Mobile Computing - Mobile Transport Layer.pptx.pdf
•
0 likes•2 views
m comp
Report
Share
Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
Cs8601 4

UNIT IV MOBILE TRANSPORT AND APPLICATION LAYER
Mobile TCP– WAP – Architecture – WDP – WTLS – WTP –WSP – WAE – WTA Architecture – WML
Mobile transportlayer

Mobile Transport Layer protocols aim to address challenges with TCP over mobile networks. Traditional TCP uses congestion control like slow start and fast retransmit/recovery that can reduce performance over mobile. Indirect TCP splits the connection at the access point to avoid wireless errors affecting the wired segment. Snooping TCP buffers packets at the access point and performs local retransmissions on errors. Mobile TCP splits the connection and uses an optimized TCP between the supervisory host and mobile host, choking the sender when the mobile is disconnected to avoid buffering large amounts of undelivered data.
Ch7-Transport_Protocols.ppt

This document discusses several proposals to modify TCP for use in mobile environments:
1. Indirect TCP splits the TCP connection to isolate the wireless link but loses end-to-end semantics.
2. Snooping TCP allows local retransmissions through buffering and "snooping" but does not fully isolate the wireless link.
3. Mobile TCP handles disconnections through a supervisory host but does not isolate wireless link losses.
4. Fast retransmit/recovery avoids the slow start algorithm after handovers but mixes network layers.
The approaches vary in their ability to isolate the wireless link, efficiency, and amount of modification required to TCP.
transport protocols

This document discusses challenges with TCP in mobile networks and various approaches to address them. It introduces indirect TCP, which splits the TCP connection to isolate the wireless link. Snooping TCP has the foreign agent snoop packets and acknowledgements to enable local retransmissions. Mobile TCP uses a supervisory host and window size adjustments to handle disconnections. Other optimizations discussed include forced fast retransmit after handovers, freezing TCP timers during disconnects, and selective retransmissions. The document compares the advantages and disadvantages of these different "mobile TCP" approaches.
Mobile transport layer - traditional TCP

This document summarizes several mechanisms proposed to improve TCP performance in wireless networks. It discusses approaches like indirect TCP, snooping TCP, and mobile TCP that split the TCP connection to isolate the wireless link. It also covers fast retransmit/recovery techniques, transmission freezing, and selective retransmission to more efficiently handle packet losses due to mobility. While each approach aims to address TCP issues in wireless networks, they often do so by mixing layers or requiring changes to the basic TCP protocol stack.
EC 6802 WIRELESS NETWORK_ BABU M_ unit 3 ,4 & 5 PPT

WIRELESS NETWORKS _ BABU M_ unit 3 ,4 & 5 PPT
EC 6802 WIRELESS NETWORKS PPT
POWER POINT PRESENTAION ON WIRELESS NETWORKS
BABU M
ASST PROFESSOR/ ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING,
RMK COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
CHENNAI, THIRUVALLUR DISTRICT
Mobile transport layer .

The document discusses several mechanisms used in TCP for mobile computing. It describes:
1) TCP congestion control mechanisms like slow-start and fast retransmit/fast recovery which are designed to address packet loss. However, these can be inappropriate for wireless networks where packet loss is often due to errors rather than congestion.
2) Approaches like Indirect TCP, Snooping TCP, and Mobile TCP which modify TCP for mobile networks by splitting connections or having a supervisory host monitor the connection to enable local retransmissions and avoid unnecessary window reductions when the mobile host disconnects.
3) Other TCP optimizations for mobile like forced fast retransmit after handovers and transmission timeout freezing to avoid slow-start
Mobile Transport layer

This document discusses various approaches to improving TCP performance over mobile networks. It describes Indirect TCP, Snooping TCP, Mobile TCP, optimizations like fast retransmit/recovery and transmission freezing, and transaction-oriented TCP. Each approach is summarized in terms of its key mechanisms, advantages, and disadvantages. Overall, the document evaluates different ways TCP has been adapted to better support mobility and address challenges like frequent disconnections, packet losses during handovers, and high bit error rates over wireless links.
Recommended
Cs8601 4

UNIT IV MOBILE TRANSPORT AND APPLICATION LAYER
Mobile TCP– WAP – Architecture – WDP – WTLS – WTP –WSP – WAE – WTA Architecture – WML
Mobile transportlayer

Mobile Transport Layer protocols aim to address challenges with TCP over mobile networks. Traditional TCP uses congestion control like slow start and fast retransmit/recovery that can reduce performance over mobile. Indirect TCP splits the connection at the access point to avoid wireless errors affecting the wired segment. Snooping TCP buffers packets at the access point and performs local retransmissions on errors. Mobile TCP splits the connection and uses an optimized TCP between the supervisory host and mobile host, choking the sender when the mobile is disconnected to avoid buffering large amounts of undelivered data.
Ch7-Transport_Protocols.ppt

This document discusses several proposals to modify TCP for use in mobile environments:
1. Indirect TCP splits the TCP connection to isolate the wireless link but loses end-to-end semantics.
2. Snooping TCP allows local retransmissions through buffering and "snooping" but does not fully isolate the wireless link.
3. Mobile TCP handles disconnections through a supervisory host but does not isolate wireless link losses.
4. Fast retransmit/recovery avoids the slow start algorithm after handovers but mixes network layers.
The approaches vary in their ability to isolate the wireless link, efficiency, and amount of modification required to TCP.
transport protocols

This document discusses challenges with TCP in mobile networks and various approaches to address them. It introduces indirect TCP, which splits the TCP connection to isolate the wireless link. Snooping TCP has the foreign agent snoop packets and acknowledgements to enable local retransmissions. Mobile TCP uses a supervisory host and window size adjustments to handle disconnections. Other optimizations discussed include forced fast retransmit after handovers, freezing TCP timers during disconnects, and selective retransmissions. The document compares the advantages and disadvantages of these different "mobile TCP" approaches.
Mobile transport layer - traditional TCP

This document summarizes several mechanisms proposed to improve TCP performance in wireless networks. It discusses approaches like indirect TCP, snooping TCP, and mobile TCP that split the TCP connection to isolate the wireless link. It also covers fast retransmit/recovery techniques, transmission freezing, and selective retransmission to more efficiently handle packet losses due to mobility. While each approach aims to address TCP issues in wireless networks, they often do so by mixing layers or requiring changes to the basic TCP protocol stack.
EC 6802 WIRELESS NETWORK_ BABU M_ unit 3 ,4 & 5 PPT

WIRELESS NETWORKS _ BABU M_ unit 3 ,4 & 5 PPT
EC 6802 WIRELESS NETWORKS PPT
POWER POINT PRESENTAION ON WIRELESS NETWORKS
BABU M
ASST PROFESSOR/ ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING,
RMK COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
CHENNAI, THIRUVALLUR DISTRICT
Mobile transport layer .

