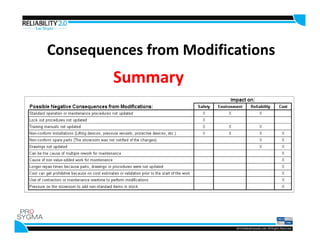
- Management of Change processes are important to implement when making modifications to improve reliability, reduce costs, and better manage risks. Without properly managing changes, standard procedures may not be updated, safety interlocks could be bypassed, and installations may not comply with regulations, posing risks to safety.
- A case study from a zinc processing plant will be presented to illustrate the benefits of a Management of Change process. Properly managing modifications can generate savings, minimize impacts and risks to safety, the environment and equipment reliability, and support objectives around compliance and profits.