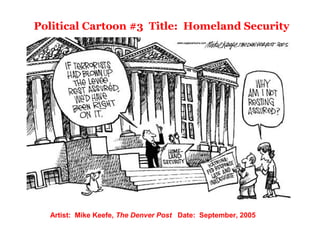
The document discusses the challenges of federalism in the United States. It describes federalism as a system that divides political authority between a national government and state/local governments. It outlines the evolution of federalism in the US from dual federalism in the late 1700s-early 1900s, where states and federal government had clearly defined separate powers, to cooperative federalism from the 1930s onward, where the federal government has intervened more in areas traditionally left to states like education and healthcare. Political cartoons from 2005 criticize the federal and state response to hurricanes Katrina and Rita, questioning the effectiveness of cooperative federalism in addressing national emergencies.