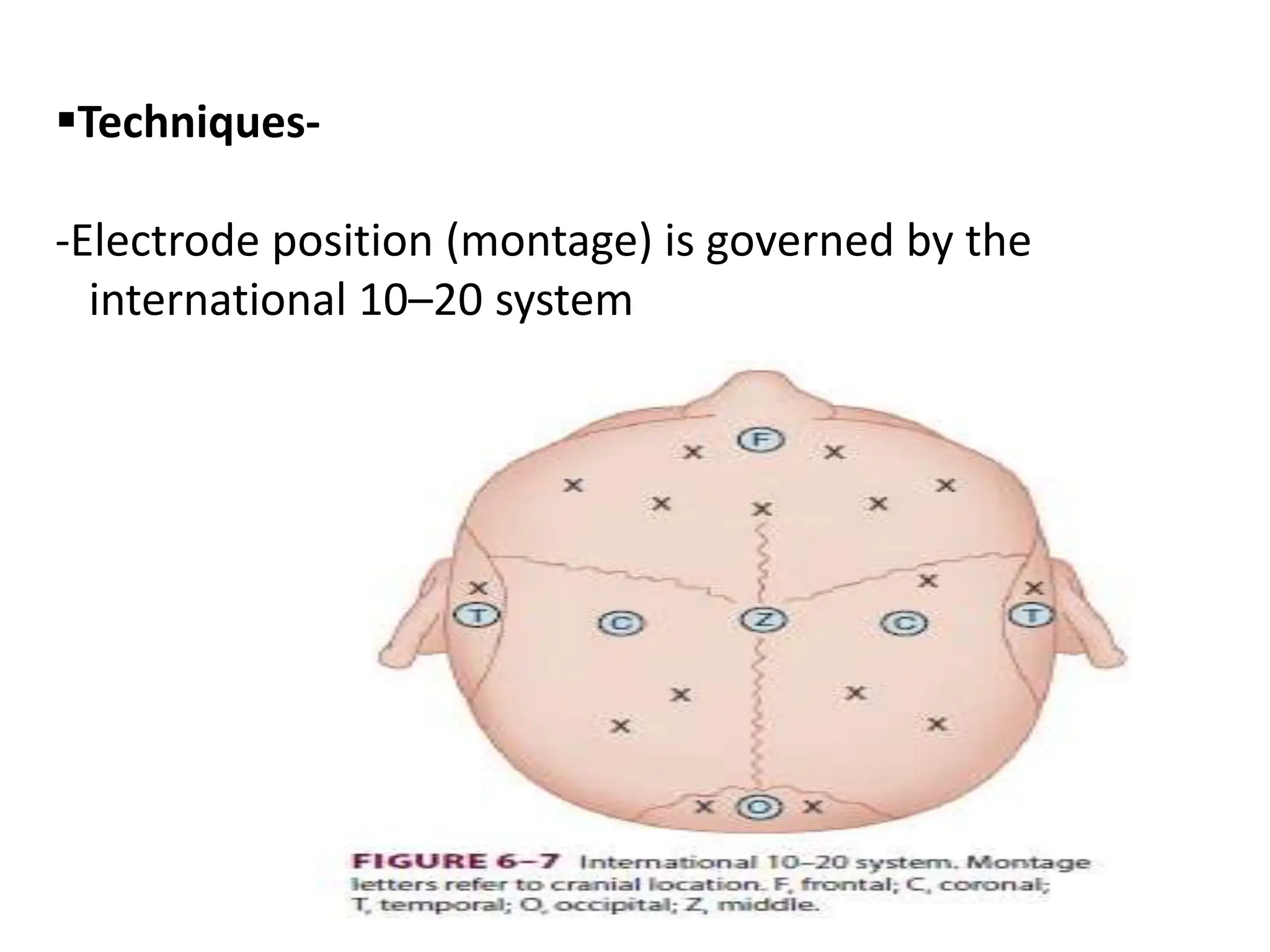
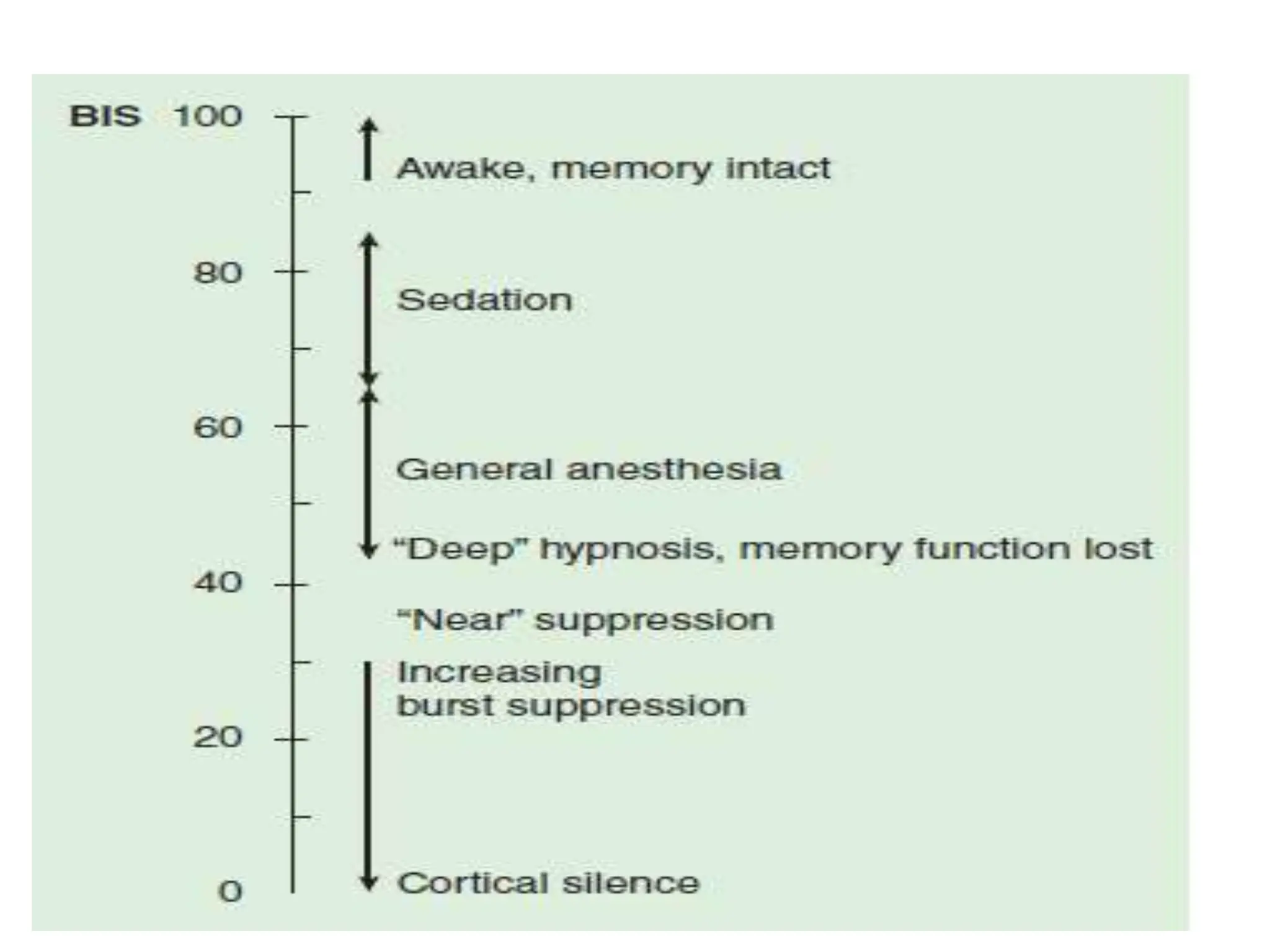
The document discusses the importance of monitoring in anesthesia care, emphasizing compliance with ASA standards and the use of various monitoring devices to ensure patient safety during procedures. It outlines both basic and advanced monitoring techniques, including cardiovascular, respiratory, neuromuscular, CNS, and temperature monitoring, highlighting their purposes and methods. The document concludes that continuous and effective monitoring is crucial for reducing poor outcomes in anesthesia.