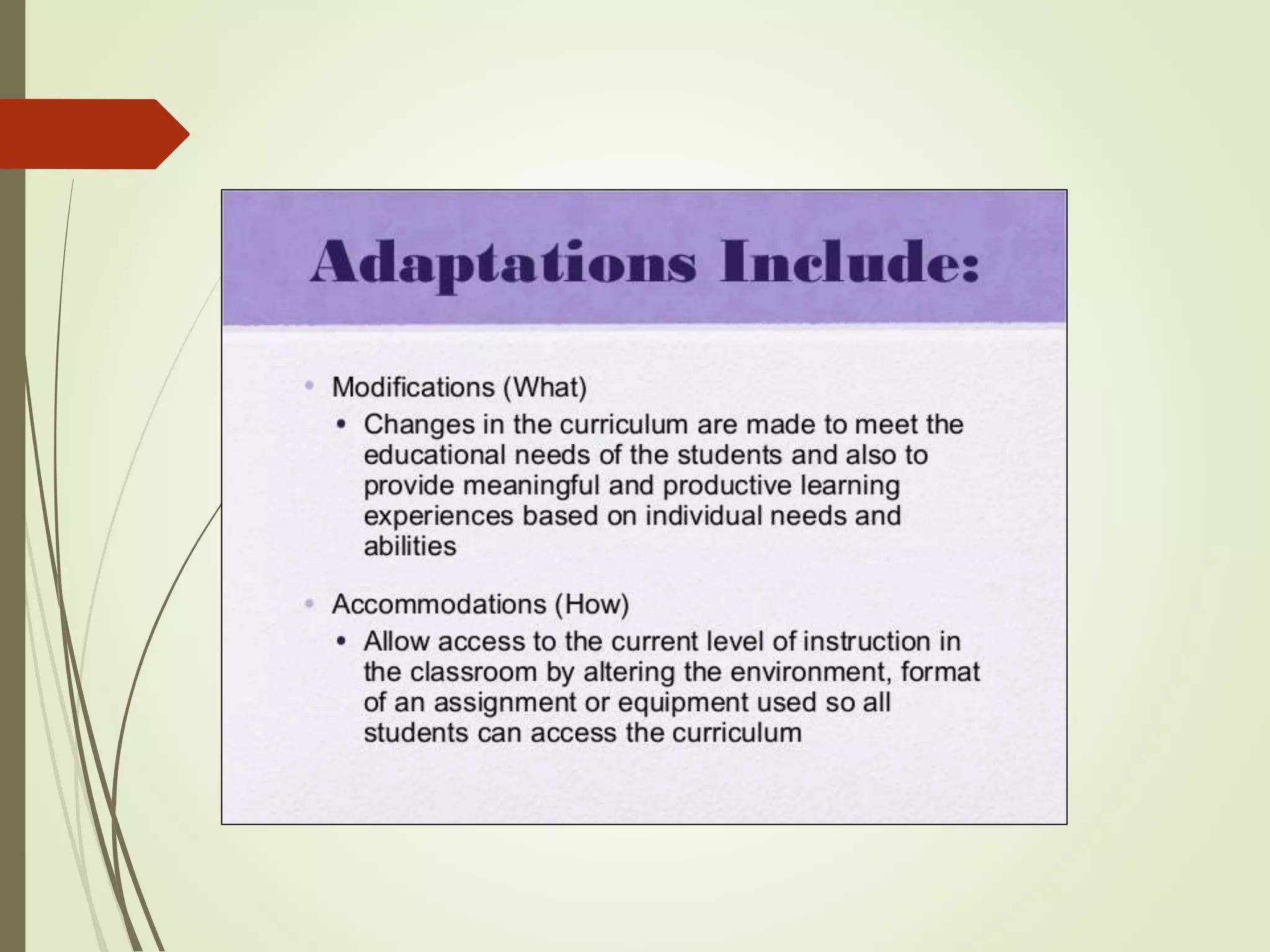
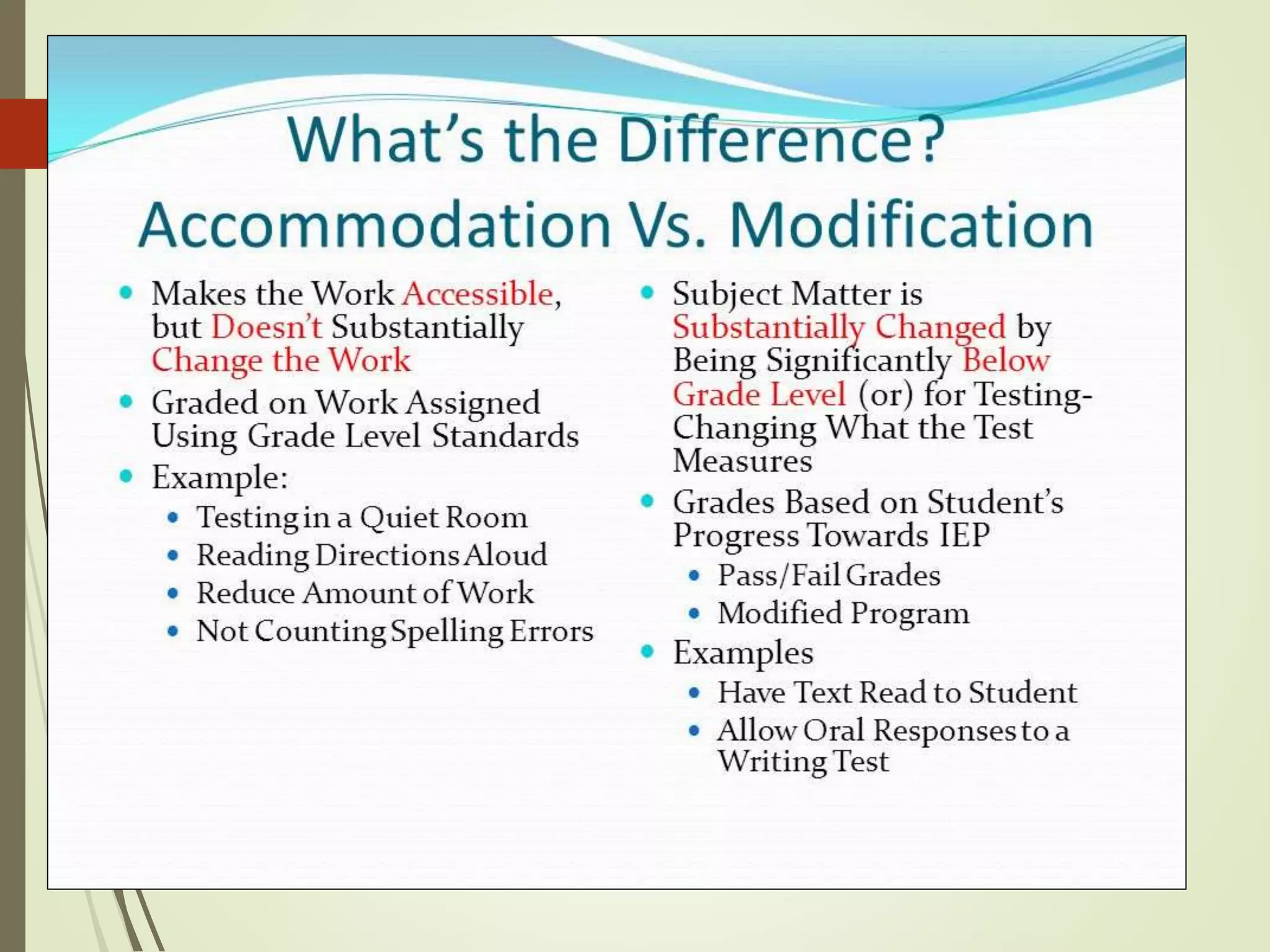
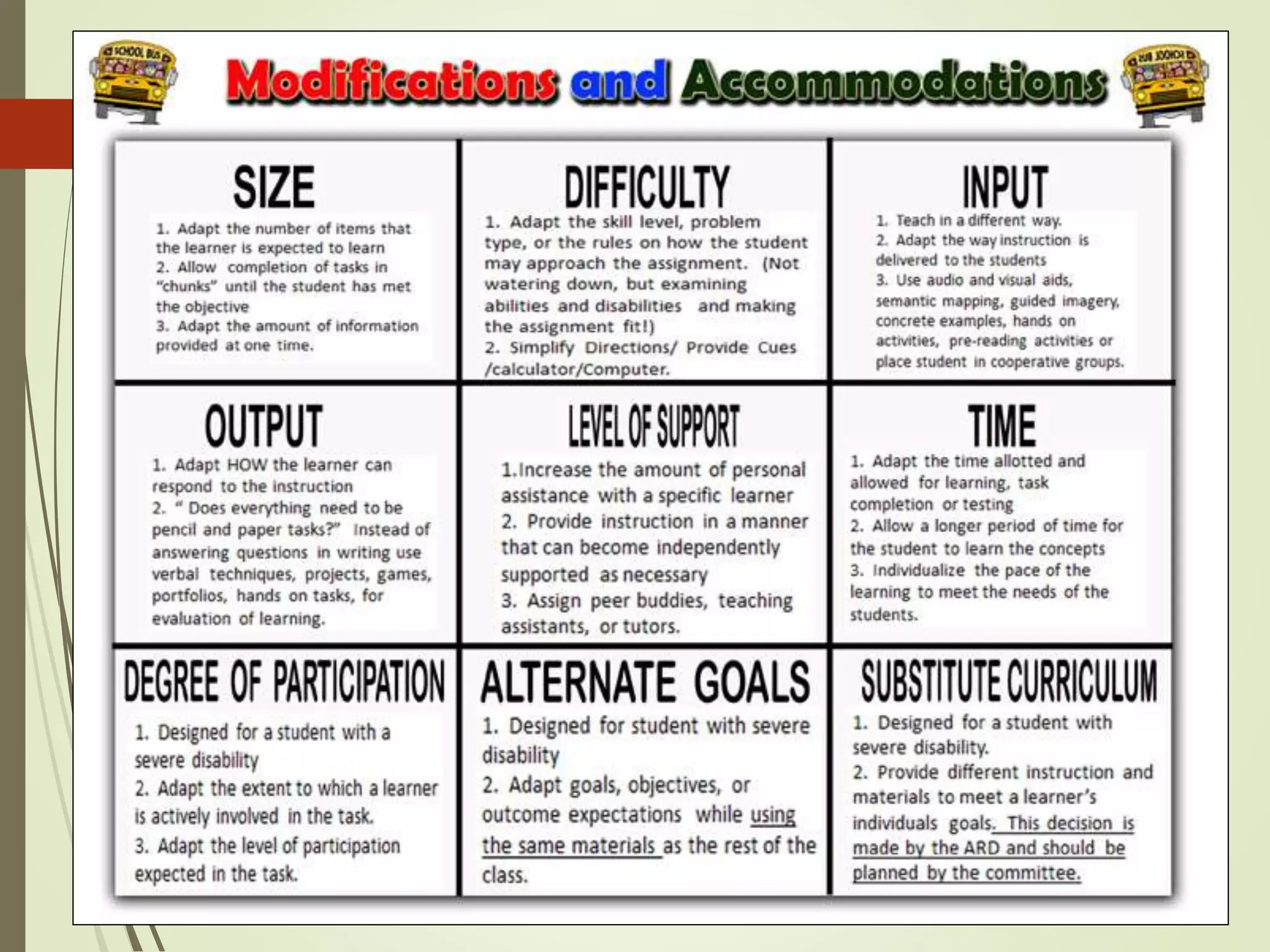
