Embed presentation
Download to read offline

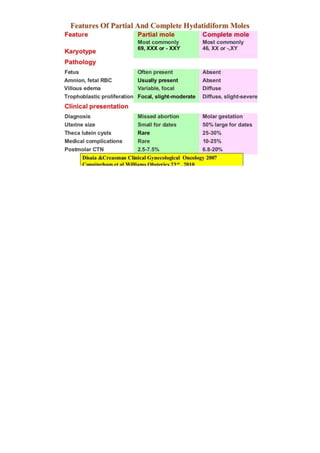
A molar pregnancy occurs when trophoblastic tissue proliferates abnormally and invades the endometrium in a more aggressive way than normal. It can be either a complete or partial mole depending on genetic factors. A complete mole results from one sperm fertilizing an empty ovum and having a purely paternal genome, while a partial mole occurs when two sperm fertilize one ovum resulting in a triploid genome. Molar pregnancies are typically treated by suction curettage to remove the abnormal tissue, followed by monitoring of HCG levels to check for persistent trophoblastic disease which may require further treatment.

