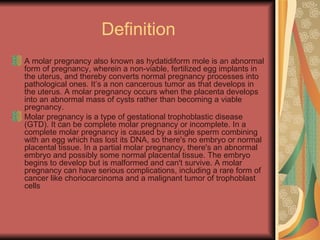
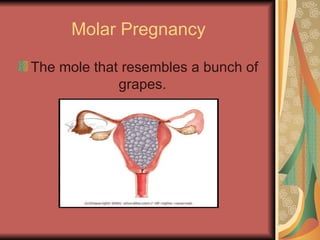
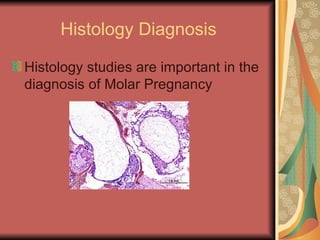
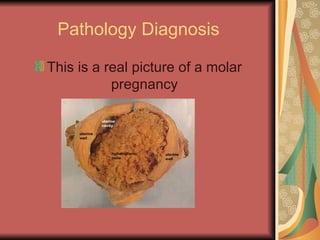
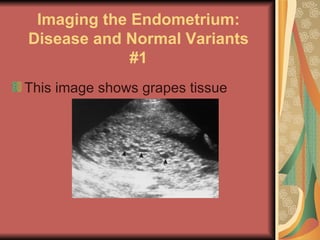
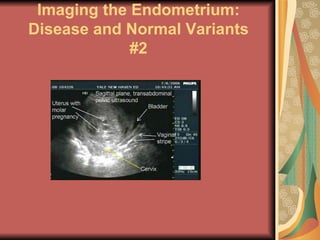
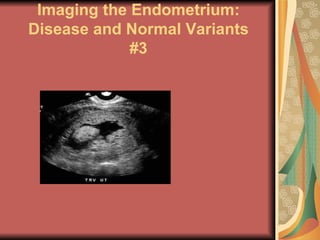
A molar pregnancy is an abnormal form of pregnancy where a non-viable, fertilized egg implants in the uterus and converts normal pregnancy processes into pathological ones. It results in a non-cancerous tumor that develops in the uterus instead of a viable pregnancy. There are two types - a complete molar pregnancy caused by a sperm fertilizing an egg without DNA, and a partial molar pregnancy with an abnormal embryo and some normal placental tissue. Molar pregnancies are diagnosed through physical exams, blood tests, ultrasound and tissue samples. They require early evacuation of the uterus to prevent risks like choriocarcinoma cancer, and patients need monitoring until human chorionic gonadotropin hormone levels fall.