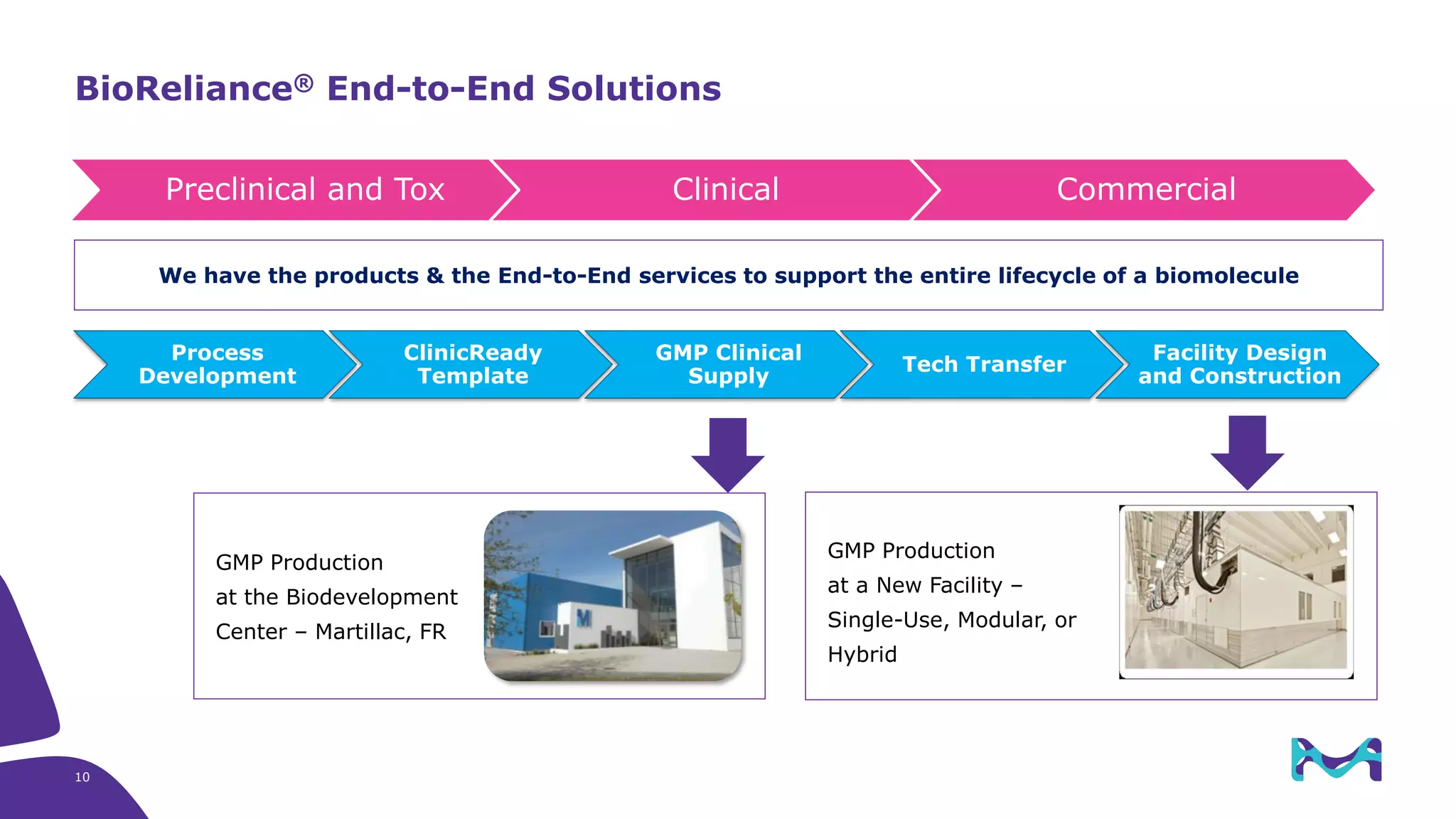
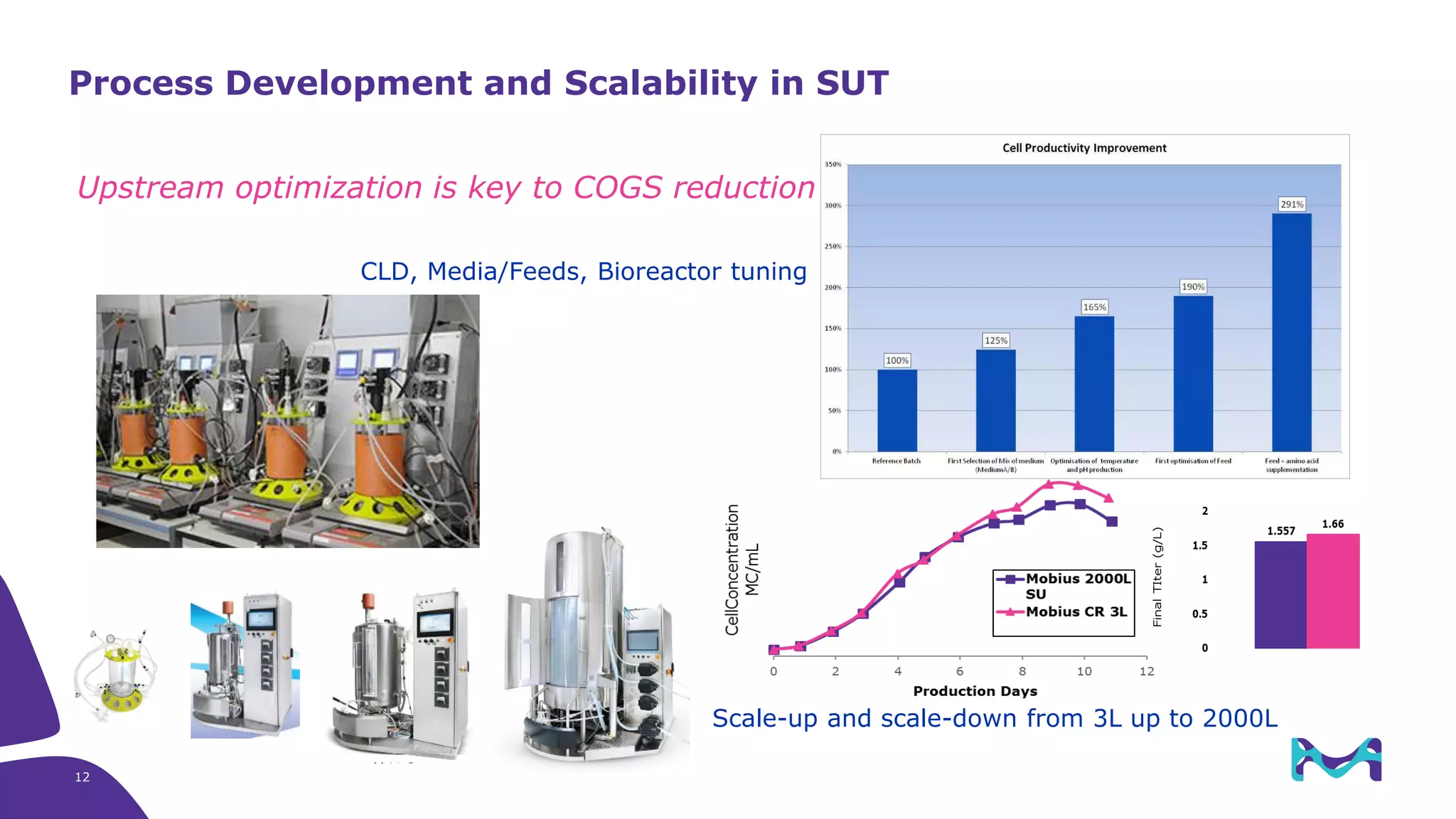
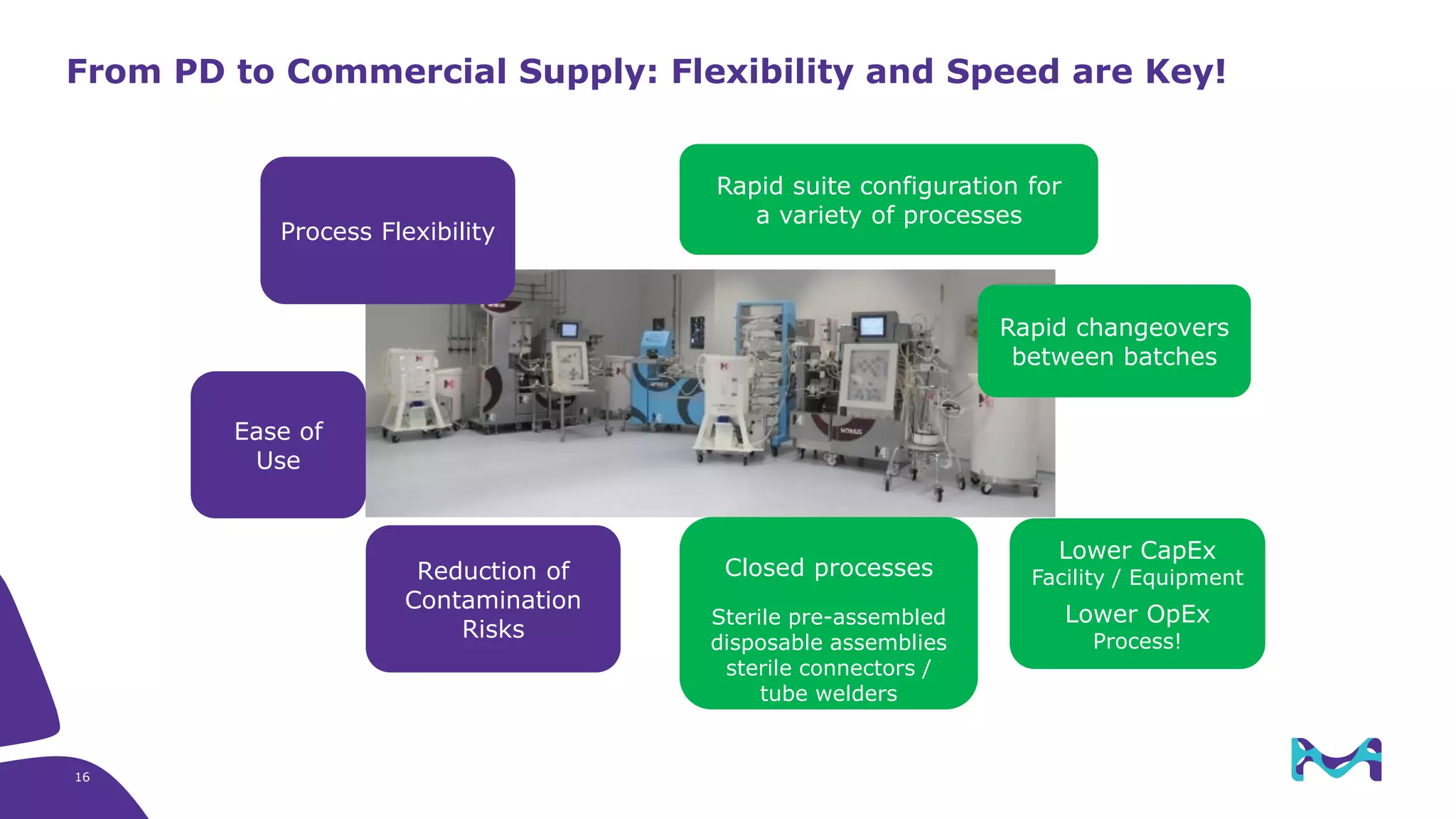
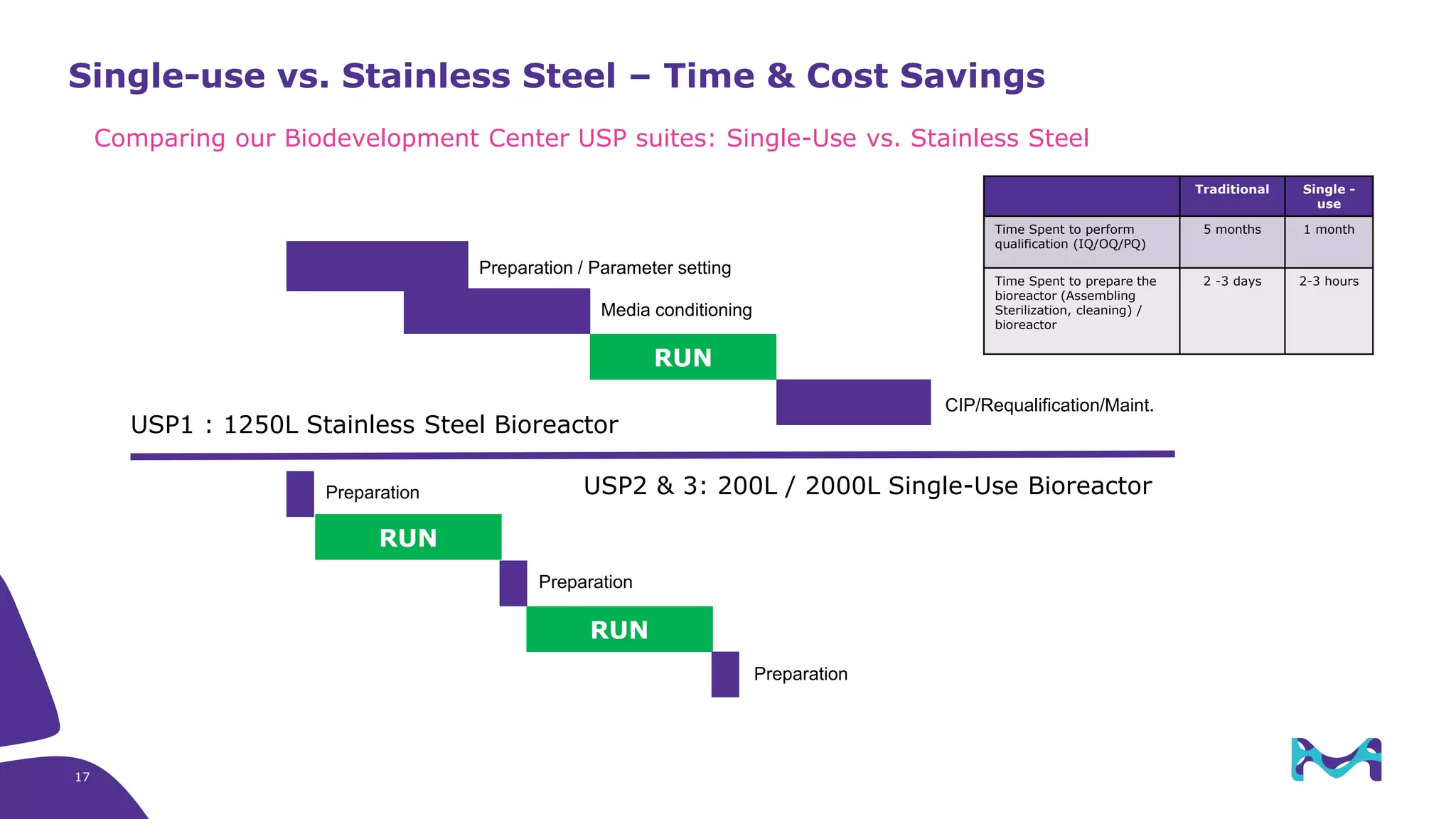
