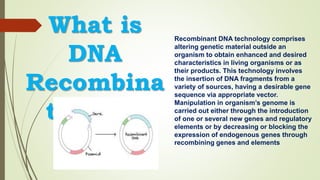
Recombinant DNA technology involves altering genetic material outside an organism to obtain desired traits. It has applications in improving human health by developing vaccines, insulin, diagnostics and more. In agriculture, genetically modified crops show increased yields, resistance to pests and tolerance of environmental stresses. The document discusses recent advances like CRISPR that allow precise genetic editing, and the roles of recombinant technologies in food production, medicine, the environment and energy. Overall, it presents recombinant DNA technology as having significantly improved human life through applications in health, food and the environment.