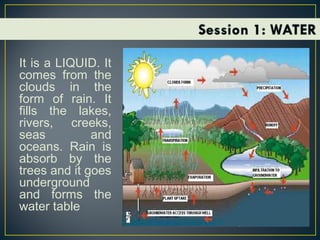
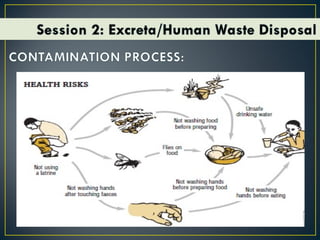
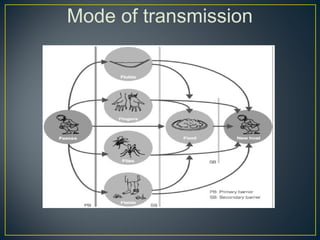
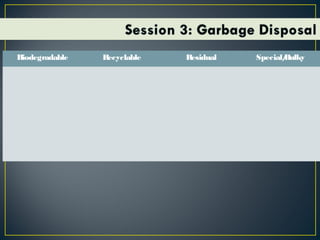
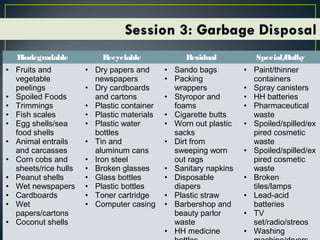
This document discusses various topics related to environmental sanitation, including water, human waste disposal, garbage disposal, and global warming. It provides information on proper water purification methods like boiling, different types of toilets and human waste disposal, categories of garbage and proper disposal techniques, and the causes and effects of global warming. The document aims to educate participants on these topics and discuss existing problems and solutions in communities.