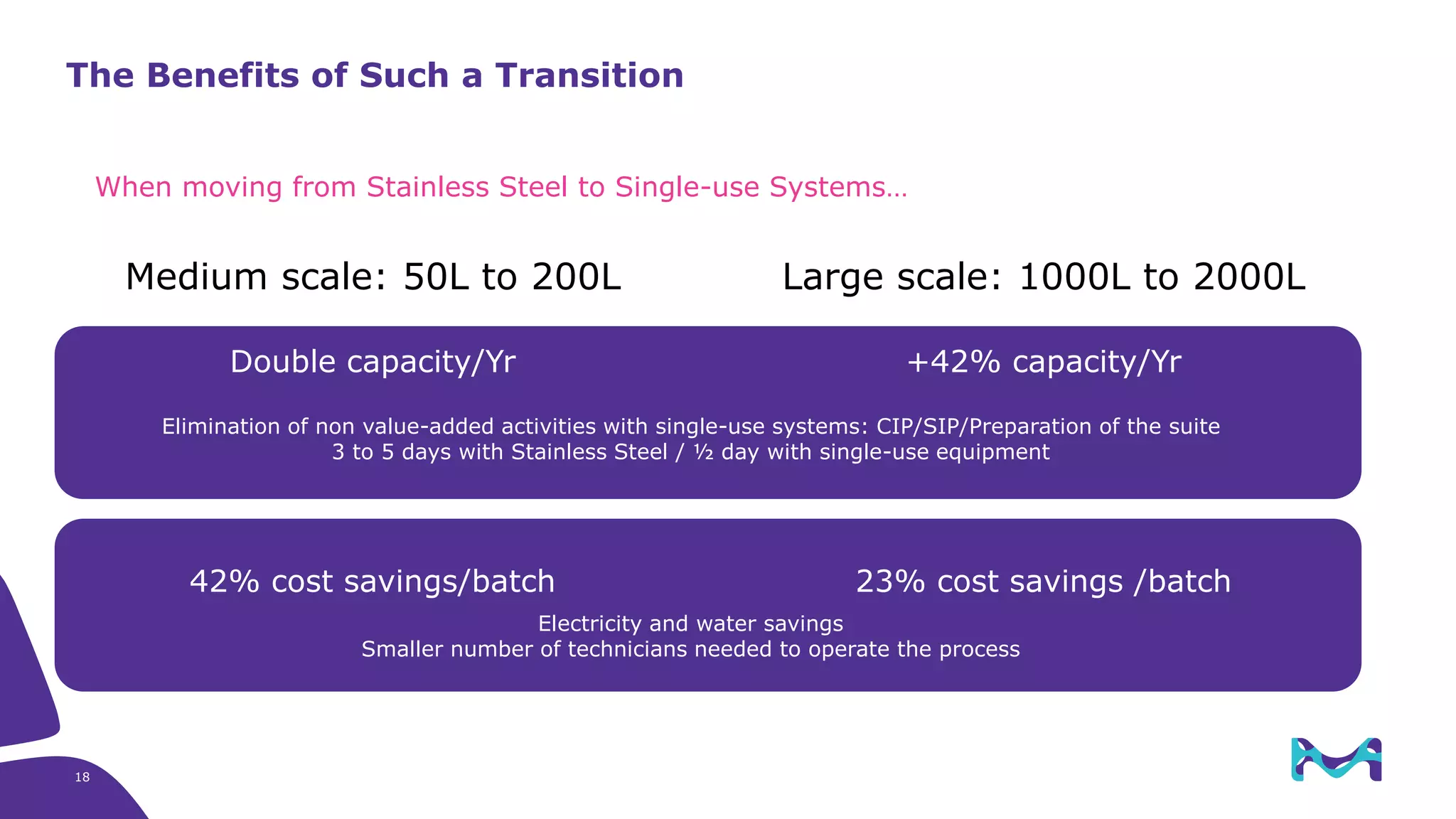
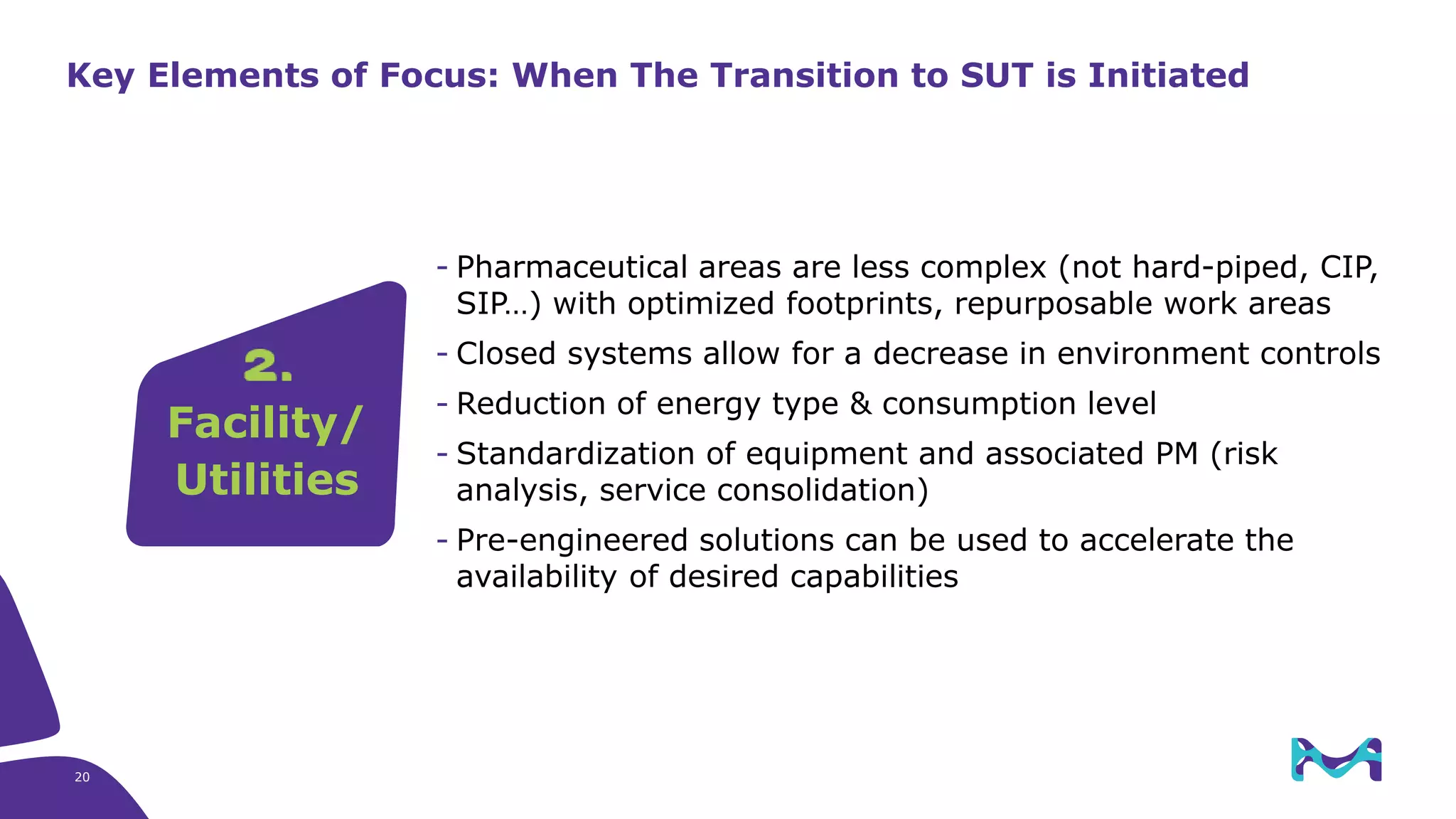
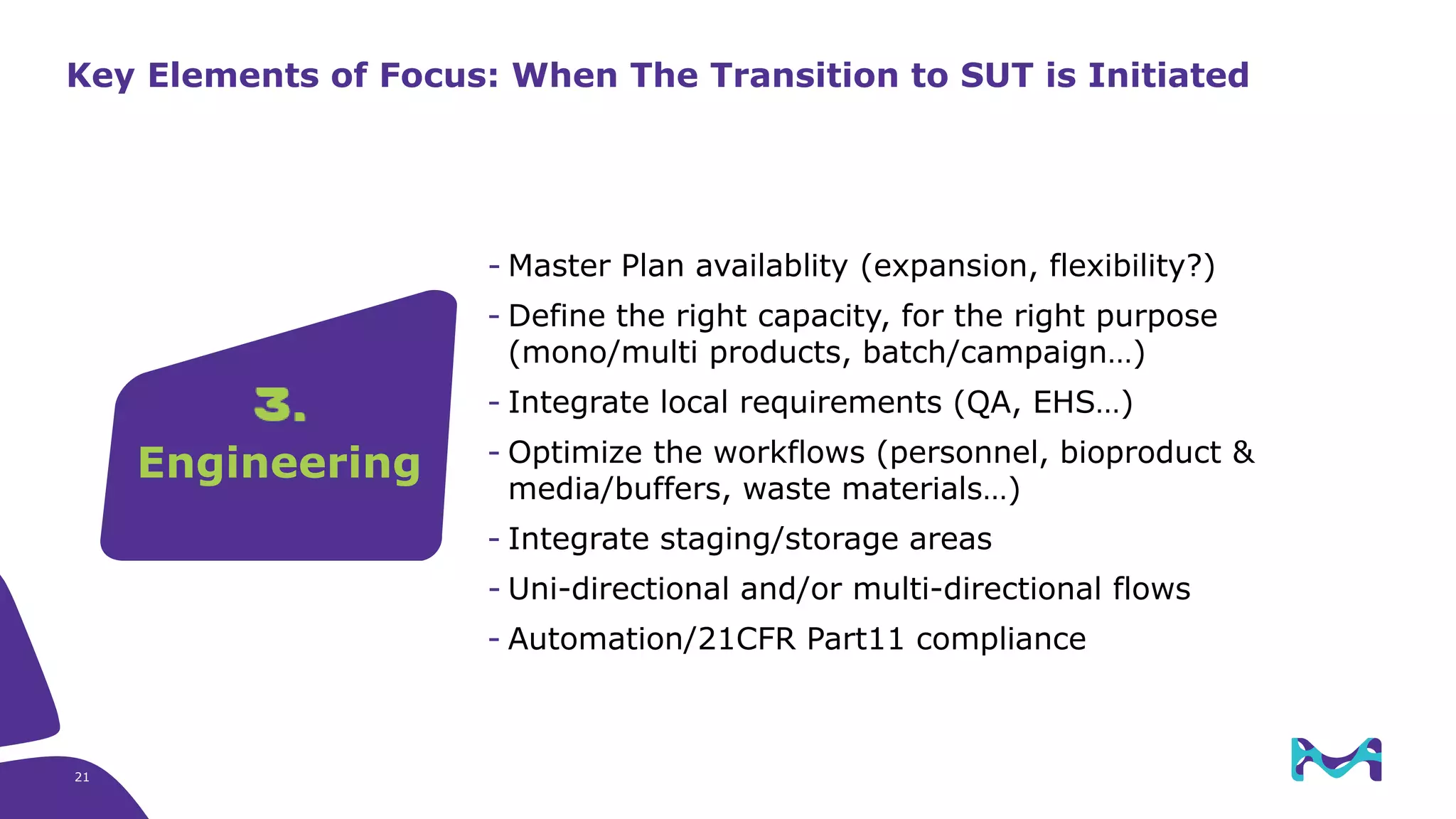
