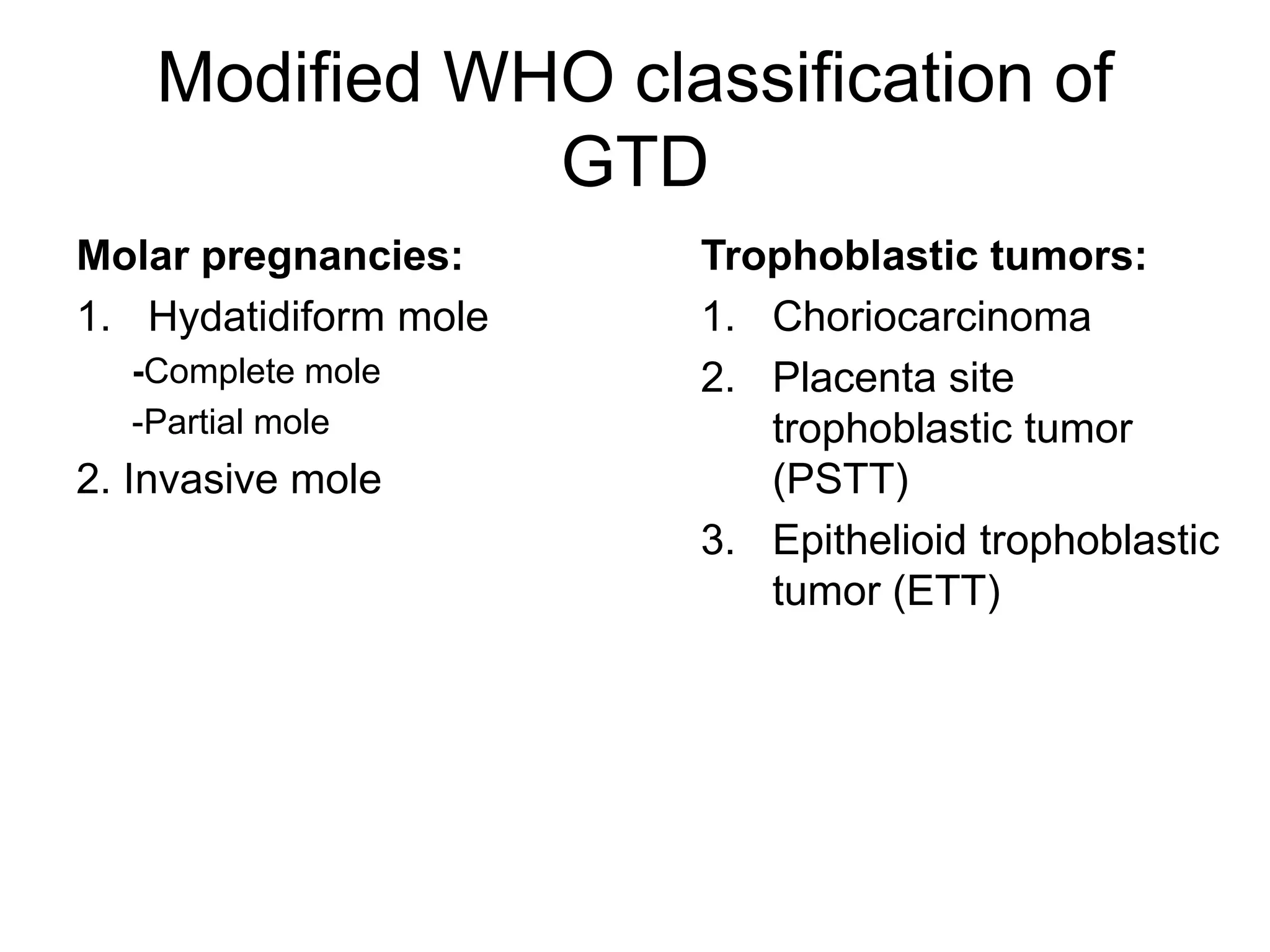
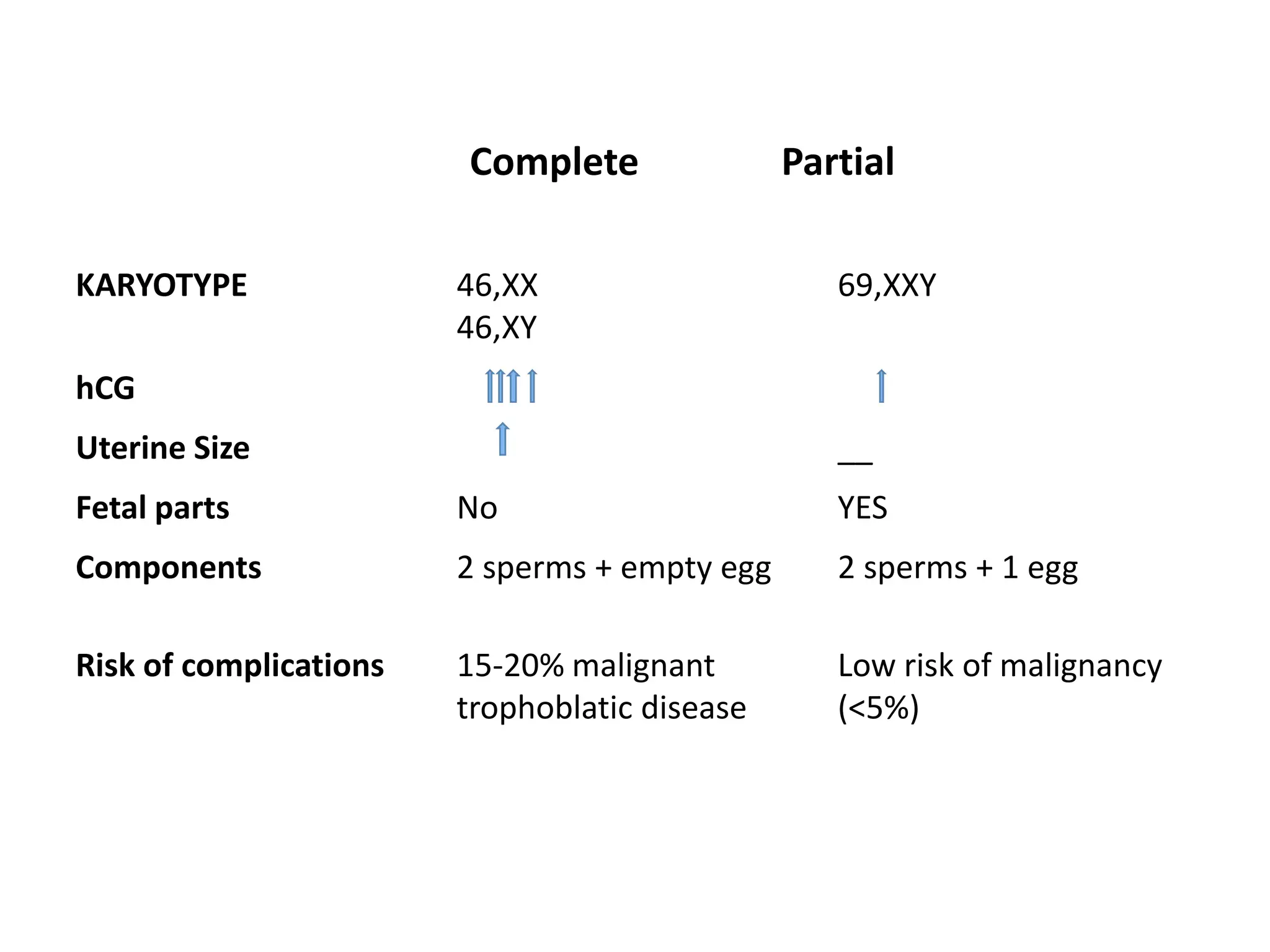
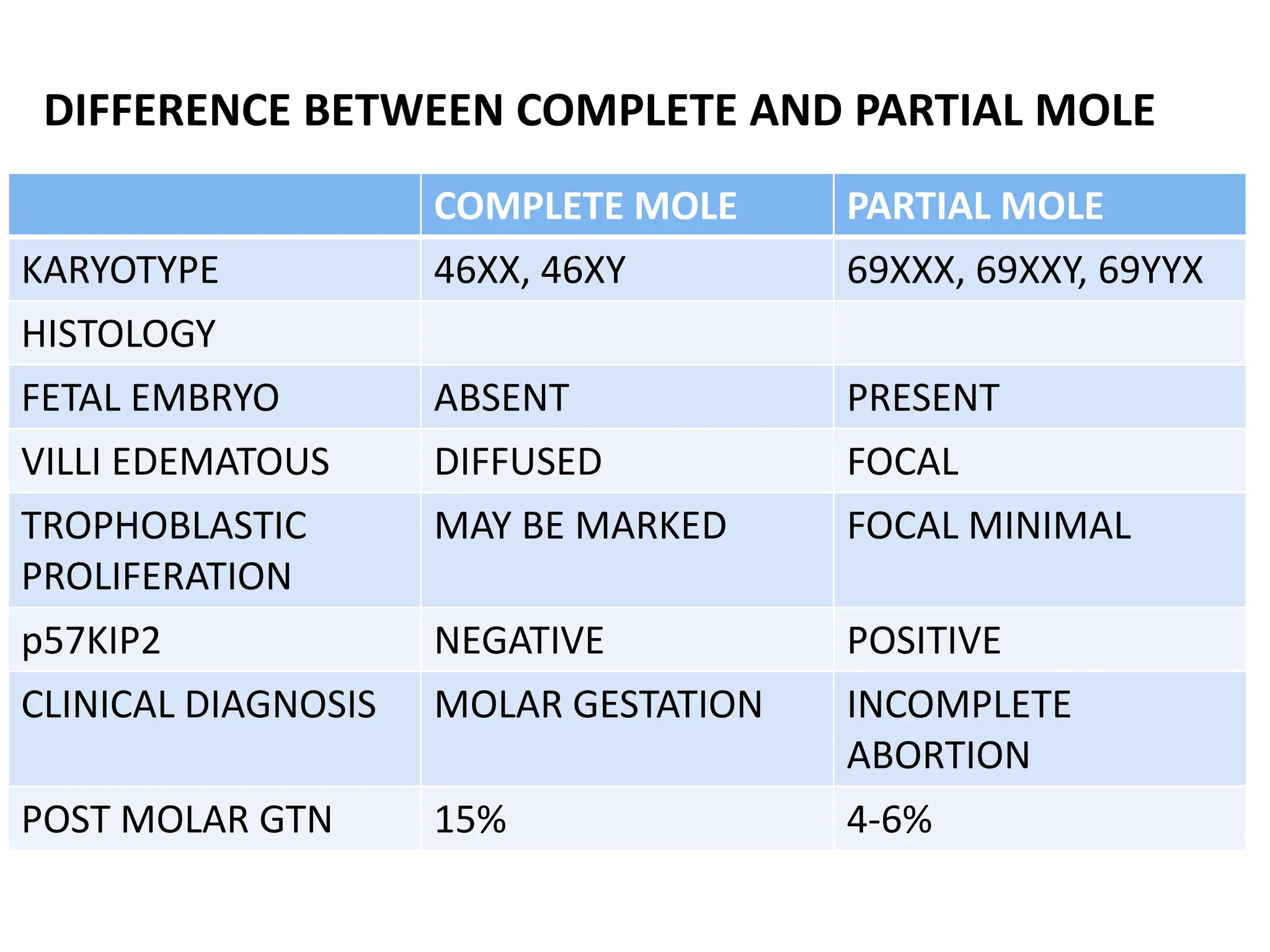
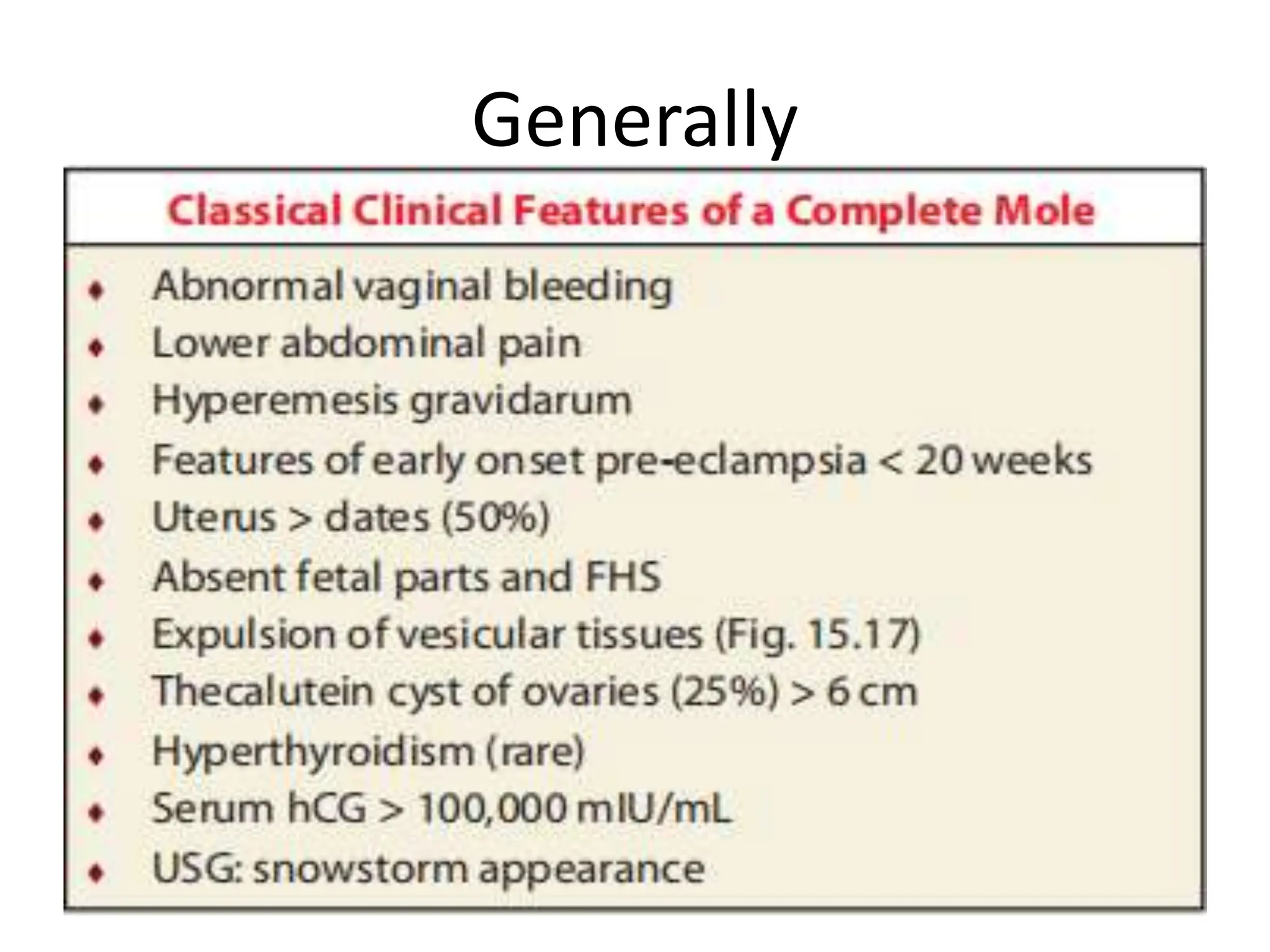