The document discusses several mechanisms used in TCP for mobile computing. It describes:
1) TCP congestion control mechanisms like slow-start and fast retransmit/fast recovery which are designed to address packet loss. However, these can be inappropriate for wireless networks where packet loss is often due to errors rather than congestion.
2) Approaches like Indirect TCP, Snooping TCP, and Mobile TCP which modify TCP for mobile networks by splitting connections or having a supervisory host monitor the connection to enable local retransmissions and avoid unnecessary window reductions when the mobile host disconnects.
3) Other TCP optimizations for mobile like forced fast retransmit after handovers and transmission timeout freezing to avoid slow-start
Mobile Transport layer

This document discusses various approaches to improving TCP performance over mobile networks. It describes Indirect TCP, Snooping TCP, Mobile TCP, optimizations like fast retransmit/recovery and transmission freezing, and transaction-oriented TCP. Each approach is summarized in terms of its key mechanisms, advantages, and disadvantages. Overall, the document evaluates different ways TCP has been adapted to better support mobility and address challenges like frequent disconnections, packet losses during handovers, and high bit error rates over wireless links.
Mobile Transpot Layer

This document discusses various transport layer protocols for mobile networks. It begins by describing TCP and its mechanisms for congestion avoidance, flow control, slow start, and retransmission. It then covers several TCP variants including Tahoe, Reno, and Vegas. It also discusses indirect TCP, Snoop TCP, and Mobile TCP which aim to optimize TCP for wireless networks by handling retransmissions locally or splitting the connection. The document provides details on the algorithms and functioning of these different protocols.
mobile_transport_layer (1).pptx

1) Standard TCP performs poorly over wireless networks due to packet loss from errors and mobility rather than congestion. This causes unnecessary slow starts and window reductions.
2) Early approaches like Indirect TCP, Snooping TCP, and Mobile TCP split or modify the TCP connection to isolate the wireless link but lose end-to-end semantics or require changes.
3) Later techniques like forced fast retransmit and selective acknowledgements improve efficiency without changing TCP but require cooperation between layers. Overall no single solution is optimal due to the need to maintain compatibility with fixed networks.
Unit 4

This document discusses several approaches to improving TCP performance over mobile networks:
Traditional TCP uses slow start and congestion control mechanisms that reduce efficiency over mobile networks. Indirect TCP segments connections and uses a proxy to improve performance. Snooping TCP buffers packets to enable fast retransmissions without changing endpoints. Mobile TCP freezes the sender's window on disconnection to avoid unnecessary retransmissions. These methods aim to isolate wireless losses from congestion responses and enable fast recovery from errors and handovers.
Mobile transport layer

The document discusses various approaches to modifying TCP for use in mobile networks. Indirect TCP splits the TCP connection at the foreign agent, keeping the fixed network unchanged but losing end-to-end semantics. Snooping TCP has the foreign agent snoop packets and retransmit lost packets locally without changing TCP. Mobile TCP uses a supervisory host to monitor disconnections and choke senders. Other approaches include forced fast retransmit after handovers, freezing TCP timers during disconnects, selective retransmission of only lost packets, and transaction-oriented TCP to combine connection setup in fewer packets. Each approach has advantages like efficiency or compatibility but also disadvantages like overhead or non-transparency.
Mc unit 4-jwfiles

The document discusses various approaches to improving TCP for mobile networks. It begins by describing traditional TCP and its mechanisms for congestion control and reliable data transmission. However, TCP was designed for fixed networks and faces challenges in mobile environments due to higher error rates, mobility-induced packet loss, and inefficient slow start behavior after losses. Several TCP improvements are then outlined, including Indirect TCP which segments connections and uses a proxy at the access point to isolate the wireless portion. This allows specialized TCP variants to be used for the wireless link without changing the fixed network. Finally, socket migration during handover is discussed to maintain connections as the mobile host moves.
Mcseminar

This document discusses various transport layer protocols for mobile networks. It begins with an overview of TCP and UDP, and then describes several strategies for improving TCP performance over mobile networks, including indirect TCP (I-TCP), snooping TCP, and Mobile TCP. It also discusses congestion control strategies like slow start and fast retransmit. Overall, the document analyzes how TCP can be optimized through techniques like connection splitting, buffering, and selective retransmission to better accommodate the characteristics of wireless networks.
Transport protocols

The document discusses various approaches to improving TCP performance over mobile networks, including:
1. Indirect TCP which splits the TCP connection to isolate errors on the wireless link. This requires no changes to fixed network hosts but loses end-to-end semantics.
2. Snooping TCP where the foreign agent buffers packets and retransmits lost packets transparently. This maintains end-to-end semantics but does not fully isolate the wireless link.
3. Mobile TCP which splits the connection and supports lengthy disconnections by freezing transmission at disconnected base stations. However, it propagates wireless losses into the fixed network.
Mobile transport layer

The document discusses various transport layer protocols for mobile networks, including traditional TCP, Indirect TCP, Snooping TCP, and Mobile TCP. Traditional TCP was designed for fixed networks and experiences issues in mobile networks due to factors like packet loss from handoffs. Indirect TCP splits the TCP connection at the access point to isolate the wireless link. Snooping TCP has the access point buffer packets and detect losses to enable local retransmissions. Mobile TCP uses a supervisory host to handle disconnections and restart the connection when needed. Each approach aims to improve TCP performance over mobile networks while maintaining compatibility with traditional TCP.
Improving Performance of TCP in Wireless Environment using TCP-P