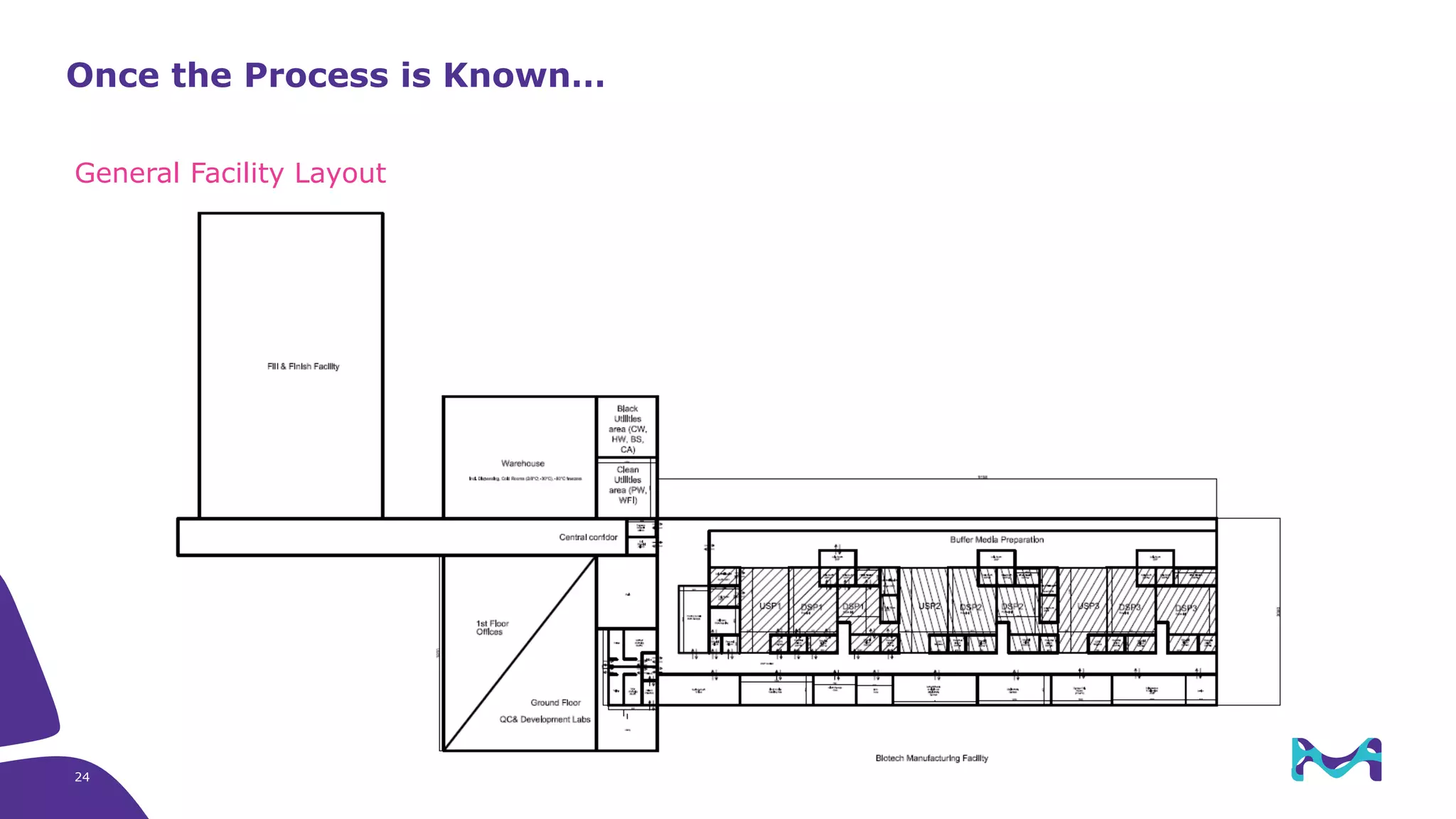
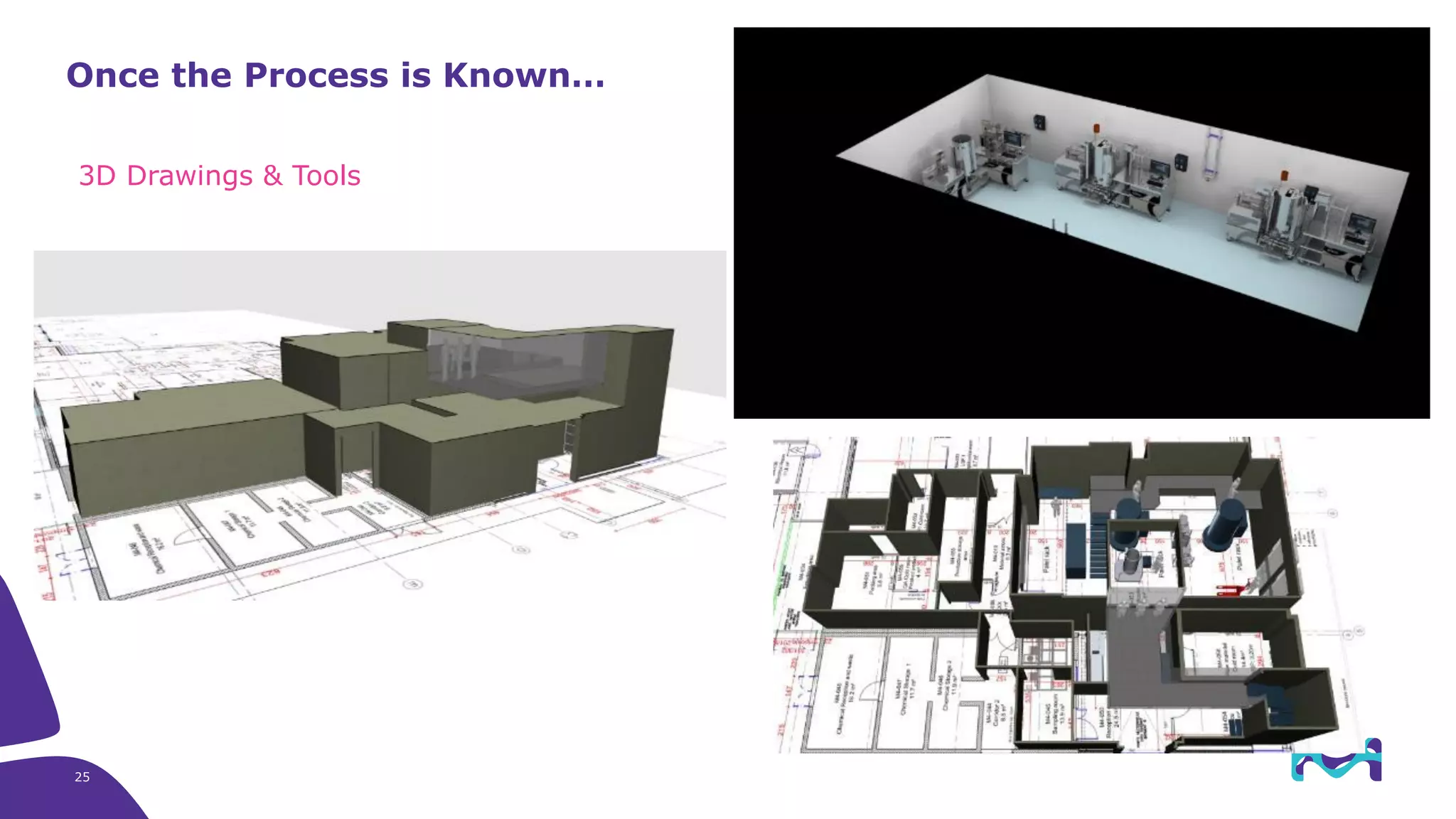
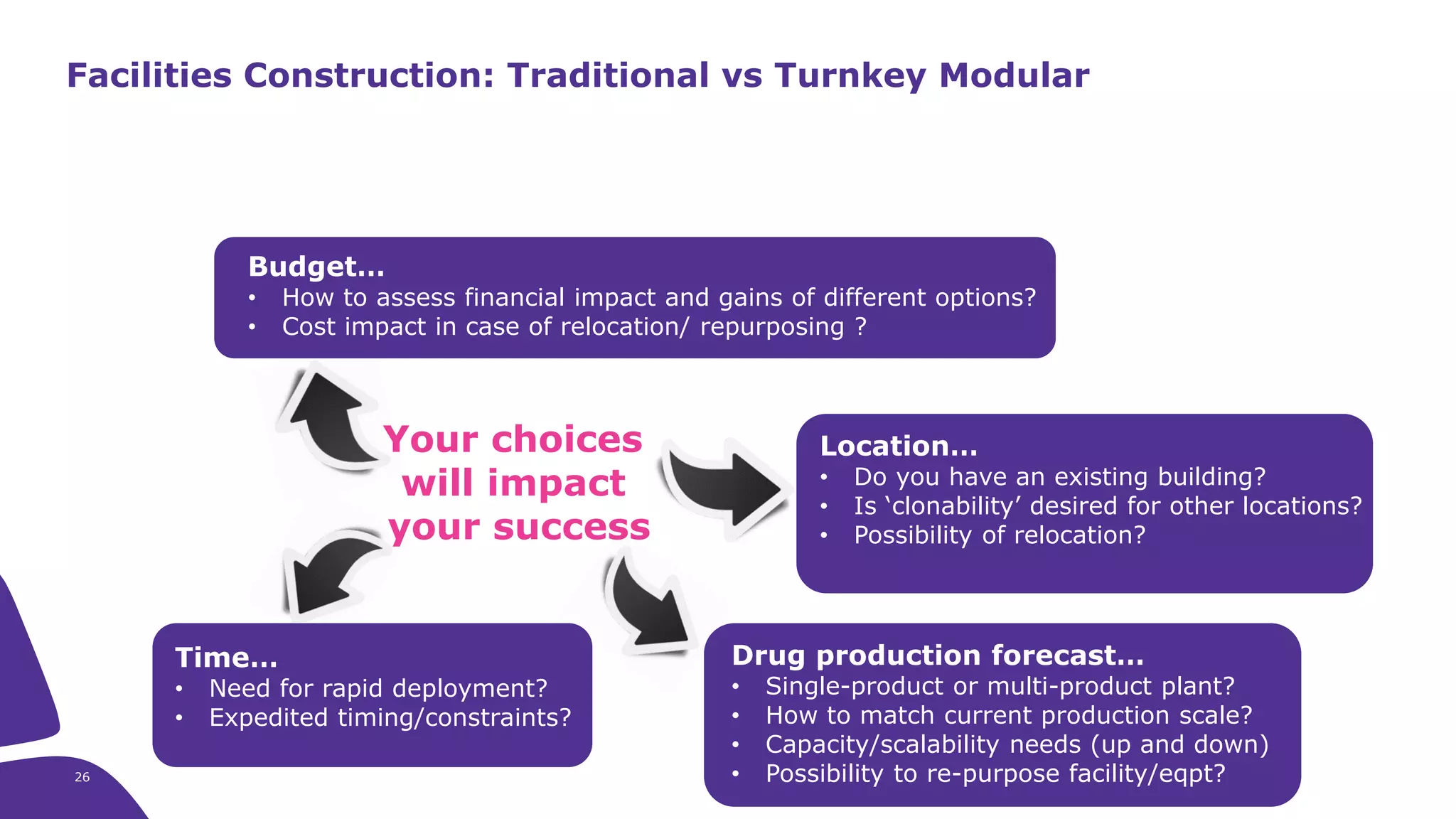
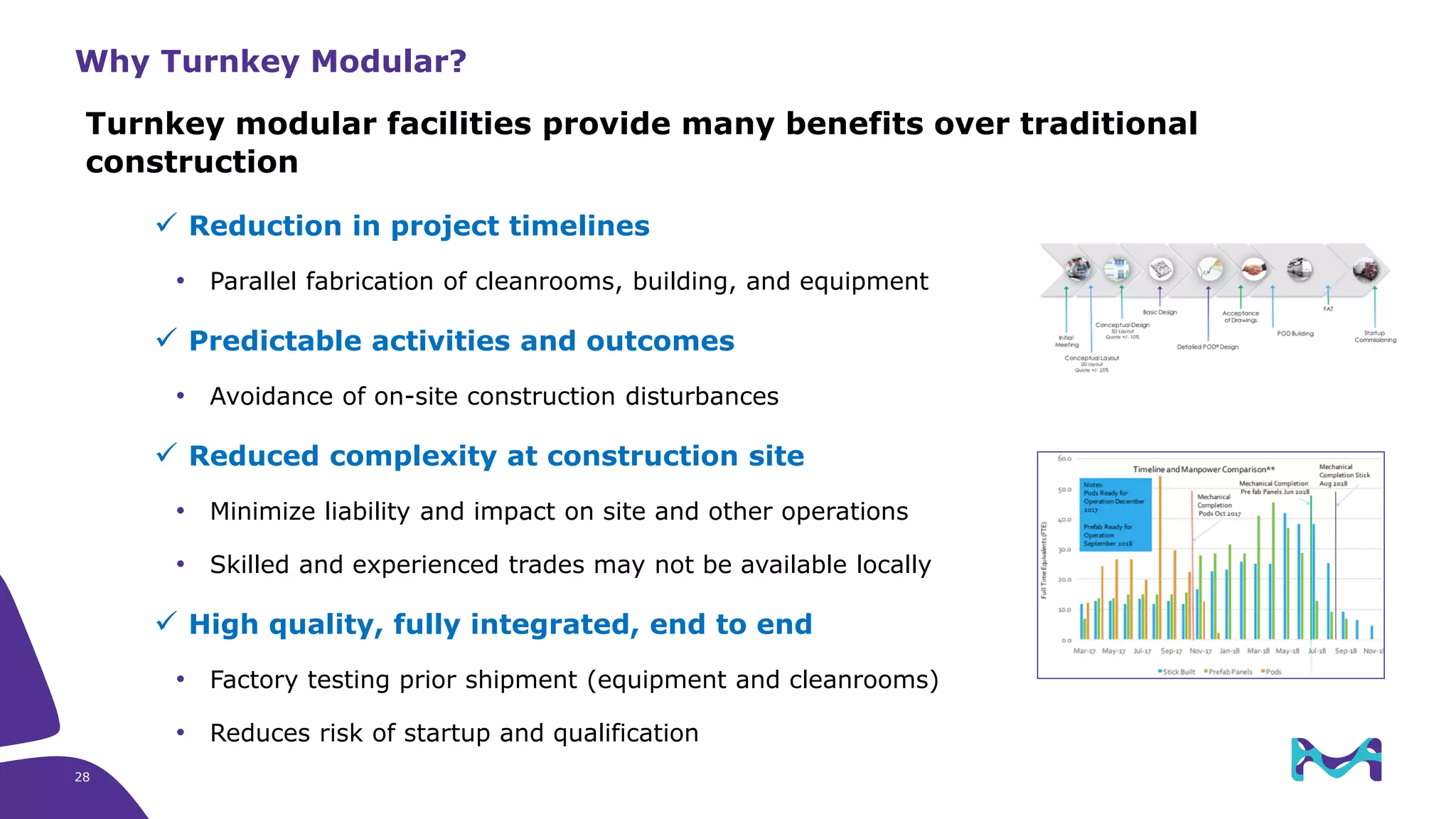