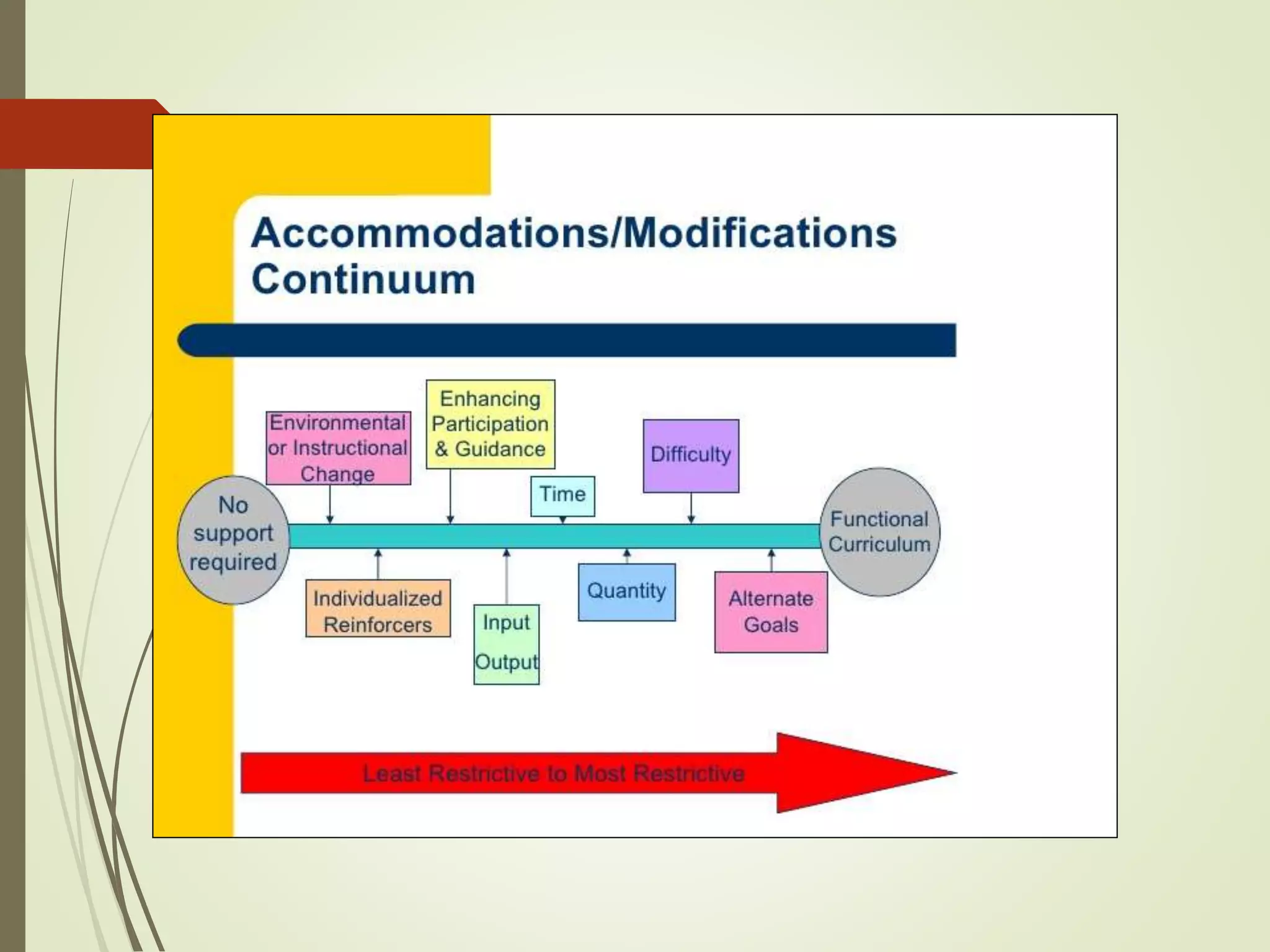
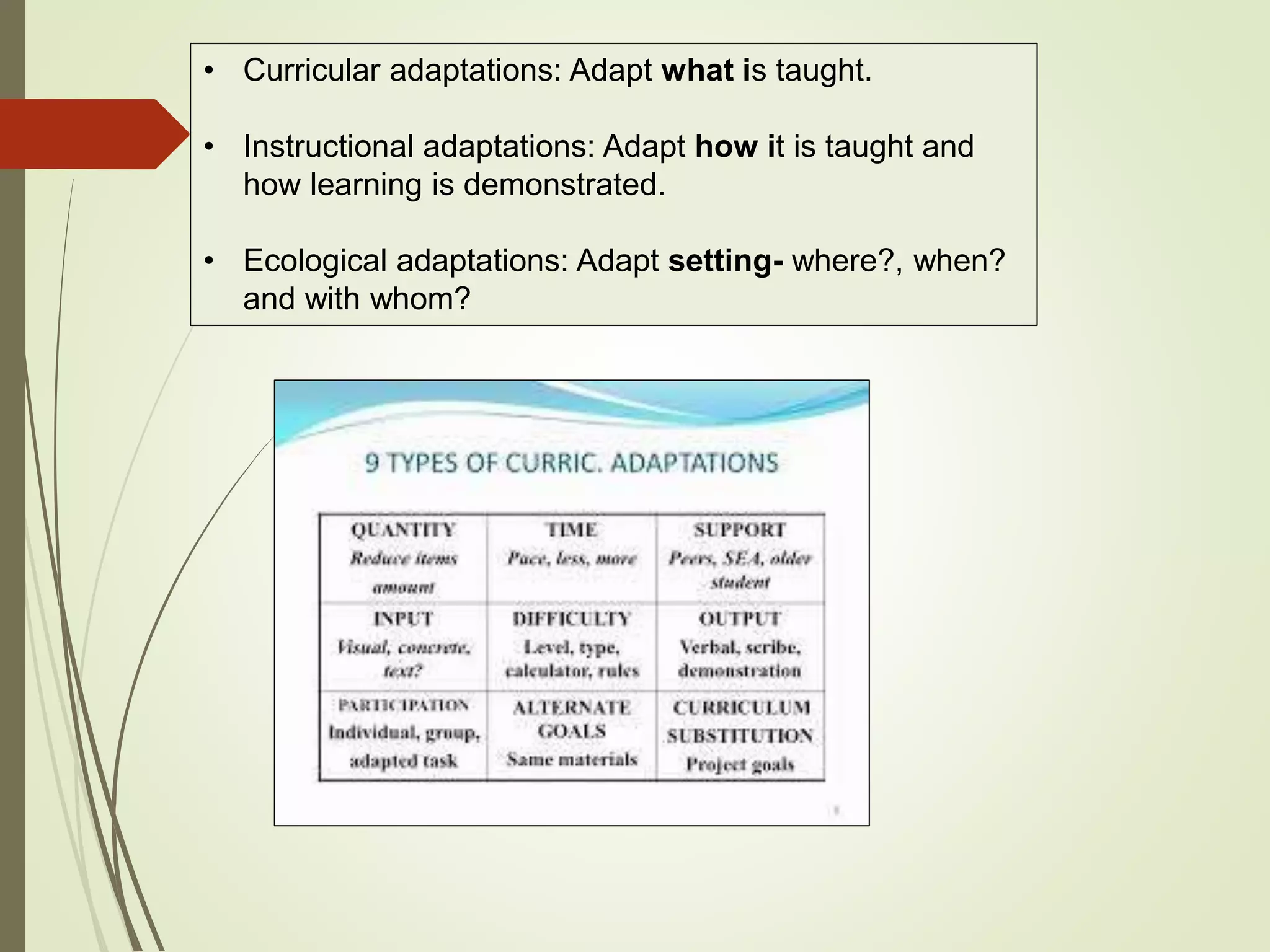
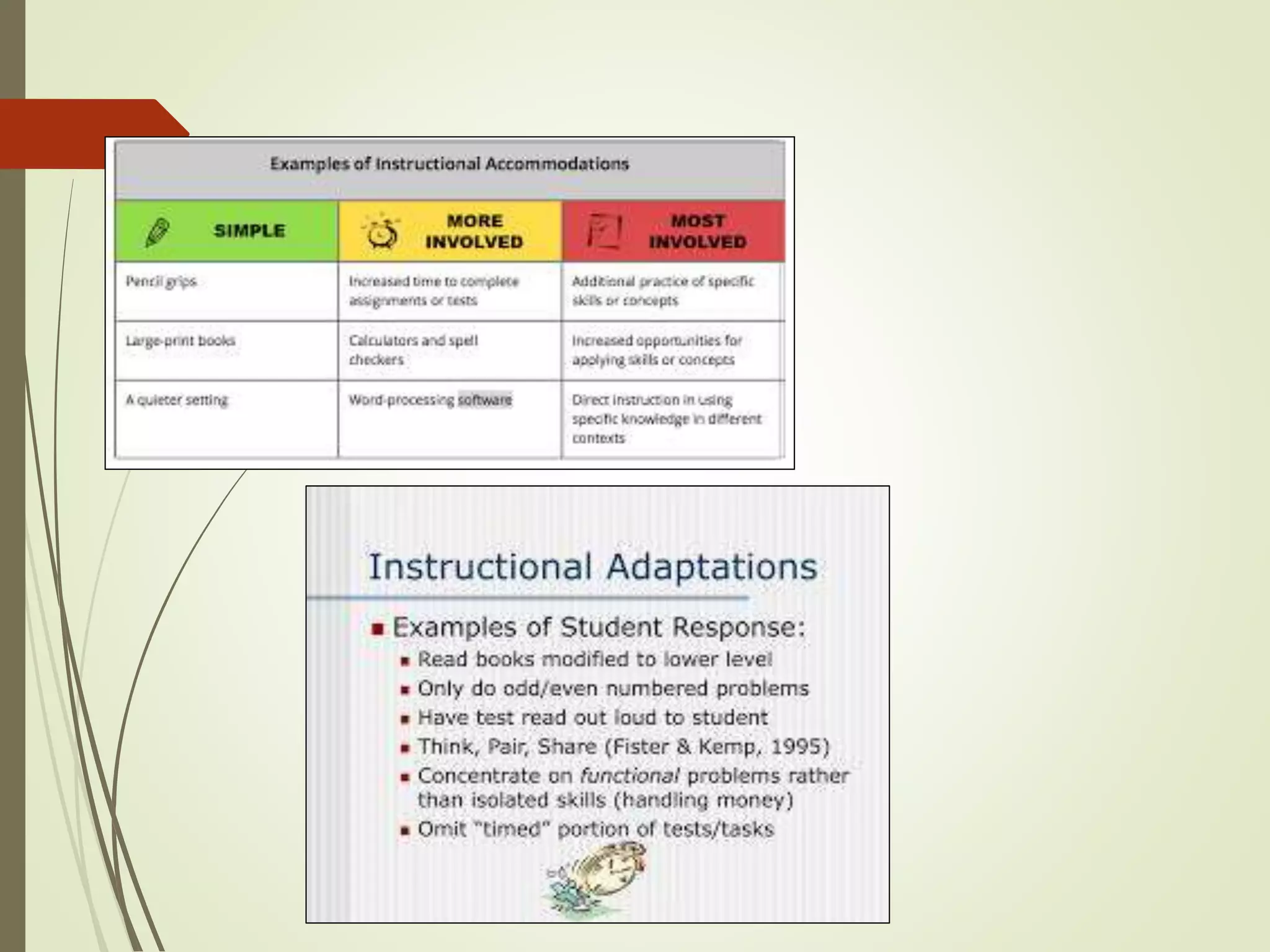
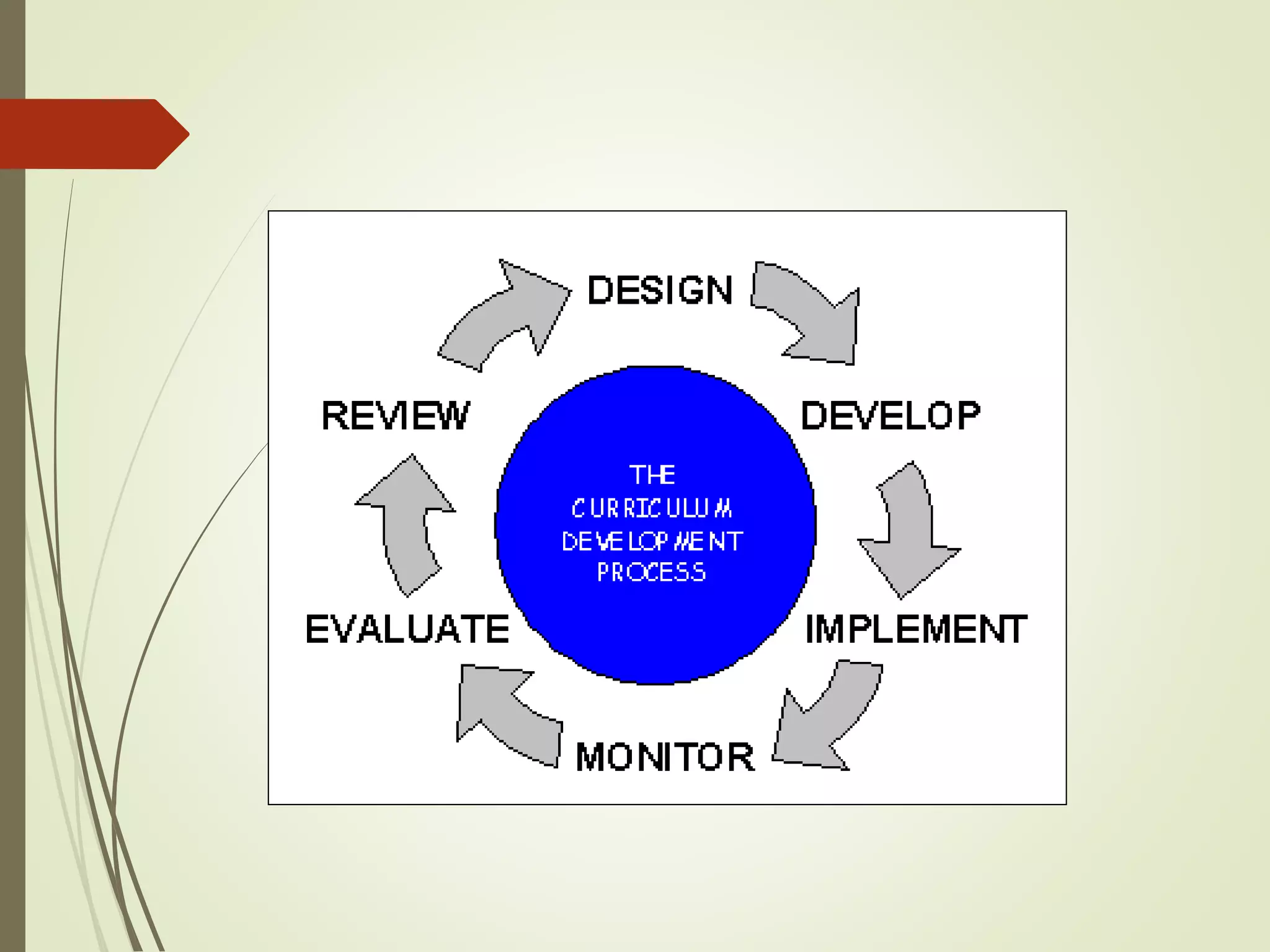
