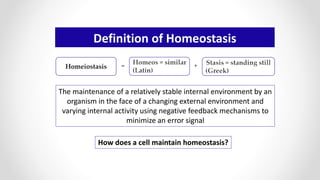
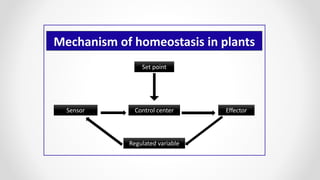
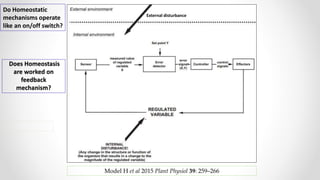
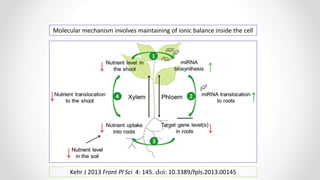
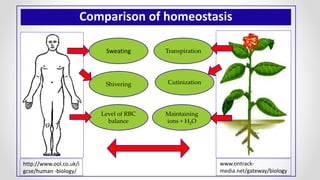
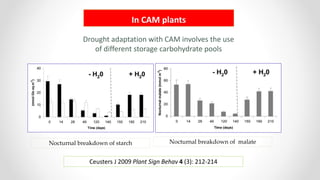
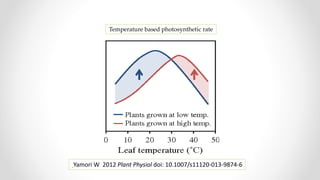
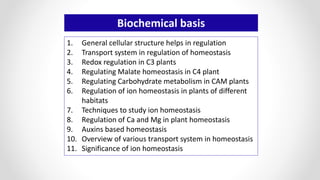
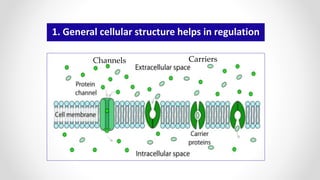
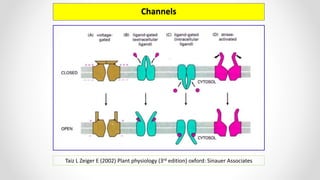
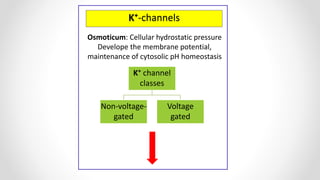
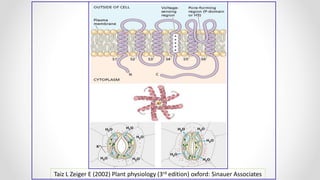
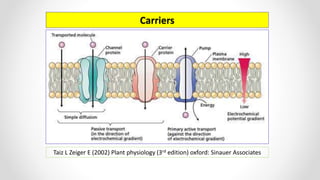
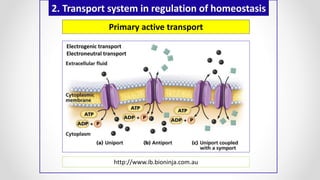
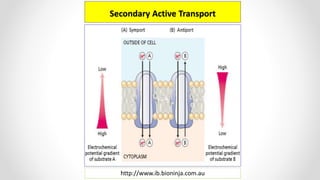
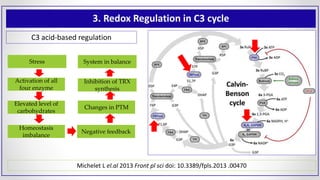
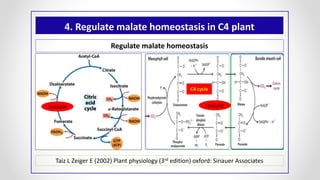
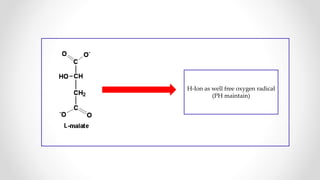
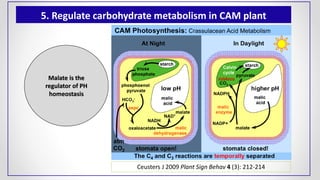
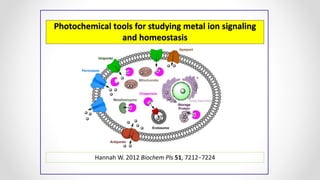
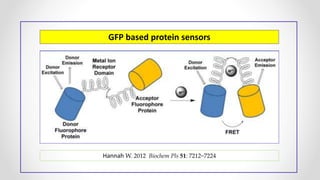
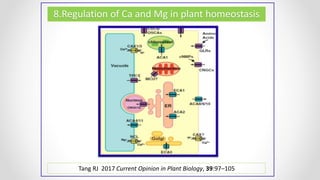
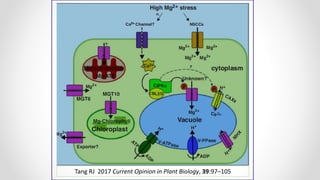
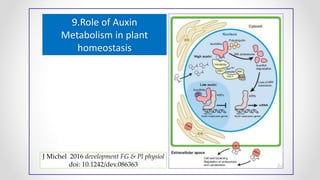
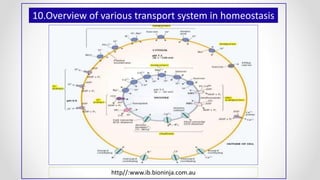
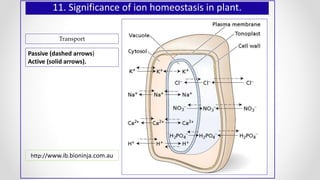
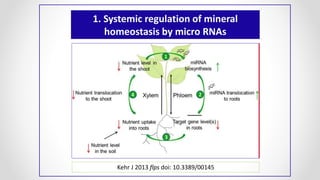