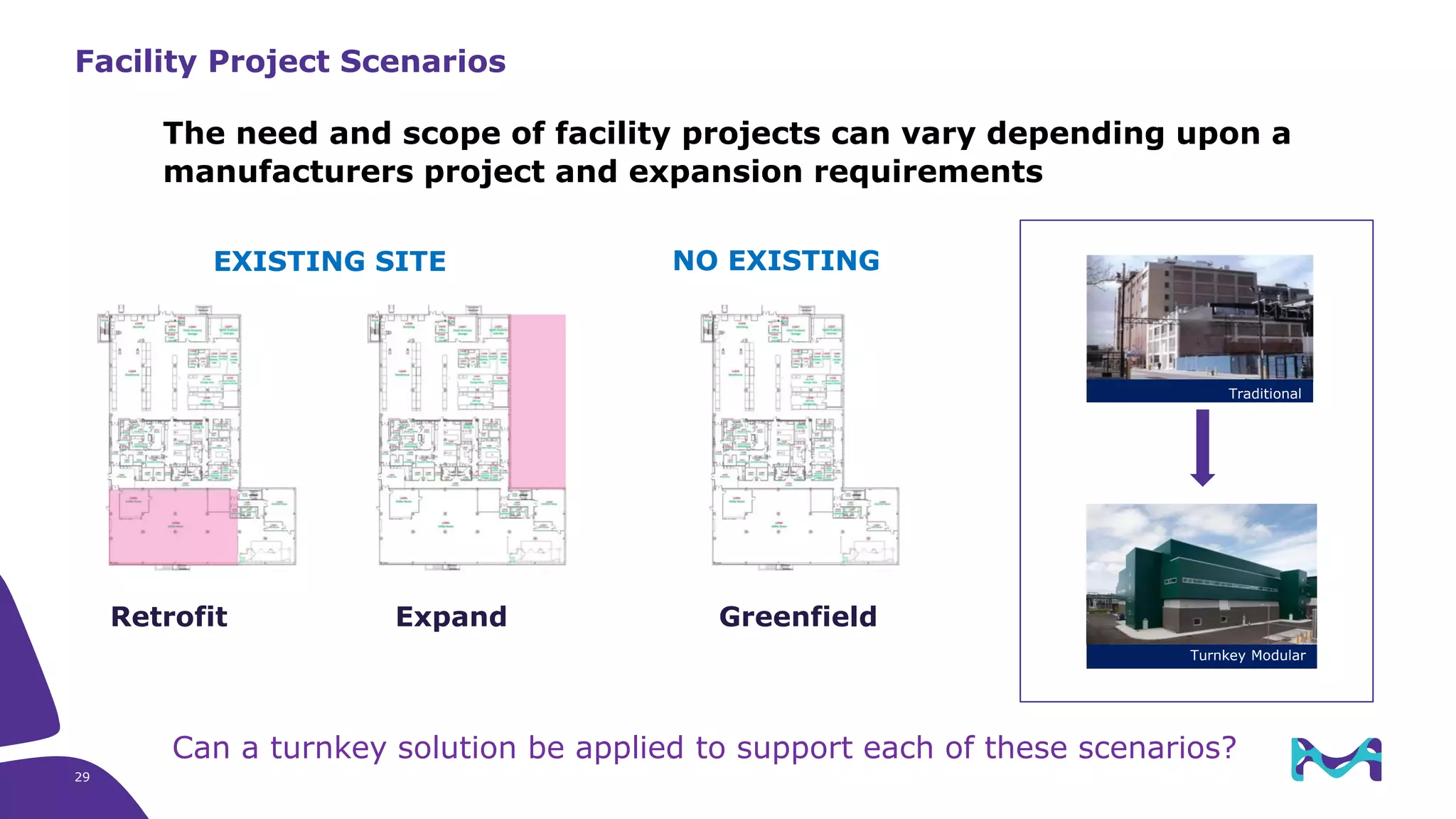
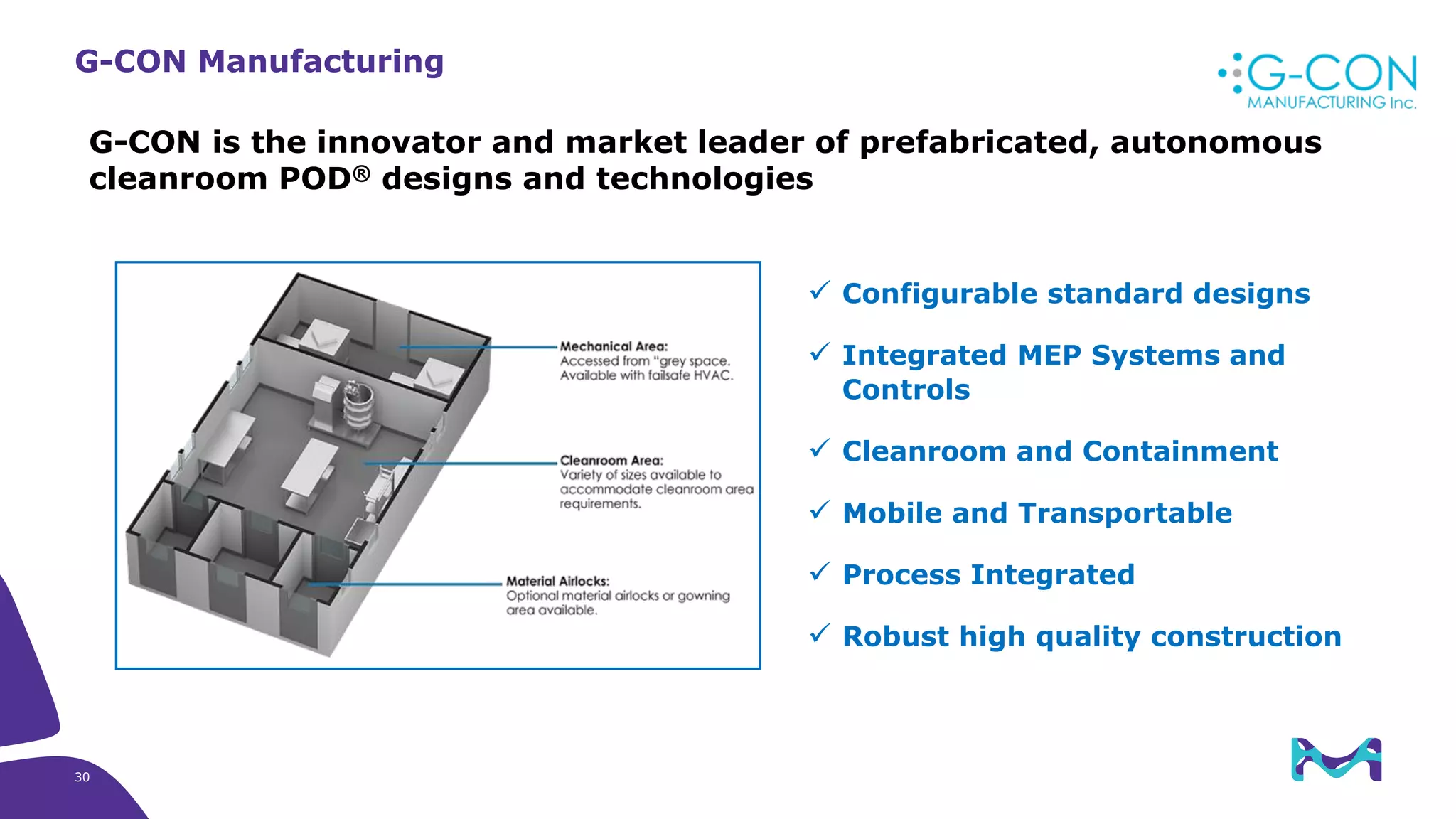
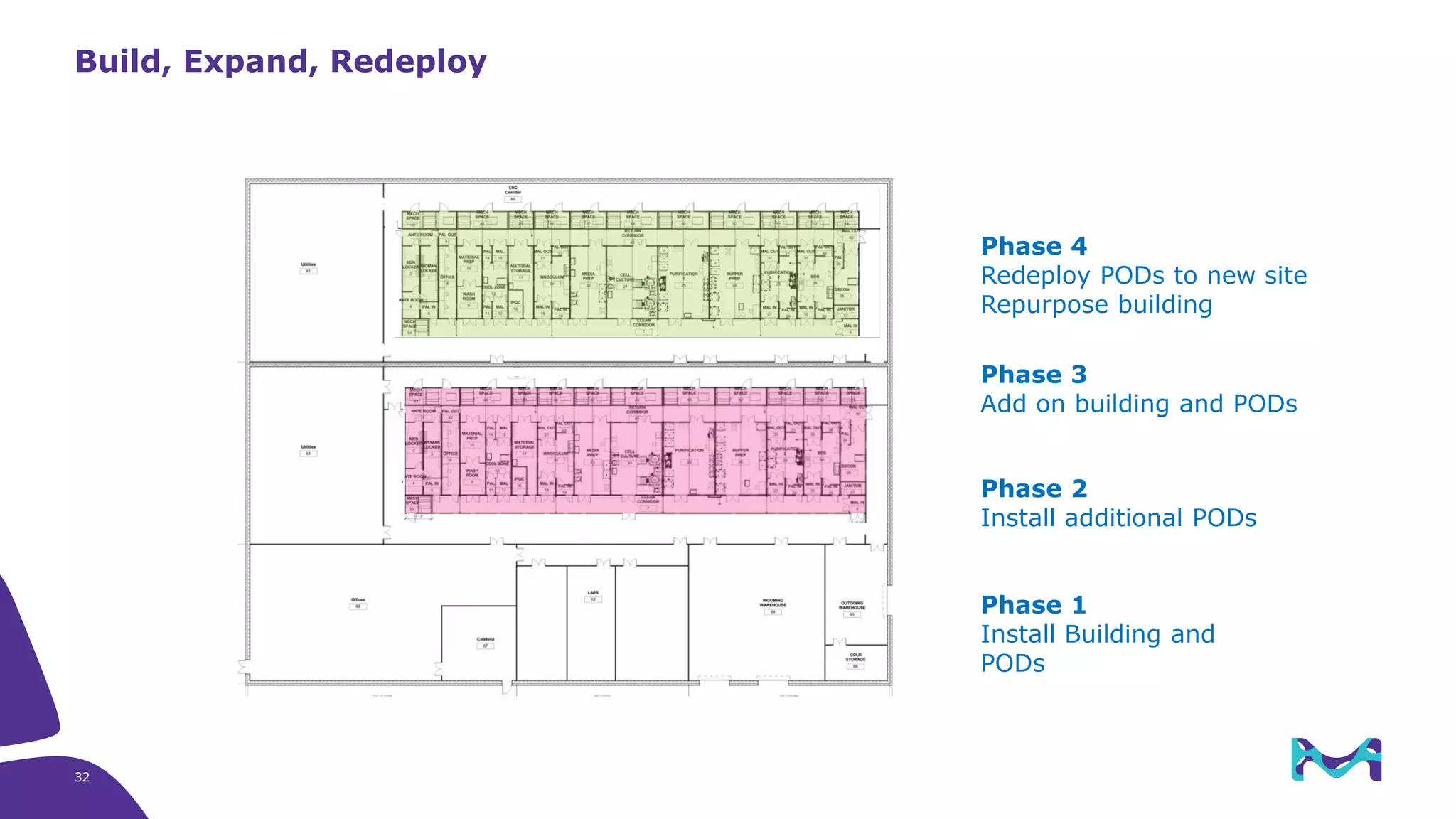
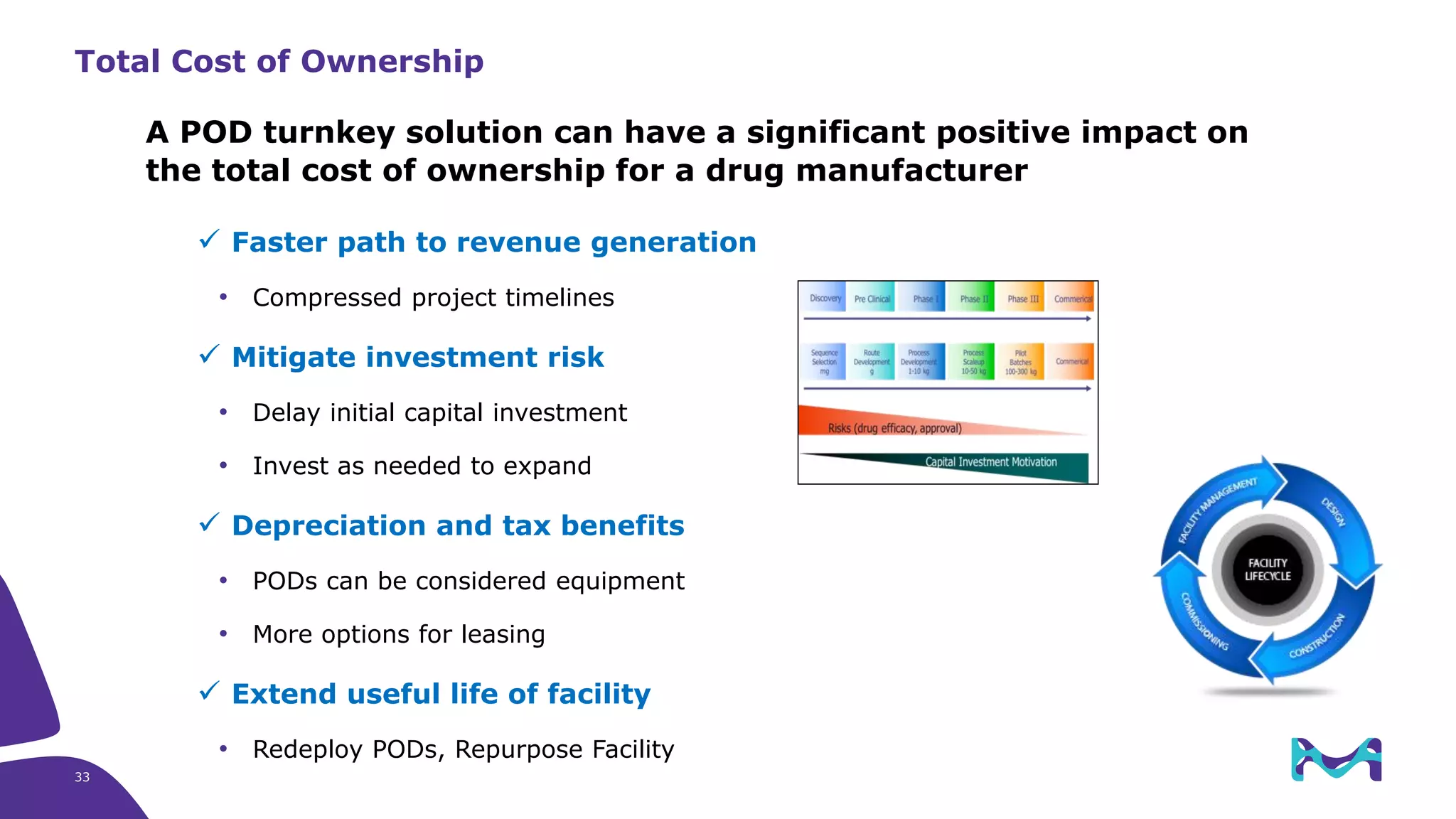
