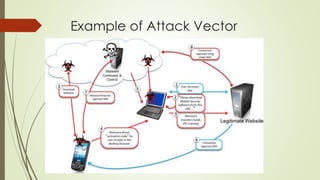
This document presents information on mobile viruses and worms. It defines various related terms like viruses, worms, and trojan horses. It discusses the motivations for creating viruses and characteristics of viruses. It provides an overview of different types of viruses and worms. It examines the attack vectors like Bluetooth, WiFi, SMS that mobile malware uses. It outlines the harms caused by mobile malware like financial loss, sending private information. It discusses protection and prevention mechanisms like keeping Bluetooth in non-discoverable mode and installing antivirus software. It examines case studies of early mobile worms like CABIR and COMWAR.