Improving the performance of the transmission
control protocol (TCP) in wireless environment has been an
active research area. Main reason behind performance
degradation of TCP is not having ability to detect actual reason
of packet losses in wireless environment. In this paper, we are
providing a simulation results for TCP-P (TCP-Performance).
TCP-P is intelligent protocol in wireless environment which
is able to distinguish actual reasons for packet losses and
applies an appropriate solution to packet loss.
TCP-P deals with main three issues, Congestion in
network, Disconnection in network and random packet losses.
TCP-P consists of Congestion avoidance algorithm and
Disconnection detection algorithm with some changes in TCP
header part. If congestion is occurring in network then
congestion avoidance algorithm is applied. In congestion
avoidance algorithm, TCP-P calculates number of sending
packets and receiving acknowledgements and accordingly set
a sending buffer value, so that it can prevent system from
happening congestion. In disconnection detection algorithm,
TCP-P senses medium continuously to detect a happening
disconnection in network. TCP-P modifies header of TCP
packet so that loss packet can itself notify sender that it is
lost.This paper describes the design of TCP-P, and presents
results from experiments using the NS-2 network simulator.
Results from simulations show that TCP-P is 4% more
efficient than TCP-Tahoe, 5% more efficient than TCP-Vegas,
7% more efficient than TCP-Sack and equally efficient in
performance as of TCP-Reno and TCP-New Reno. But we can
say TCP-P is more efficient than TCP-Reno and TCP-New
Reno since it is able to solve more issues of TCP in wireless
environment.
Transaction TCP

T/TCP is a protocol that aims to reduce the number of packets needed for transaction-style applications by allowing a client to open a connection, send data, and close the connection in a single packet. It utilizes a mechanism called TCP Accelerated Open (TAO) to bypass the standard 3-way TCP handshake. Testing showed T/TCP saved an average of 5 packets per transaction compared to TCP. However, the percentage savings decreased with larger data transfers as T/TCP is most beneficial for small transactions. While improving performance, T/TCP also introduced some security and operational issues that needed to be addressed for broader adoption.
High Performance Networking with Advanced TCP

High Performance Networking with TCP. TCP properties, UDP, flow control, Congestion Avoidance & Control, slow start, Congestion Control Review, TCP Tahoe & Reno
UAV Data Link Design for Dependable Real-Time Communications

Communication over the kinds of Data-Links used for unmanned vehicles presents important challenges dues to the low bandwidth, intermittent, and lower reliability of these links. Classic network protocols such as TCP do not operate well in this environment forcing application developers to implement their own reliability and session management. This presentation describes he issues and alternatives.
A THROUGHPUT ANALYSIS OF TCP IN ADHOC NETWORKS

This document analyzes the throughput of TCP in mobile ad hoc networks through simulations. It finds that TCP throughput decreases initially as the number of hops increases, then stabilizes at higher hop counts. This is due to hidden terminal problems at low hops. The number of retransmissions increases with payloads and flows due to buffering and congestion. TCP performance degrades in wireless networks because it cannot differentiate between congestion and non-congestion packet losses. Mobility, interference, and dynamic topology changes specific to wireless networks cause unnecessary triggering of TCP congestion control mechanisms.
A throughput analysis of tcp in adhoc networks

Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is a connection oriented end-end reliable byte stream
transport layer protocol. It is widely used in the Internet.TCP is fine tuned to perform well in
wired networks. However the performance degrades in mobile ad hoc networks. This is due to
the characteristics specific to wireless networks, such as signal fading, mobility, unavailability
of routes. This leads to loss of packets which may arise either from congestion or due to other
non-congestion events. However TCP assumes every loss as loss due to congestion and invokes
the congestion control procedures. TCP reduces congestion window in response, causing unnecessary
degradation in throughput. In mobile ad hoc networks multi-hop path forwarding further
worsens the packet loss and throughput. To understand the TCP behavior and improve the
TCP performance over mobile ad hoc networks considerable research has been carried out. As
the research is still active in this area a comprehensive and in-depth study on the TCP throughput
and the various parameters that degrade the performance of TCP have been analyzed. The
analysis is done using simulations in Qualnet 5.0
C10 transport protocols

The document discusses various approaches to improving TCP performance over mobile networks. Indirect TCP splits the TCP connection at the foreign agent to isolate the wireless link. Snooping TCP has the foreign agent buffer packets and retransmit lost packets locally. Mobile TCP uses a supervisory host to monitor connections and choke the sender window during disconnections. Other techniques discussed include fast retransmit/recovery after handovers, freezing TCP states during interruptions, selective retransmission of only lost packets, and transaction-oriented TCP to reduce overhead of short messages. Each approach has advantages but also disadvantages related to compatibility, transparency, and complexity.
connection establishment flowand congestion.pptx

Connection establishment involves a handshake process between two endpoints to synchronize sequence numbers and establish communication. Transport protocols like TCP require a connection to be set up before data can be exchanged. This allows each end to verify the other's existence, negotiate parameters, and allocate resources. Common connection establishment methods are two-way and three-way handshakes, with three-way involving SYN, SYN-ACK and ACK packets. Flow control mechanisms like stop-and-wait and sliding windows ensure transmission rates match receiver capabilities to prevent buffer overruns. Congestion control is also important to manage network traffic loads and avoid degrading performance due to delays or reduced throughput when congestion occurs.
Lecture 19 22. transport protocol for ad-hoc 

This document discusses transport layer protocols for mobile ad hoc networks (MANETs). It begins with an introduction to MANETs and the need for new network architectures and protocols to support new types of networks. It then provides an overview of TCP/IP and how TCP works, including congestion control mechanisms. The document discusses challenges for TCP over wireless networks, where packet losses are often due to errors rather than congestion. It covers different versions of TCP and their approaches to congestion control. The goal is to design transport layer protocols that can address the unreliable links and frequent topology changes in MANETs.
Transport layer

here discussed about each topic of network layer like congestion control mechanism , error control , flow, tcp , udp, etc
TCP over wireless slides

The document discusses various protocols and approaches for improving the performance of TCP over wireless networks. It notes that wireless networks have higher bit error rates, lower bandwidth, and mobility issues compared to wired networks. Several protocols are described that aim to distinguish wireless losses from congestion losses to avoid unnecessary TCP reactions:
- Indirect TCP splits the connection and handles losses locally at the base station. Snoop caches packets at the base station for retransmission.
- Mobile TCP further splits the connection and has the base station defer acknowledgments. It can also inform the sender about handoffs versus interface switches.
- Multiple acknowledgments uses two types of ACKs to isolate the wireless and wired portions of the network.
-
connection establishment flow and congestion control.pptx

