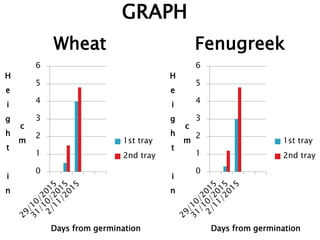
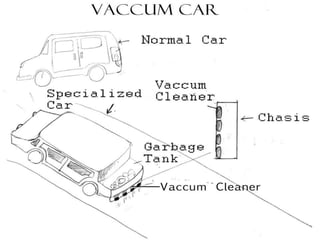
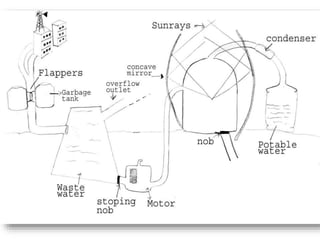
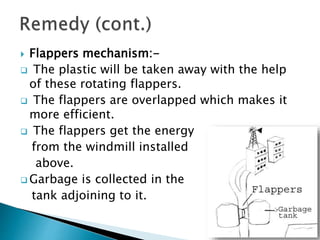
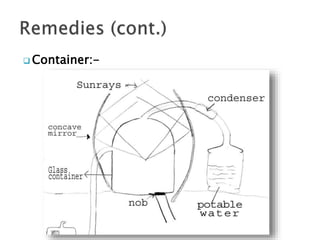
The document discusses various types of waste and their environmental impact, emphasizing the importance of cleanliness and hygiene in maintaining health. It details different waste types such as biodegradable, chemical, e-waste, and domestic waste, and highlights recycling methods to mitigate waste generation. Additionally, it presents innovative uses for waste materials and mentions governmental actions aimed at addressing the growing garbage problem.