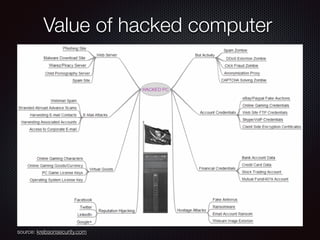
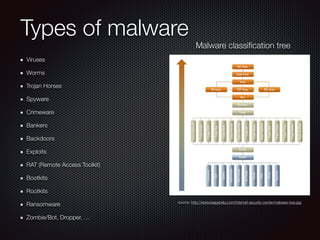
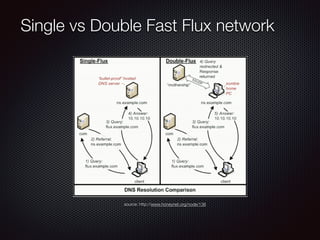
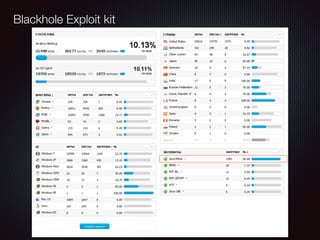
This document discusses modern malware threats and techniques. It defines malware and describes traditional vs modern malware approaches. Modern malware uses stealthy techniques like obfuscation and rootkits to avoid detection. It communicates through various protocols and services to command and control systems. The document outlines threat actors like cybercriminals, nation-states and hacktivists and recommends defenses like antivirus, firewalls, and employee training to mitigate risks.