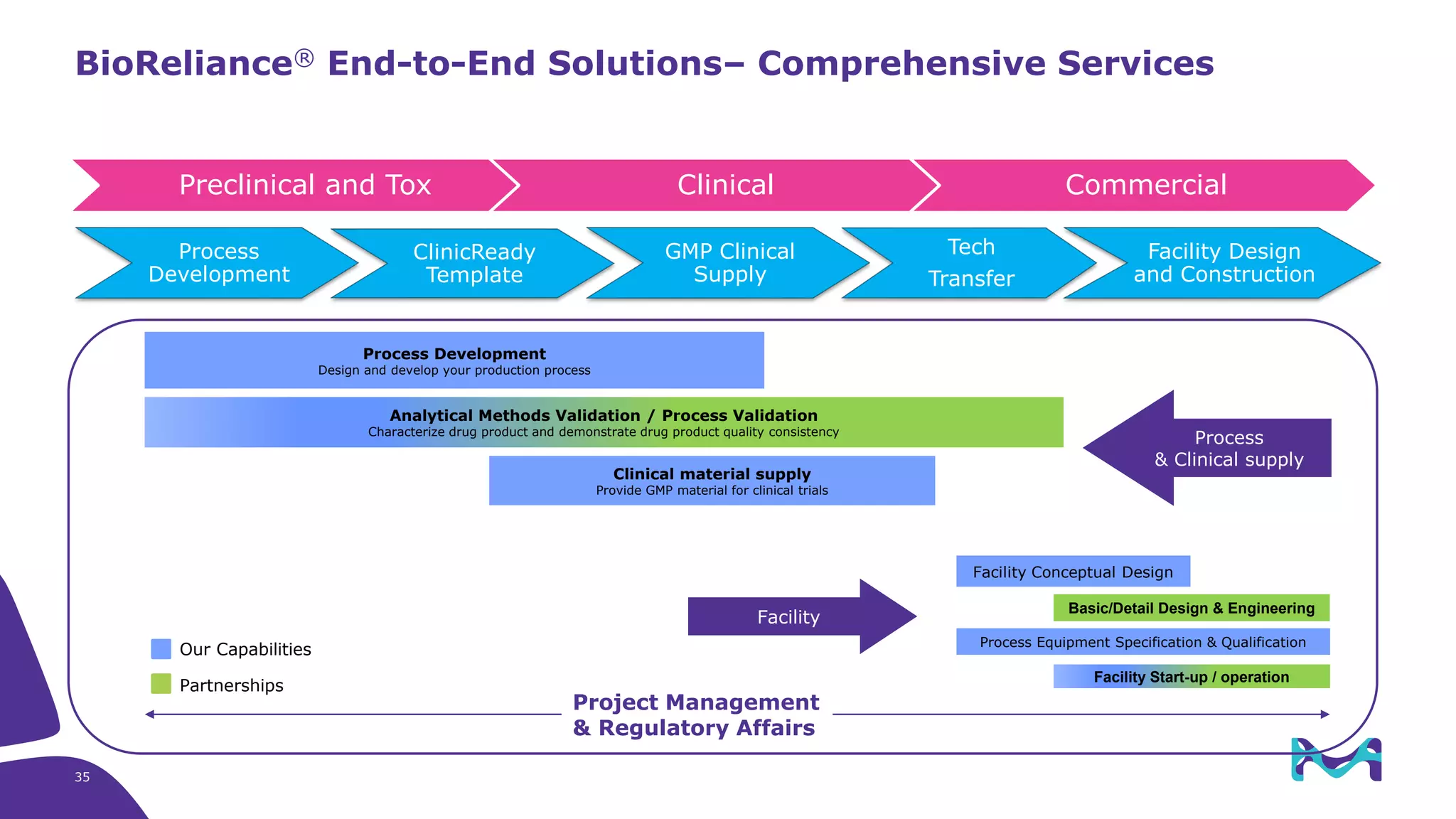
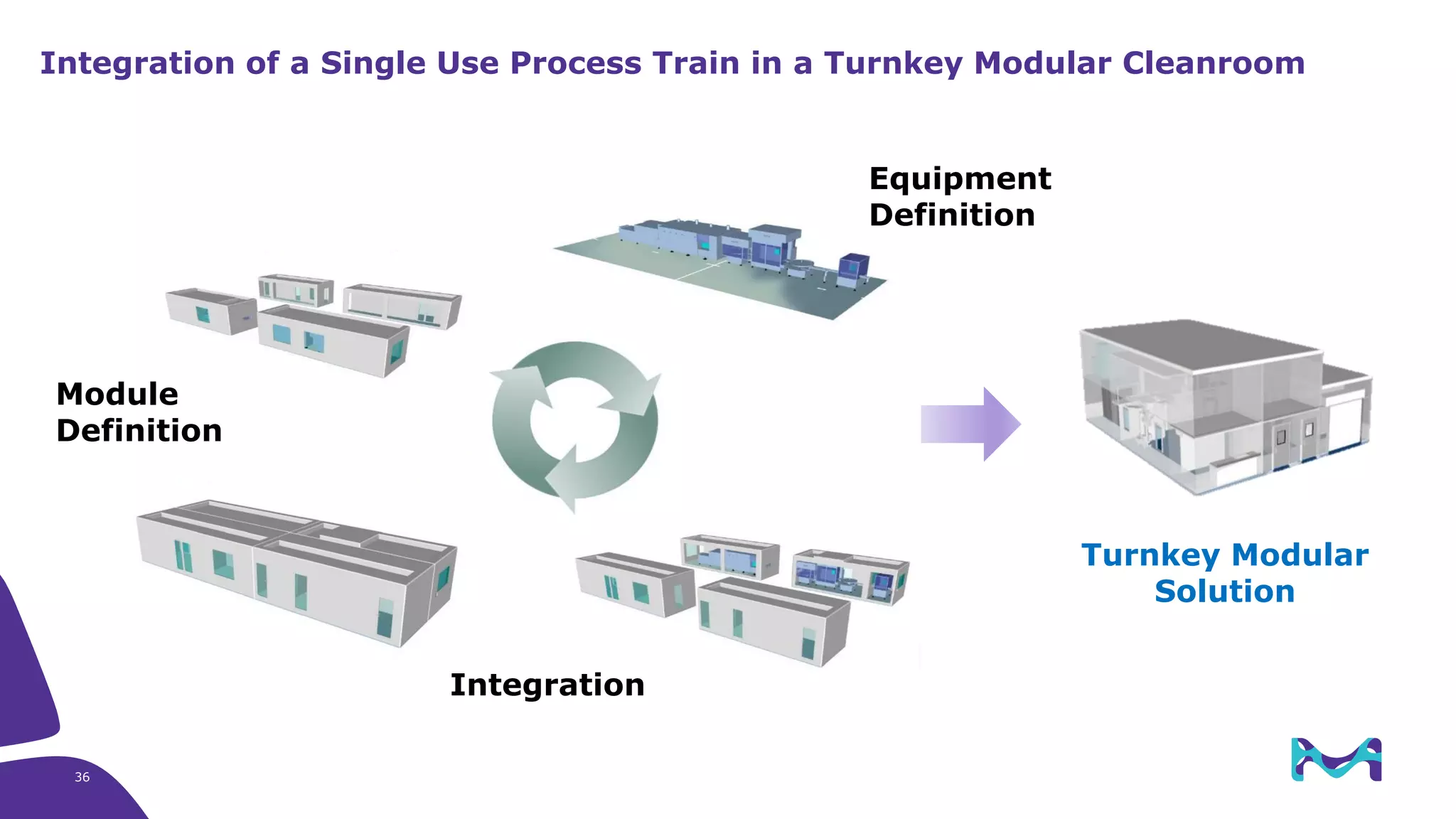
Merck KGaA provides end-to-end solutions for biomanufacturing facilities including process development, clinical supply, and GMP production. They are partnering with G-CON Manufacturing to offer a turnkey modular solution that integrates a single-use process train within a prefabricated and rapidly deployable cleanroom module. This allows clients to scale biomanufacturing capacity quickly and flexibly in a cost-effective and clonable manner to address challenges in emerging biopharma markets.