The document discusses various aspects of connection establishment and data transmission reliability in computer networks. It describes how connection-oriented transport protocols like TCP require a connection to be established before data exchange using either a two-way or three-way handshake. The three-way handshake involves a SYN, SYN-ACK, and ACK sequence to synchronize sequence numbers and negotiate parameters. Flow control mechanisms like stop-and-wait and sliding windows are used to ensure reliable data delivery. Congestion control is also important to manage network load and avoid degradation in performance.
DEEP LEARNING FOR SMART GRID INTRUSION DETECTION: A HYBRID CNN-LSTM-BASED MODEL

As digital technology becomes more deeply embedded in power systems, protecting the communication
networks of Smart Grids (SG) has emerged as a critical concern. Distributed Network Protocol 3 (DNP3)
represents a multi-tiered application layer protocol extensively utilized in Supervisory Control and Data
Acquisition (SCADA)-based smart grids to facilitate real-time data gathering and control functionalities.
Robust Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are necessary for early threat detection and mitigation because
of the interconnection of these networks, which makes them vulnerable to a variety of cyberattacks. To
solve this issue, this paper develops a hybrid Deep Learning (DL) model specifically designed for intrusion
detection in smart grids. The proposed approach is a combination of the Convolutional Neural Network
(CNN) and the Long-Short-Term Memory algorithms (LSTM). We employed a recent intrusion detection
dataset (DNP3), which focuses on unauthorized commands and Denial of Service (DoS) cyberattacks, to
train and test our model. The results of our experiments show that our CNN-LSTM method is much better
at finding smart grid intrusions than other deep learning algorithms used for classification. In addition,
our proposed approach improves accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score, achieving a high detection
accuracy rate of 99.50%.
Electric vehicle and photovoltaic advanced roles in enhancing the financial p...

Climate change's impact on the planet forced the United Nations and governments to promote green energies and electric transportation. The deployments of photovoltaic (PV) and electric vehicle (EV) systems gained stronger momentum due to their numerous advantages over fossil fuel types. The advantages go beyond sustainability to reach financial support and stability. The work in this paper introduces the hybrid system between PV and EV to support industrial and commercial plants. This paper covers the theoretical framework of the proposed hybrid system including the required equation to complete the cost analysis when PV and EV are present. In addition, the proposed design diagram which sets the priorities and requirements of the system is presented. The proposed approach allows setup to advance their power stability, especially during power outages. The presented information supports researchers and plant owners to complete the necessary analysis while promoting the deployment of clean energy. The result of a case study that represents a dairy milk farmer supports the theoretical works and highlights its advanced benefits to existing plants. The short return on investment of the proposed approach supports the paper's novelty approach for the sustainable electrical system. In addition, the proposed system allows for an isolated power setup without the need for a transmission line which enhances the safety of the electrical network
More Related Content
Similar to Mobile Computing - Mobile Transport Layer.pptx.pdf
Mobile Transpot Layer

This document discusses various transport layer protocols for mobile networks. It begins by describing TCP and its mechanisms for congestion avoidance, flow control, slow start, and retransmission. It then covers several TCP variants including Tahoe, Reno, and Vegas. It also discusses indirect TCP, Snoop TCP, and Mobile TCP which aim to optimize TCP for wireless networks by handling retransmissions locally or splitting the connection. The document provides details on the algorithms and functioning of these different protocols.
mobile_transport_layer (1).pptx

1) Standard TCP performs poorly over wireless networks due to packet loss from errors and mobility rather than congestion. This causes unnecessary slow starts and window reductions.
2) Early approaches like Indirect TCP, Snooping TCP, and Mobile TCP split or modify the TCP connection to isolate the wireless link but lose end-to-end semantics or require changes.
3) Later techniques like forced fast retransmit and selective acknowledgements improve efficiency without changing TCP but require cooperation between layers. Overall no single solution is optimal due to the need to maintain compatibility with fixed networks.
Unit 4

This document discusses several approaches to improving TCP performance over mobile networks:
Traditional TCP uses slow start and congestion control mechanisms that reduce efficiency over mobile networks. Indirect TCP segments connections and uses a proxy to improve performance. Snooping TCP buffers packets to enable fast retransmissions without changing endpoints. Mobile TCP freezes the sender's window on disconnection to avoid unnecessary retransmissions. These methods aim to isolate wireless losses from congestion responses and enable fast recovery from errors and handovers.
Mobile transport layer

The document discusses various approaches to modifying TCP for use in mobile networks. Indirect TCP splits the TCP connection at the foreign agent, keeping the fixed network unchanged but losing end-to-end semantics. Snooping TCP has the foreign agent snoop packets and retransmit lost packets locally without changing TCP. Mobile TCP uses a supervisory host to monitor disconnections and choke senders. Other approaches include forced fast retransmit after handovers, freezing TCP timers during disconnects, selective retransmission of only lost packets, and transaction-oriented TCP to combine connection setup in fewer packets. Each approach has advantages like efficiency or compatibility but also disadvantages like overhead or non-transparency.
Mc unit 4-jwfiles

The document discusses various approaches to improving TCP for mobile networks. It begins by describing traditional TCP and its mechanisms for congestion control and reliable data transmission. However, TCP was designed for fixed networks and faces challenges in mobile environments due to higher error rates, mobility-induced packet loss, and inefficient slow start behavior after losses. Several TCP improvements are then outlined, including Indirect TCP which segments connections and uses a proxy at the access point to isolate the wireless portion. This allows specialized TCP variants to be used for the wireless link without changing the fixed network. Finally, socket migration during handover is discussed to maintain connections as the mobile host moves.
Mcseminar

This document discusses various transport layer protocols for mobile networks. It begins with an overview of TCP and UDP, and then describes several strategies for improving TCP performance over mobile networks, including indirect TCP (I-TCP), snooping TCP, and Mobile TCP. It also discusses congestion control strategies like slow start and fast retransmit. Overall, the document analyzes how TCP can be optimized through techniques like connection splitting, buffering, and selective retransmission to better accommodate the characteristics of wireless networks.
Transport protocols