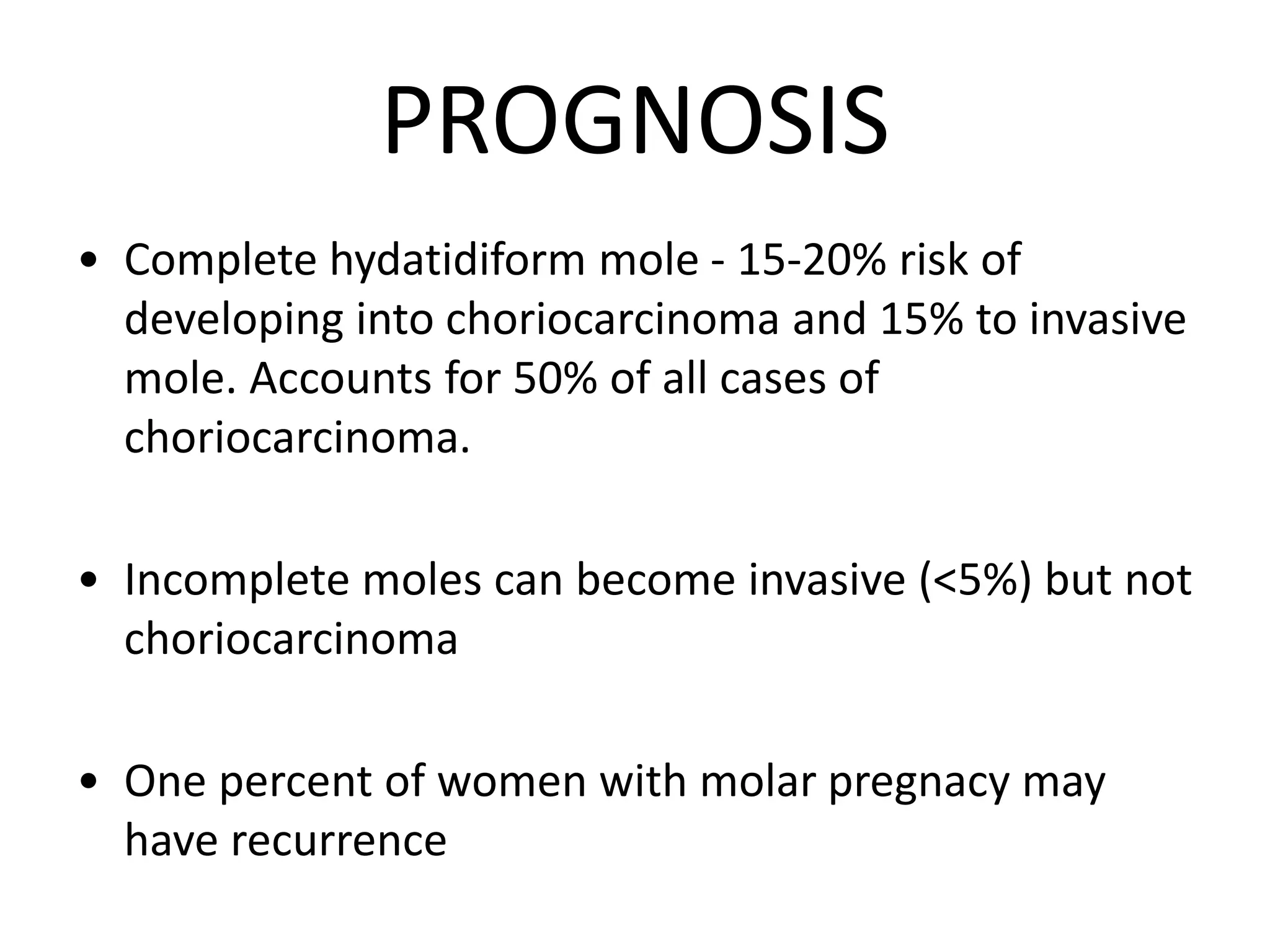
Molar pregnancy, a form of gestational trophoblastic disease, occurs when a fertilized egg implants in the uterus without a viable embryo, resulting in either a complete or partial mole. Key clinical features include vaginal bleeding, abdominal pain, and potential complications such as hemorrhage and choriocarcinoma. Diagnosis is typically made through quantification of beta-hCG, ultrasound imaging, and histological examination, with treatment involving surgical evacuation and close monitoring for potential malignancy.