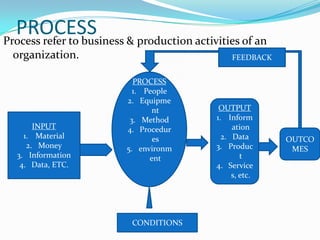
This document discusses continuous improvement in organizations. It defines continuous improvement as striving for perfection through continuously analyzing and improving processes, anticipating customer needs, and eliminating waste. The key aspects covered are: the inputs, outputs, and feedback loops involved in processes; strategies for improvement including repair, refinement, renovation, and reinvention; types of problems organizations may encounter; and a problem-solving method involving identifying opportunities, analyzing current processes, developing solutions, implementing changes, and planning for the future. The conclusion emphasizes that continuous improvement is organization-wide and involves all employees developing ideas and skills for incremental improvements to better meet customer needs.