The document discusses various approaches to improving TCP performance over mobile networks, including:
1. Indirect TCP which splits the TCP connection to isolate errors on the wireless link. This requires no changes to fixed network hosts but loses end-to-end semantics.
2. Snooping TCP where the foreign agent buffers packets and retransmits lost packets transparently. This maintains end-to-end semantics but does not fully isolate the wireless link.
3. Mobile TCP which splits the connection and supports lengthy disconnections by freezing transmission at disconnected base stations. However, it propagates wireless losses into the fixed network.
Mobile transport layer

The document discusses various transport layer protocols for mobile networks, including traditional TCP, Indirect TCP, Snooping TCP, and Mobile TCP. Traditional TCP was designed for fixed networks and experiences issues in mobile networks due to factors like packet loss from handoffs. Indirect TCP splits the TCP connection at the access point to isolate the wireless link. Snooping TCP has the access point buffer packets and detect losses to enable local retransmissions. Mobile TCP uses a supervisory host to handle disconnections and restart the connection when needed. Each approach aims to improve TCP performance over mobile networks while maintaining compatibility with traditional TCP.
Improving Performance of TCP in Wireless Environment using TCP-P

Improving the performance of the transmission
control protocol (TCP) in wireless environment has been an
active research area. Main reason behind performance
degradation of TCP is not having ability to detect actual reason
of packet losses in wireless environment. In this paper, we are
providing a simulation results for TCP-P (TCP-Performance).
TCP-P is intelligent protocol in wireless environment which
is able to distinguish actual reasons for packet losses and
applies an appropriate solution to packet loss.
TCP-P deals with main three issues, Congestion in
network, Disconnection in network and random packet losses.
TCP-P consists of Congestion avoidance algorithm and
Disconnection detection algorithm with some changes in TCP
header part. If congestion is occurring in network then
congestion avoidance algorithm is applied. In congestion
avoidance algorithm, TCP-P calculates number of sending
packets and receiving acknowledgements and accordingly set
a sending buffer value, so that it can prevent system from
happening congestion. In disconnection detection algorithm,
TCP-P senses medium continuously to detect a happening
disconnection in network. TCP-P modifies header of TCP
packet so that loss packet can itself notify sender that it is
lost.This paper describes the design of TCP-P, and presents
results from experiments using the NS-2 network simulator.
Results from simulations show that TCP-P is 4% more
efficient than TCP-Tahoe, 5% more efficient than TCP-Vegas,
7% more efficient than TCP-Sack and equally efficient in
performance as of TCP-Reno and TCP-New Reno. But we can
say TCP-P is more efficient than TCP-Reno and TCP-New
Reno since it is able to solve more issues of TCP in wireless
environment.
Transaction TCP

T/TCP is a protocol that aims to reduce the number of packets needed for transaction-style applications by allowing a client to open a connection, send data, and close the connection in a single packet. It utilizes a mechanism called TCP Accelerated Open (TAO) to bypass the standard 3-way TCP handshake. Testing showed T/TCP saved an average of 5 packets per transaction compared to TCP. However, the percentage savings decreased with larger data transfers as T/TCP is most beneficial for small transactions. While improving performance, T/TCP also introduced some security and operational issues that needed to be addressed for broader adoption.
High Performance Networking with Advanced TCP

High Performance Networking with TCP. TCP properties, UDP, flow control, Congestion Avoidance & Control, slow start, Congestion Control Review, TCP Tahoe & Reno
UAV Data Link Design for Dependable Real-Time Communications

Communication over the kinds of Data-Links used for unmanned vehicles presents important challenges dues to the low bandwidth, intermittent, and lower reliability of these links. Classic network protocols such as TCP do not operate well in this environment forcing application developers to implement their own reliability and session management. This presentation describes he issues and alternatives.
A THROUGHPUT ANALYSIS OF TCP IN ADHOC NETWORKS

This document analyzes the throughput of TCP in mobile ad hoc networks through simulations. It finds that TCP throughput decreases initially as the number of hops increases, then stabilizes at higher hop counts. This is due to hidden terminal problems at low hops. The number of retransmissions increases with payloads and flows due to buffering and congestion. TCP performance degrades in wireless networks because it cannot differentiate between congestion and non-congestion packet losses. Mobility, interference, and dynamic topology changes specific to wireless networks cause unnecessary triggering of TCP congestion control mechanisms.
A throughput analysis of tcp in adhoc networks

Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is a connection oriented end-end reliable byte stream
transport layer protocol. It is widely used in the Internet.TCP is fine tuned to perform well in
wired networks. However the performance degrades in mobile ad hoc networks. This is due to
the characteristics specific to wireless networks, such as signal fading, mobility, unavailability
of routes. This leads to loss of packets which may arise either from congestion or due to other
non-congestion events. However TCP assumes every loss as loss due to congestion and invokes
the congestion control procedures. TCP reduces congestion window in response, causing unnecessary
degradation in throughput. In mobile ad hoc networks multi-hop path forwarding further
worsens the packet loss and throughput. To understand the TCP behavior and improve the
TCP performance over mobile ad hoc networks considerable research has been carried out. As
the research is still active in this area a comprehensive and in-depth study on the TCP throughput
and the various parameters that degrade the performance of TCP have been analyzed. The
analysis is done using simulations in Qualnet 5.0
C10 transport protocols

The document discusses various approaches to improving TCP performance over mobile networks. Indirect TCP splits the TCP connection at the foreign agent to isolate the wireless link. Snooping TCP has the foreign agent buffer packets and retransmit lost packets locally. Mobile TCP uses a supervisory host to monitor connections and choke the sender window during disconnections. Other techniques discussed include fast retransmit/recovery after handovers, freezing TCP states during interruptions, selective retransmission of only lost packets, and transaction-oriented TCP to reduce overhead of short messages. Each approach has advantages but also disadvantages related to compatibility, transparency, and complexity.
connection establishment flowand congestion.pptx

Connection establishment involves a handshake process between two endpoints to synchronize sequence numbers and establish communication. Transport protocols like TCP require a connection to be set up before data can be exchanged. This allows each end to verify the other's existence, negotiate parameters, and allocate resources. Common connection establishment methods are two-way and three-way handshakes, with three-way involving SYN, SYN-ACK and ACK packets. Flow control mechanisms like stop-and-wait and sliding windows ensure transmission rates match receiver capabilities to prevent buffer overruns. Congestion control is also important to manage network traffic loads and avoid degrading performance due to delays or reduced throughput when congestion occurs.
Lecture 19 22. transport protocol for ad-hoc 