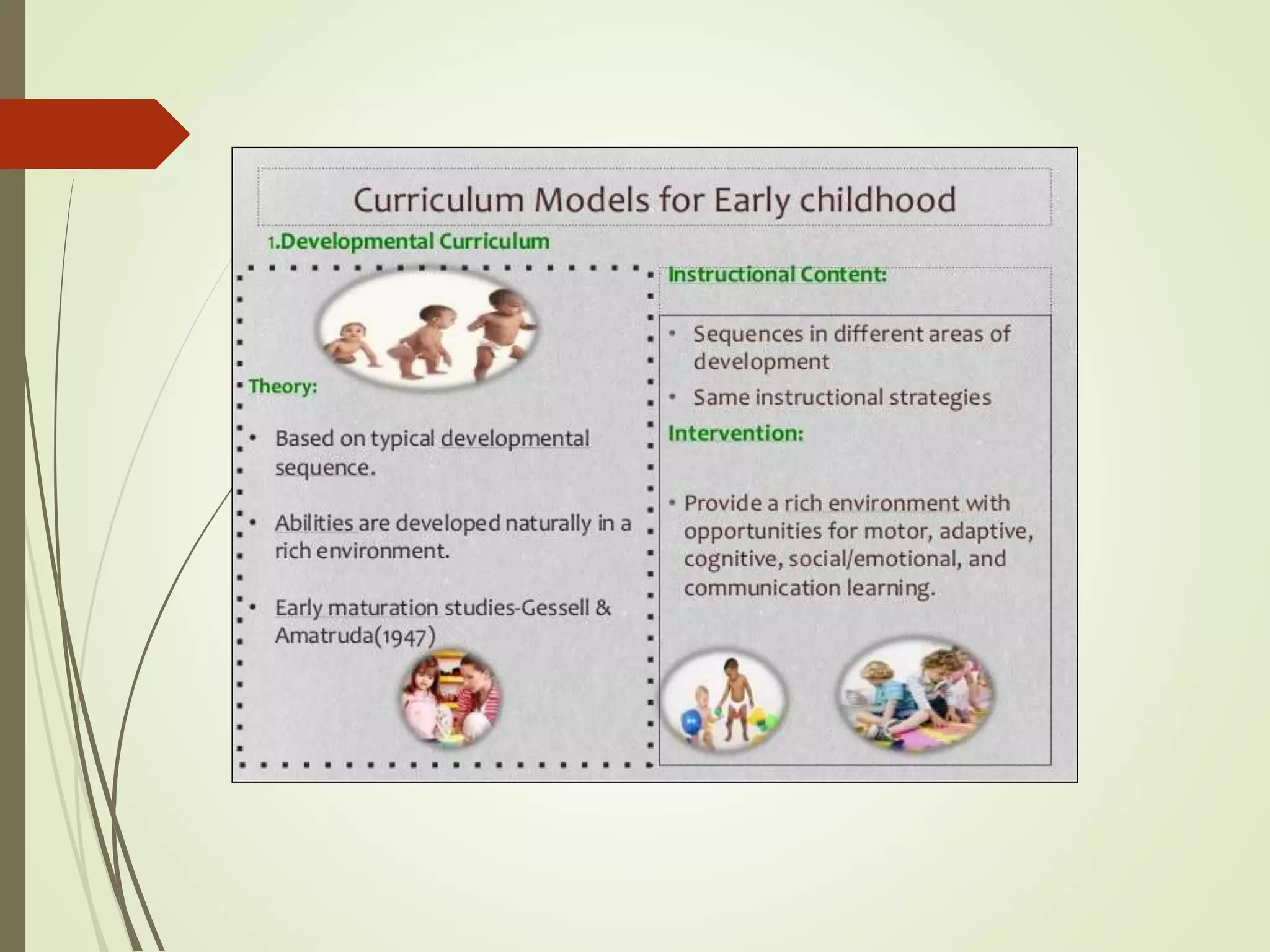
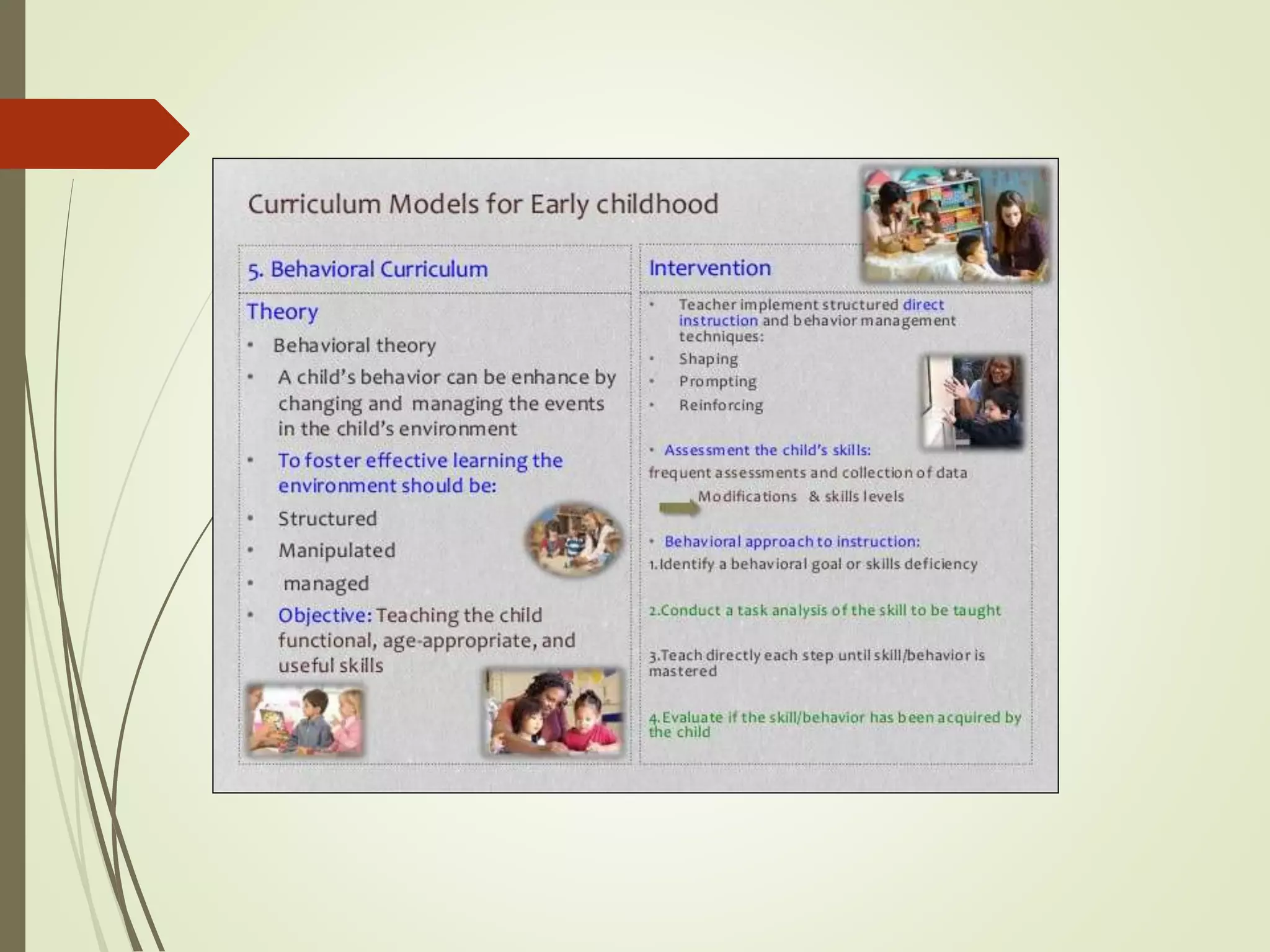
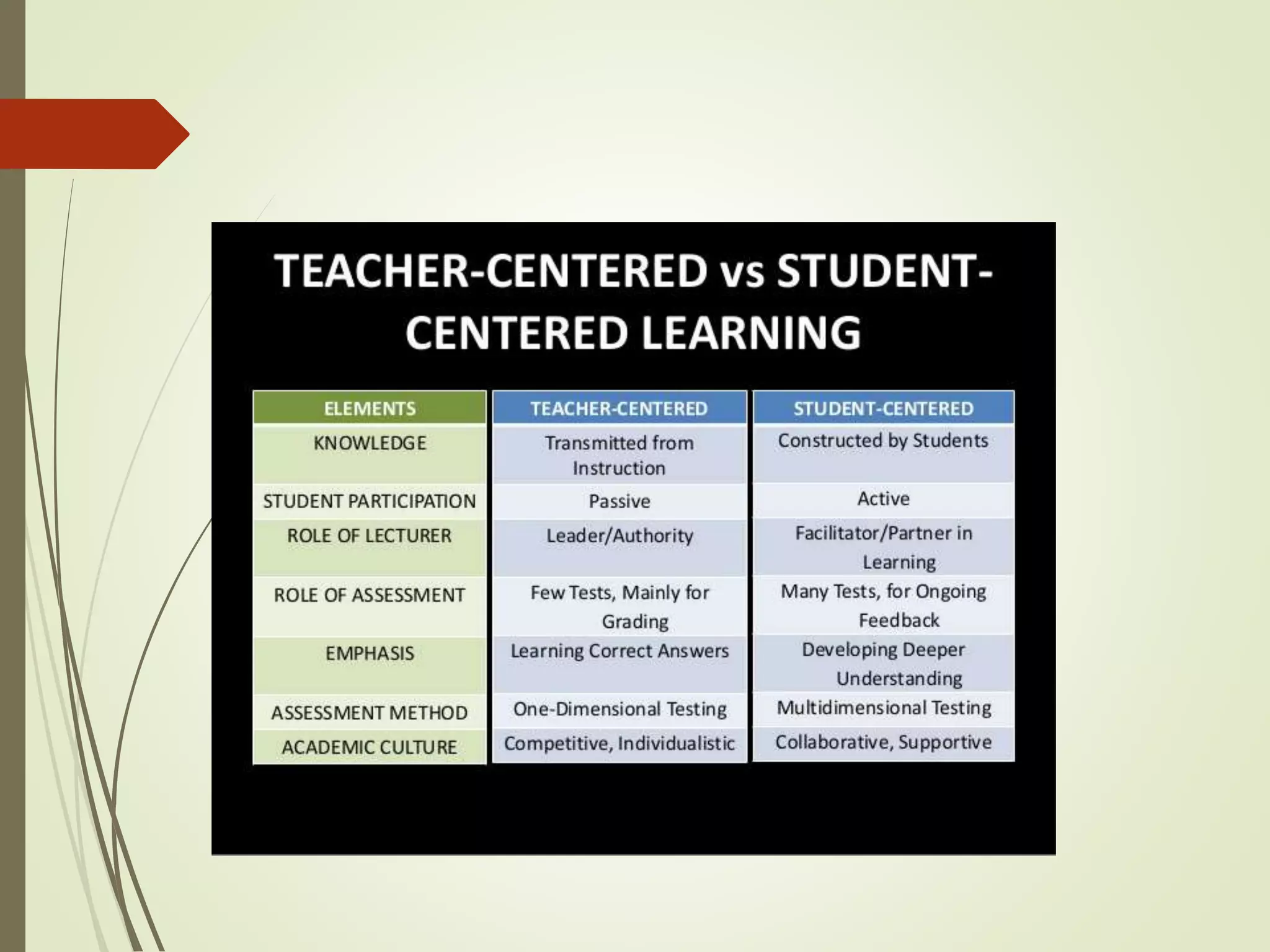
