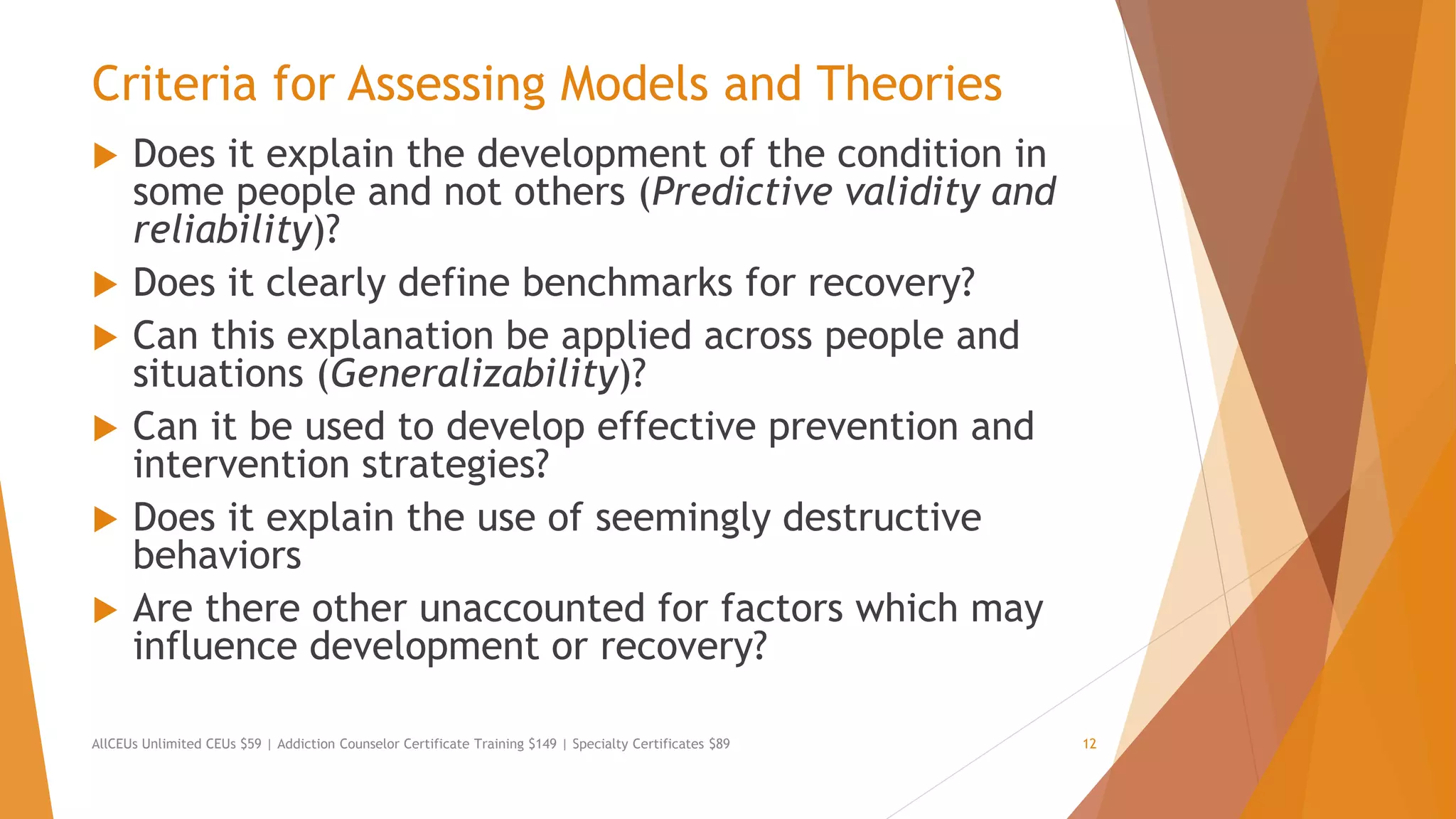
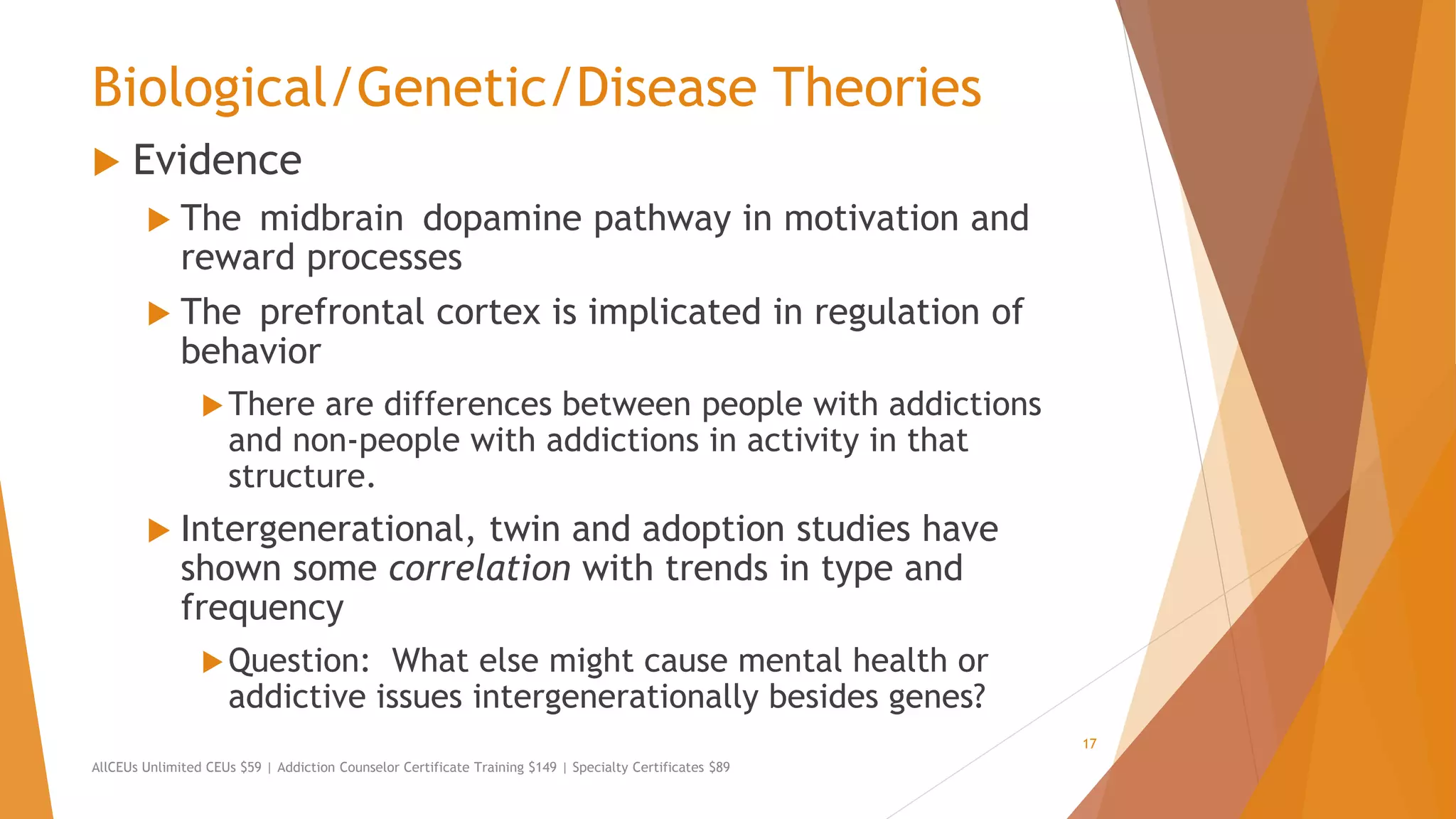
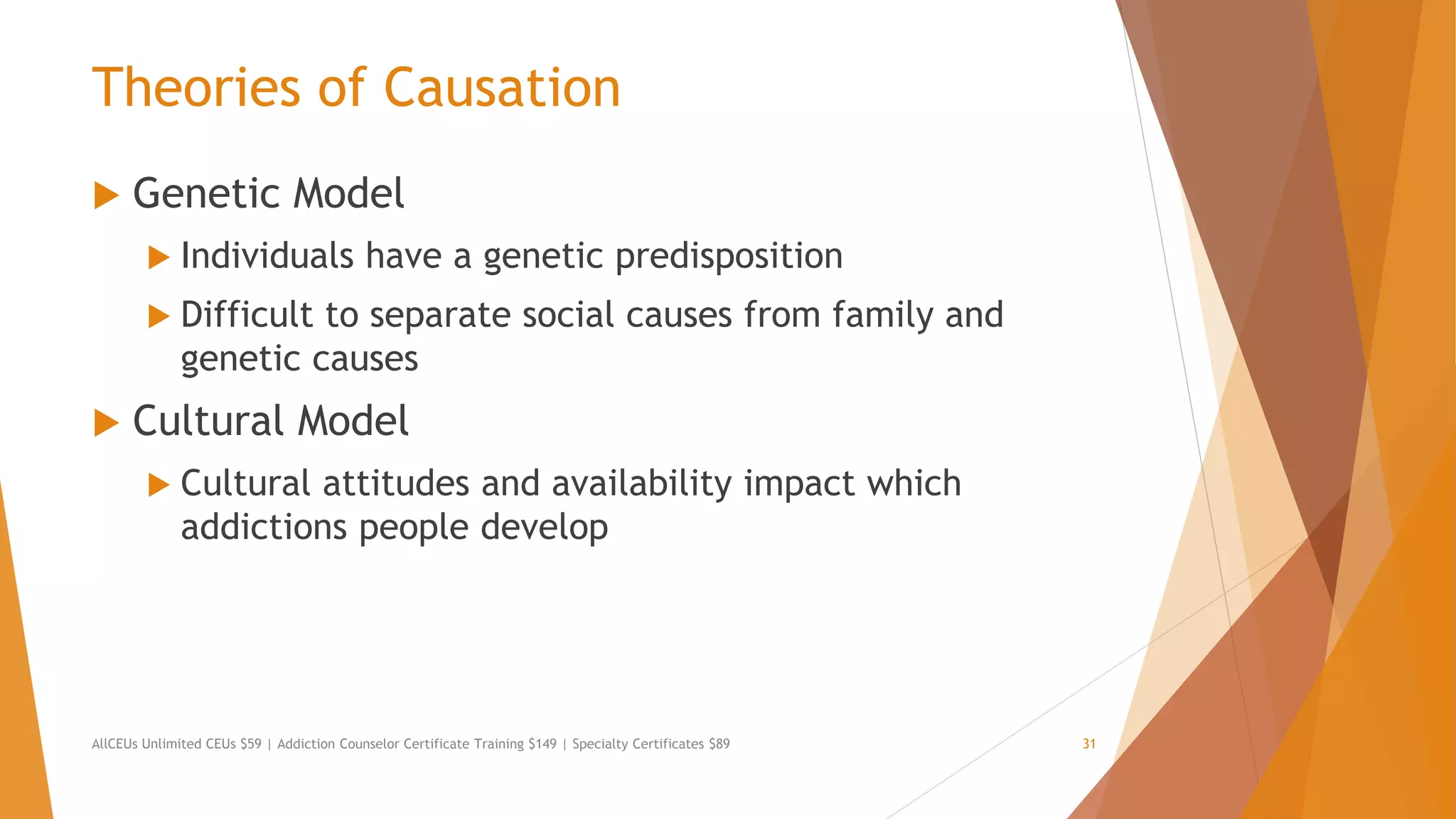
The document outlines the importance of understanding addiction and mental health theories for counselors, emphasizing the increasing prevalence of addiction and the necessity for ethical treatment. It discusses various models of addiction, including biological, behavioral, and socio-cultural theories, while addressing the challenges faced in treating individuals with addictive behaviors. Additionally, it highlights the need for clinicians to keep up-to-date with relevant research and assessment criteria to improve treatment outcomes.