This document discusses transport layer protocols for mobile ad hoc networks (MANETs). It begins with an introduction to MANETs and the need for new network architectures and protocols to support new types of networks. It then provides an overview of TCP/IP and how TCP works, including congestion control mechanisms. The document discusses challenges for TCP over wireless networks, where packet losses are often due to errors rather than congestion. It covers different versions of TCP and their approaches to congestion control. The goal is to design transport layer protocols that can address the unreliable links and frequent topology changes in MANETs.
Transport layer

here discussed about each topic of network layer like congestion control mechanism , error control , flow, tcp , udp, etc
TCP over wireless slides

The document discusses various protocols and approaches for improving the performance of TCP over wireless networks. It notes that wireless networks have higher bit error rates, lower bandwidth, and mobility issues compared to wired networks. Several protocols are described that aim to distinguish wireless losses from congestion losses to avoid unnecessary TCP reactions:
- Indirect TCP splits the connection and handles losses locally at the base station. Snoop caches packets at the base station for retransmission.
- Mobile TCP further splits the connection and has the base station defer acknowledgments. It can also inform the sender about handoffs versus interface switches.
- Multiple acknowledgments uses two types of ACKs to isolate the wireless and wired portions of the network.
-
connection establishment flow and congestion control.pptx

The document discusses various aspects of connection establishment and data transmission reliability in computer networks. It describes how connection-oriented transport protocols like TCP require a connection to be established before data exchange using either a two-way or three-way handshake. The three-way handshake involves a SYN, SYN-ACK, and ACK sequence to synchronize sequence numbers and negotiate parameters. Flow control mechanisms like stop-and-wait and sliding windows are used to ensure reliable data delivery. Congestion control is also important to manage network load and avoid degradation in performance.
Similar to Mobile Computing - Mobile Transport Layer.pptx.pdf (20)
Improving Performance of TCP in Wireless Environment using TCP-P

Improving Performance of TCP in Wireless Environment using TCP-P
UAV Data Link Design for Dependable Real-Time Communications

UAV Data Link Design for Dependable Real-Time Communications
connection establishment flow and congestion control.pptx

connection establishment flow and congestion control.pptx
Recently uploaded
DEEP LEARNING FOR SMART GRID INTRUSION DETECTION: A HYBRID CNN-LSTM-BASED MODEL

As digital technology becomes more deeply embedded in power systems, protecting the communication
networks of Smart Grids (SG) has emerged as a critical concern. Distributed Network Protocol 3 (DNP3)
represents a multi-tiered application layer protocol extensively utilized in Supervisory Control and Data
Acquisition (SCADA)-based smart grids to facilitate real-time data gathering and control functionalities.
Robust Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are necessary for early threat detection and mitigation because
of the interconnection of these networks, which makes them vulnerable to a variety of cyberattacks. To
solve this issue, this paper develops a hybrid Deep Learning (DL) model specifically designed for intrusion
detection in smart grids. The proposed approach is a combination of the Convolutional Neural Network
(CNN) and the Long-Short-Term Memory algorithms (LSTM). We employed a recent intrusion detection
dataset (DNP3), which focuses on unauthorized commands and Denial of Service (DoS) cyberattacks, to
train and test our model. The results of our experiments show that our CNN-LSTM method is much better
at finding smart grid intrusions than other deep learning algorithms used for classification. In addition,
our proposed approach improves accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score, achieving a high detection
accuracy rate of 99.50%.
Electric vehicle and photovoltaic advanced roles in enhancing the financial p...

Climate change's impact on the planet forced the United Nations and governments to promote green energies and electric transportation. The deployments of photovoltaic (PV) and electric vehicle (EV) systems gained stronger momentum due to their numerous advantages over fossil fuel types. The advantages go beyond sustainability to reach financial support and stability. The work in this paper introduces the hybrid system between PV and EV to support industrial and commercial plants. This paper covers the theoretical framework of the proposed hybrid system including the required equation to complete the cost analysis when PV and EV are present. In addition, the proposed design diagram which sets the priorities and requirements of the system is presented. The proposed approach allows setup to advance their power stability, especially during power outages. The presented information supports researchers and plant owners to complete the necessary analysis while promoting the deployment of clean energy. The result of a case study that represents a dairy milk farmer supports the theoretical works and highlights its advanced benefits to existing plants. The short return on investment of the proposed approach supports the paper's novelty approach for the sustainable electrical system. In addition, the proposed system allows for an isolated power setup without the need for a transmission line which enhances the safety of the electrical network
A review on techniques and modelling methodologies used for checking electrom...

The proper function of the integrated circuit (IC) in an inhibiting electromagnetic environment has always been a serious concern throughout the decades of revolution in the world of electronics, from disjunct devices to today’s integrated circuit technology, where billions of transistors are combined on a single chip. The automotive industry and smart vehicles in particular, are confronting design issues such as being prone to electromagnetic interference (EMI). Electronic control devices calculate incorrect outputs because of EMI and sensors give misleading values which can prove fatal in case of automotives. In this paper, the authors have non exhaustively tried to review research work concerned with the investigation of EMI in ICs and prediction of this EMI using various modelling methodologies and measurement setups.
CHINA’S GEO-ECONOMIC OUTREACH IN CENTRAL ASIAN COUNTRIES AND FUTURE PROSPECT

The rivalry between prominent international actors for dominance over Central Asia's hydrocarbon
reserves and the ancient silk trade route, along with China's diplomatic endeavours in the area, has been
referred to as the "New Great Game." This research centres on the power struggle, considering
geopolitical, geostrategic, and geoeconomic variables. Topics including trade, political hegemony, oil
politics, and conventional and nontraditional security are all explored and explained by the researcher.
Using Mackinder's Heartland, Spykman Rimland, and Hegemonic Stability theories, examines China's role
in Central Asia. This study adheres to the empirical epistemological method and has taken care of
objectivity. This study analyze primary and secondary research documents critically to elaborate role of
china’s geo economic outreach in central Asian countries and its future prospect. China is thriving in trade,
pipeline politics, and winning states, according to this study, thanks to important instruments like the
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation and the Belt and Road Economic Initiative. According to this study,
China is seeing significant success in commerce, pipeline politics, and gaining influence on other
governments. This success may be attributed to the effective utilisation of key tools such as the Shanghai
Cooperation Organisation and the Belt and Road Economic Initiative.
ACEP Magazine edition 4th launched on 05.06.2024

