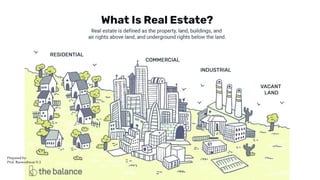
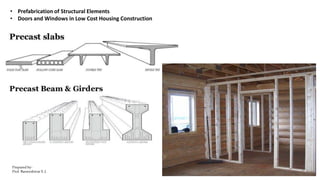
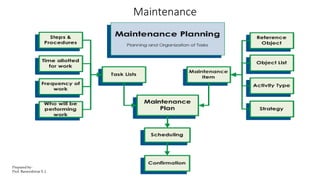
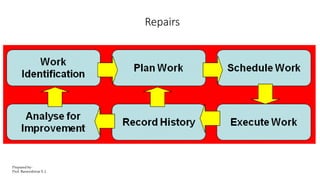
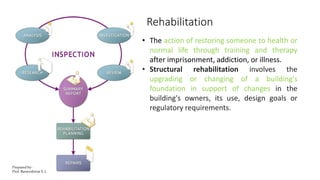
This document discusses traditional building materials like stone, brick, timber, bamboo, mud, and lime. It then discusses low-cost housing materials and methods, focusing on using low-cost materials and efficient construction techniques. Specific low-cost materials mentioned include hollow concrete blocks, filler slabs for ceilings, prefabricated structural elements, and doors and windows. The document emphasizes selecting materials based on cost, energy efficiency, durability, and other factors. It also briefly discusses maintenance, repairs, and rehabilitation of housing.