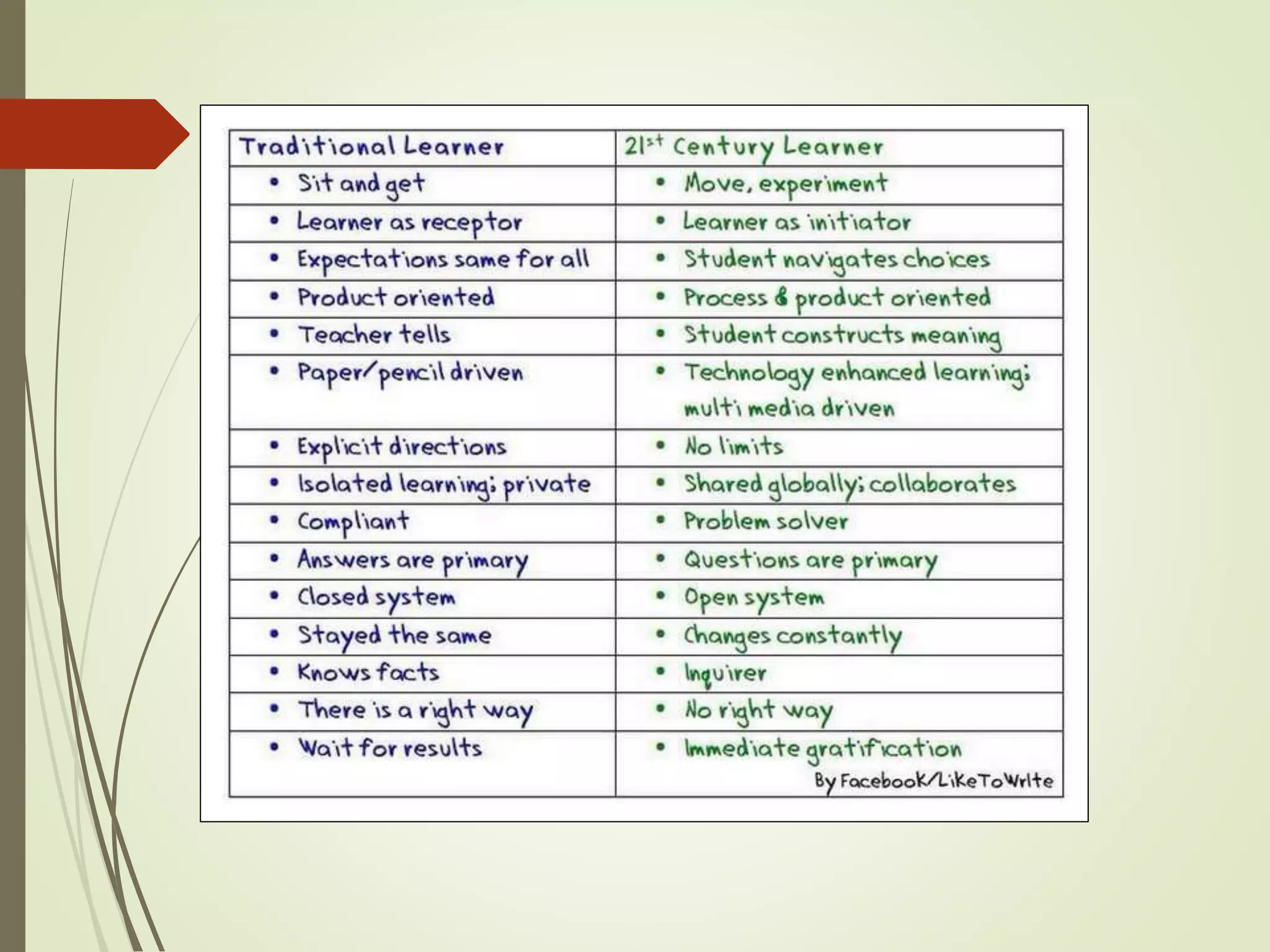
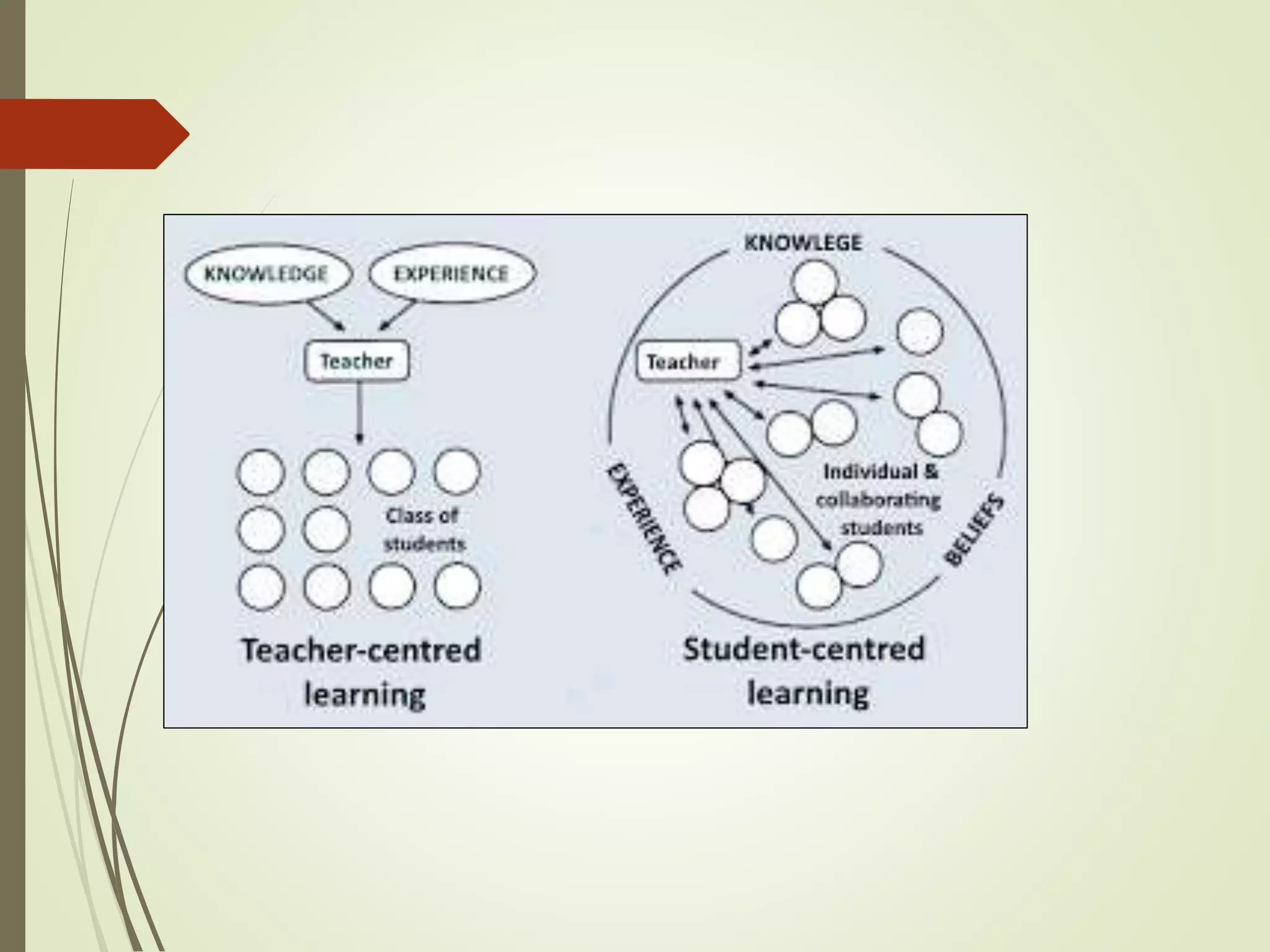
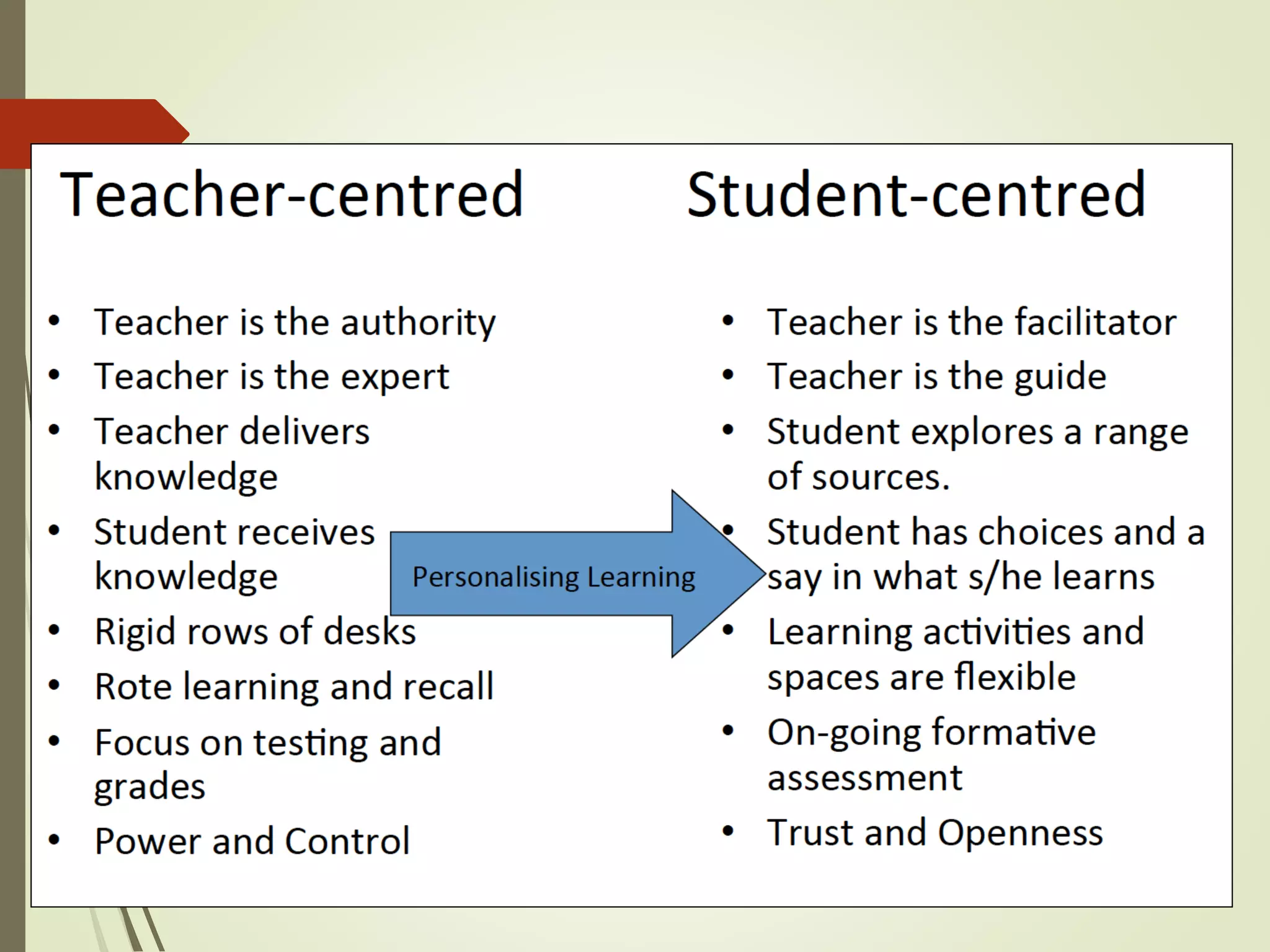
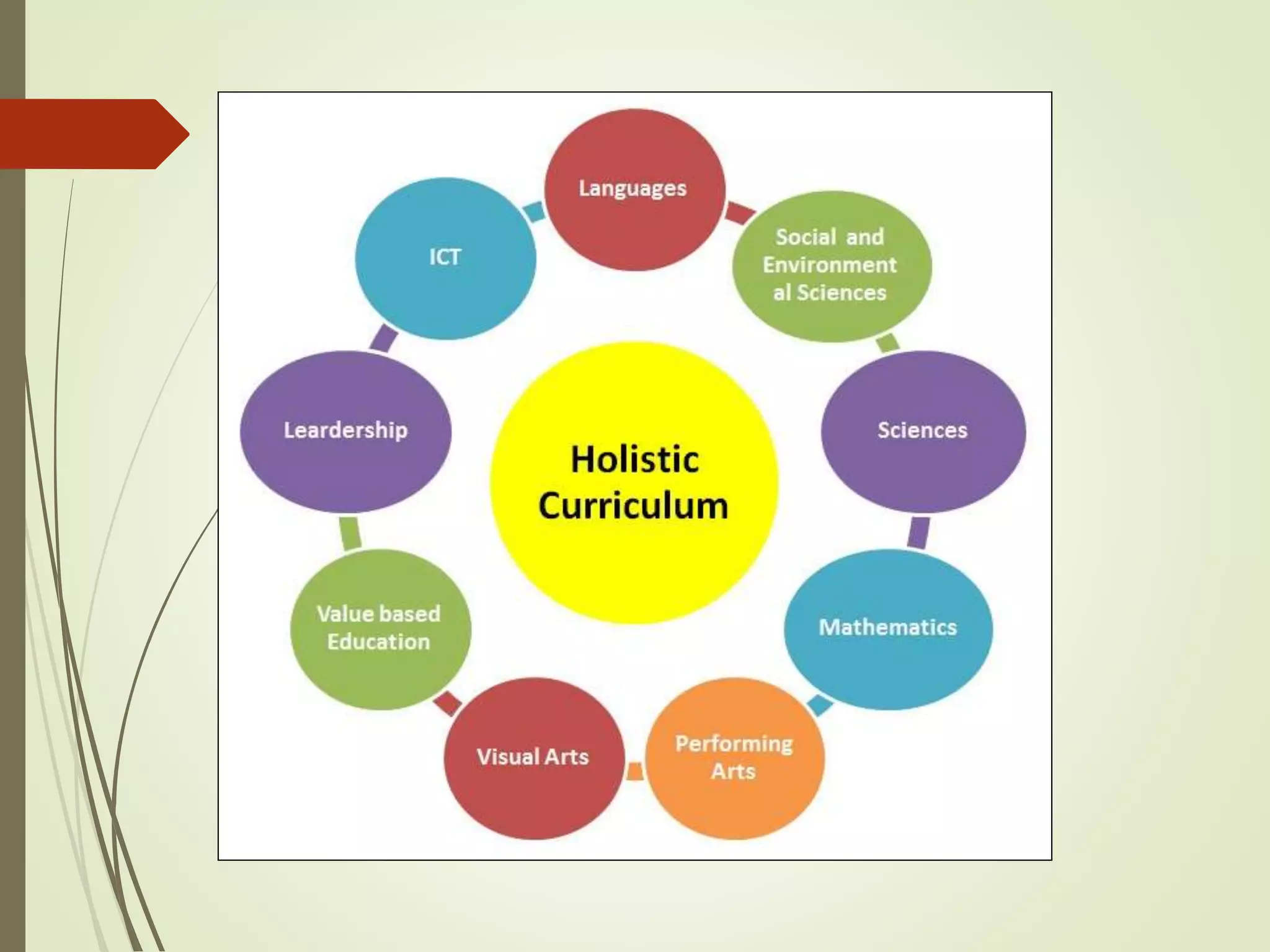
