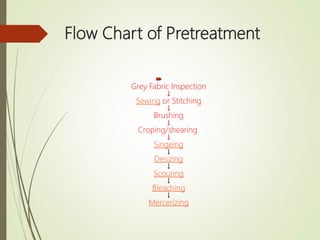
This document provides an overview of different wet processing treatments for textiles. It begins with introducing the presenters and then provides a flow chart showing the sequence of various pretreatment processes like grey fabric inspection, sewing, brushing, cropping, singeing, desizing, scouring, bleaching, and mercerizing. It then proceeds to describe each process in 1-2 paragraphs with details about the purpose and method involved. The key processes covered are grey fabric inspection, sewing, brushing, cropping, singeing, desizing, scouring, bleaching and mercerizing.