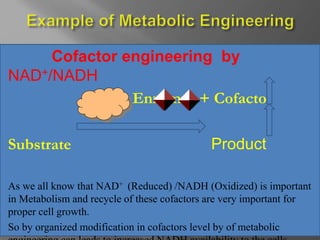
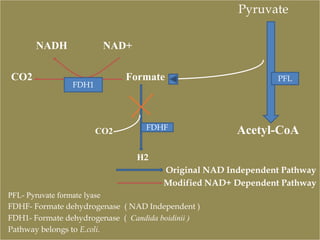
This document discusses metabolic engineering. Metabolic engineering modifies cellular properties through recombinant DNA technology to alter metabolic pathways for production of chemicals, fuels, pharmaceuticals and medicine. It requires overexpression or downregulation of proteins in pathways so cells produce new products. The first step is understanding the host cell environment for genetic modifications, and the effect of modifications on growth should be examined. Genetic manipulation may negatively impact metabolic burden. Metabolic engineering is used to produce various compounds through methods like eliminating competing pathways, expressing foreign enzymes, and optimizing cofactors like NAD+/NADH.