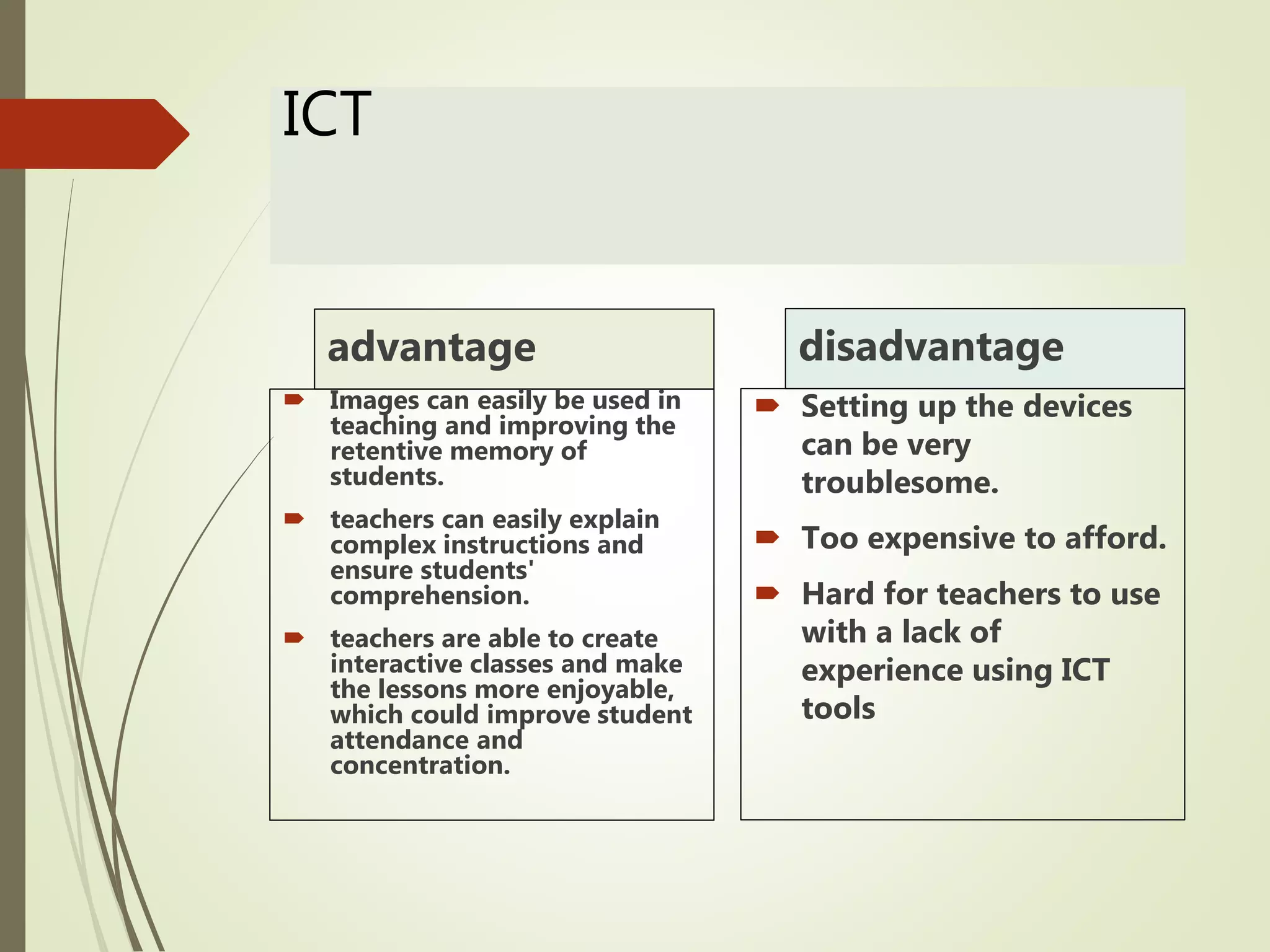
The document discusses curriculum adaptations and teaching strategies designed to facilitate equal learning opportunities for students with individualized education plans (IEPs). It emphasizes holistic education principles, including collaboration, skill development, and community engagement, and highlights the advantages and disadvantages of integrating information and communication technologies (ICT) in the classroom. Additionally, it provides a series of questions related to curriculum design and educational philosophies.