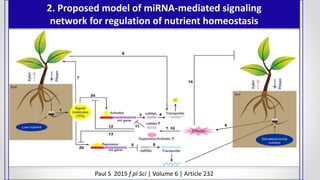
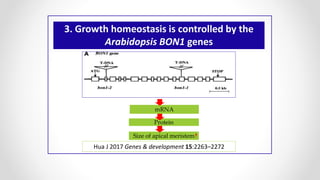
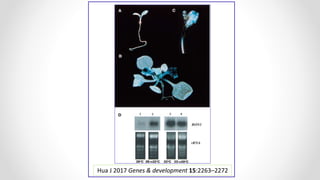
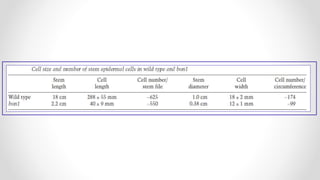
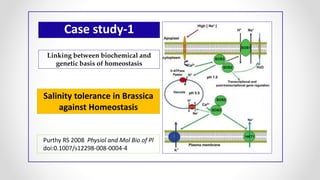
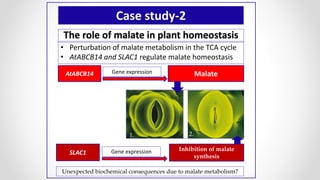
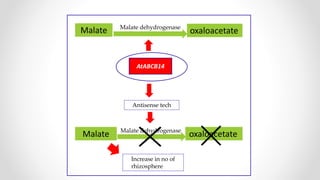
This document discusses molecular basis and regulation of homeostasis in plants. It begins with a brief history of homeostasis and provides definitions. It then outlines the main topics to be covered, including hypotheses, mechanisms, physiological, biochemical and genetic regulation of homeostasis, case studies, and conclusions. The main points are that homeostasis involves maintaining a stable internal environment through negative feedback mechanisms. It is regulated at the physiological level through adaptations, at the biochemical level through transport systems and redox regulation, and at the genetic level through microRNAs and growth genes. Case studies examine salinity tolerance and malate metabolism. The conclusion restates that homeostasis maintains nutrient and ion balance internally through various mechanisms.