This document provides information about the third edition of the magazine "Sthapatya" published by the Association of Civil Engineers (Practicing) Aurangabad. It includes messages from current and past presidents of ACEP, memories and photos from past ACEP events, information on life time achievement awards given by ACEP, and a technical article on concrete maintenance, repairs and strengthening. The document highlights activities of ACEP and provides a technical educational article for members.
KuberTENes Birthday Bash Guadalajara - K8sGPT first impressions

K8sGPT is a tool that analyzes and diagnoses Kubernetes clusters. This presentation was used to share the requirements and dependencies to deploy K8sGPT in a local environment.
[JPP-1] - (JEE 3.0) - Kinematics 1D - 14th May..pdf![[JPP-1] - (JEE 3.0) - Kinematics 1D - 14th May..pdf](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![[JPP-1] - (JEE 3.0) - Kinematics 1D - 14th May..pdf](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
Kinematics 11th jpp- 01. ( Solved ) unacademy namo kaul on 14th may...
Harnessing WebAssembly for Real-time Stateless Streaming Pipelines

Traditionally, dealing with real-time data pipelines has involved significant overhead, even for straightforward tasks like data transformation or masking. However, in this talk, we’ll venture into the dynamic realm of WebAssembly (WASM) and discover how it can revolutionize the creation of stateless streaming pipelines within a Kafka (Redpanda) broker. These pipelines are adept at managing low-latency, high-data-volume scenarios.
International Conference on NLP, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning an...

International Conference on NLP, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and Applications (NLAIM 2024) offers a premier global platform for exchanging insights and findings in the theory, methodology, and applications of NLP, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and their applications. The conference seeks substantial contributions across all key domains of NLP, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and their practical applications, aiming to foster both theoretical advancements and real-world implementations. With a focus on facilitating collaboration between researchers and practitioners from academia and industry, the conference serves as a nexus for sharing the latest developments in the field.
IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Society as a Graduate Student Member

IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Society as a Graduate Student Member
Recently uploaded (20)
DEEP LEARNING FOR SMART GRID INTRUSION DETECTION: A HYBRID CNN-LSTM-BASED MODEL

DEEP LEARNING FOR SMART GRID INTRUSION DETECTION: A HYBRID CNN-LSTM-BASED MODEL
Electric vehicle and photovoltaic advanced roles in enhancing the financial p...

Electric vehicle and photovoltaic advanced roles in enhancing the financial p...
A review on techniques and modelling methodologies used for checking electrom...

A review on techniques and modelling methodologies used for checking electrom...
ML Based Model for NIDS MSc Updated Presentation.v2.pptx

ML Based Model for NIDS MSc Updated Presentation.v2.pptx
CHINA’S GEO-ECONOMIC OUTREACH IN CENTRAL ASIAN COUNTRIES AND FUTURE PROSPECT

CHINA’S GEO-ECONOMIC OUTREACH IN CENTRAL ASIAN COUNTRIES AND FUTURE PROSPECT
KuberTENes Birthday Bash Guadalajara - K8sGPT first impressions

KuberTENes Birthday Bash Guadalajara - K8sGPT first impressions
[JPP-1] - (JEE 3.0) - Kinematics 1D - 14th May..pdf![[JPP-1] - (JEE 3.0) - Kinematics 1D - 14th May..pdf](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![[JPP-1] - (JEE 3.0) - Kinematics 1D - 14th May..pdf](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
[JPP-1] - (JEE 3.0) - Kinematics 1D - 14th May..pdf
BPV-GUI-01-Guide-for-ASME-Review-Teams-(General)-10-10-2023.pdf

BPV-GUI-01-Guide-for-ASME-Review-Teams-(General)-10-10-2023.pdf
Harnessing WebAssembly for Real-time Stateless Streaming Pipelines

Harnessing WebAssembly for Real-time Stateless Streaming Pipelines
International Conference on NLP, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning an...

International Conference on NLP, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning an...
IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Society as a Graduate Student Member

IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Society as a Graduate Student Member
Mobile Computing - Mobile Transport Layer.pptx.pdf
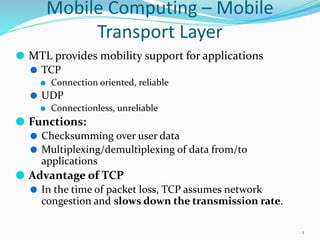
- 1. Mobile Computing – Mobile Transport Layer ⚫ MTL provides mobility support for applications ⚫ TCP ⚫ Connection oriented, reliable ⚫ UDP ⚫ Connectionless, unreliable ⚫ Functions: ⚫ Checksumming over user data ⚫ Multiplexing/demultiplexing of data from/to applications ⚫ Advantage of TCP ⚫ In the time of packet loss, TCP assumes network congestion and slows down the transmission rate. 1
- 3. Traditional TCP 3 ⚫ Congestion Control ⚫ Payload (packet) data could be more – router cannot forward the packet ⚫ Control : router drops the packet ⚫ Receiver informs the sender missed packet using sequence number – ack ⚫ Tcp –slows down the transmission rate when congestion takes place – to mitigate the congestion ⚫ Slow Start – the way TCP acts after detection of congestion ⚫ Congestion window – sender calculates the CW for a receiver ⚫ Sender sends one packet and waits for ack ⚫ After the ack is received, CW is increased everytime (exponential growth) ⚫ Congestion Threshold – sender reduces the CW to 1 packet ⚫ Linear increase continues till time-out occurs at sender due to a missing ack or until sender gets ack for same packet for long time
- 4. Traditional TCP ⚫ Fast retransmit/fast recovery ⚫ TCP sends an acknowledgement only after receiving a packet ⚫ If a sender receives several acknowledgements for the same packet ⚫ This implies that receiver received all packets up to the acknowledged packet in sequence. ⚫ Gap in the packet stream is not due to congestion, but packet loss due to a transmission error. ⚫ Fast retransmit: sender retransmit the missing packet(s) before the timer expires. ⚫ Fast recovery: since the receipt of ack shows that there is no congestion to justify a slow start ⚫ Sender can continue with the current congestion window. 4
- 5. Influences of mobility on TCP-mechanisms ⚫ TCP assumes congestion if packets are dropped ⚫ If the ack for a packet is missed, TCP assumes problem is because of congestion in network ⚫ Mobility factor ⚫ Mobile & wireless end-systems creates more packet loss ⚫ Trying to retransmit packet on layer 2 may take too long ⚫ Mobility – handover problem ⚫ Mobility from old to new foreign agent 5
- 6. Classical TCP Improvements - Indirect TCP 6 ⚫ Indirect TCP: I-TCP segments a TCP connection into a fixed part and a wireless part ⚫ Reason ⚫ TCP performs poorly with wireless links ⚫ TCP within the fixed network cannot be changed
- 7. I-TCP- Working of TCP segments 7 ⚫ Standard TCP is used between the fixed host and the access point ⚫ Access point – acts as a proxy ⚫ i.e it is seen as mobile host for the fixed host and as the fixed host for the mobile host. ⚫ Special TCP adapted to wireless links is used between access point and mobile host ⚫ Foreign agent: - is acting as a access point – between fixed host and mobile host ⚫ FA –controls the mobility of the MH and can hand over the connection to the next FA ⚫ FA forwards the packet from MH to FH
- 8. I-TCP- Working – Handover (Socket & State migration) 8 ⚫ After the handover, old proxy must forward buffered data to the new proxy ⚫ New FA informs the old FA about its location to enable packet forwarding.
- 9. I-TCP – Advantages & Disadvantages 9 ⚫ Advantages ⚫ No changes in the fixed network are necessary. ⚫ Transmission errors on the wireless link do not propagate into the fixed network ⚫ Simple to control, mobile TCP is used only for one hop between, e.g., a foreign agent and mobile host ⚫ Very fast retransmission of packets is possible. ⚫ Disadvantages ⚫ Loss of end-to-end semantics: foreign agents might crash – false positive ack ⚫ Higher latency possible due to buffering of data within the foreign agent and forwarding to a new foreign agent
- 10. Classical TCP Improvements - Snooping TCP ⚫ Drawback of I-TCP: segmentation of the single TCP connection into two TCP connections ⚫ This looses the original end-to-end TCP semantic. ⚫ Solution: Snooping TCP ⚫ “Extension of TCP within the foreign agent ⚫ Buffering of packets sent to the mobile host ⚫ Lost packets on the wireless link (both directions) will be retransmitted immediately by the mobile host or foreign agent, respectively (so called “local” retransmission) ⚫ The foreign agent “snoops” the packet flow and recognizes acknowledgements in both directions, it also filters ACKs 10
- 11. Snooping TCP 11
- 12. Snooping TCP – Advantages & Disadvantages ⚫ Advantages: ⚫ End-to-end TCP semantic is preserved ⚫ CH does not need to be changed ⚫ Enhancements are done in FA ⚫ Disadvantages: ⚫ It takes some time until the FA can successfully retransmit a packet from its buffer due to problems on the wireless link. 12
- 13. Classical TCP Improvements - Mobile TCP ⚫ It handles the occurrence of lengthy and/or frequent disconnections ⚫ Problems: ⚫ sender tries to retransmit data controlled by a retransmission timer that doubles with each unsuccessful retransmission attempt. ⚫ the longer the period of disconnection, the more buffer is needed. ⚫ Creates problem in handover 13
- 14. Mobile TCP 14 ⚫ M-TCP- same goals as I-TCP & snooping TCP ⚫ Tries to improve overall throughput, lower delay, maintain end-to-end semantics of TCP, handover ⚫ Provides solution to lengthy/frequent disconnections ⚫ M-TCP splits the TCP connection into two parts: ⚫ Unmodified TCP connection – supervisory host (SH) ⚫ Optimized TCP connection – optimization techniques ⚫ Supervisory host ⚫ monitors all packets, if disconnection detected ⚫ Set sender window size to 0 ⚫ Sender automatically goes into persistent mode ⚫ If it detects connectivity again ⚫ Reopens the window of the sender ⚫ Advantages ⚫ Maintains semantics, supports disconnection, no buffer forwarding ⚫ Disadvantages ⚫ Loss on wireless link propagated into fixed network
- 15. Classical TCP Improvements – Fast retransmit/fast recovery ⚫ Change of foreign agent often results in packet loss ⚫ TCP reacts with slow-start although there is no congestion ⚫ Solution ⚫ Forced fast retransmit ⚫ As soon as the mobile host has registered with a new foreign agent, the MH sends duplicated acknowledgements on purpose ⚫ This forces the fast retransmit mode at the communication partners ⚫ Additionally, the TCP on the MH is forced to continue sending with the actual window size and not to go into slow-start after registration ⚫ Advantage ⚫ Simple changes result in significant higher performance ⚫ Disadvantage ⚫ It requires more cooperation between the mobile IP and TCP layer . 15
- 16. Classical TCP Improvements – Transmission/Time-out freezing ⚫ Mobile hosts can be disconnected for a longer time ⚫ No packet exchange possible, e.g., in a tunnel, disconnection due to overloaded cells . with higher priority traffic ⚫ TCP disconnects after time-out completely ⚫ Solution ⚫ TCP freezing ⚫ MAC layer is often able to detect interruption in advance ⚫ MAC can inform TCP layer of upcoming loss of connection ⚫ TCP stops sending, but does now not assume a congested link ⚫ MAC layer signals again if reconnected ⚫ Advantage ⚫ It is independent of TCP mechanism ⚫ Disadvantage ⚫ TCP on mobile host has to be changed, mechanism depends on MAC layer 16
- 17. Classical TCP Improvements – Selective retransmission 17 ⚫ TCP acknowledgements are often cumulative ⚫ If single packets are missing quite often a whole packet sequence beginning at the gap has to be retransmitted (go-back-n), thus wasting bandwidth ⚫ Solution ⚫ Selective retransmission as one solution ⚫ RFC2018 allows for acknowledgements of single packets, not only acknowledgements of in-sequence packet streams without gaps ⚫ sender can now retransmit only the missing packets ⚫ Advantage ⚫ much higher efficiency ⚫ Disadvantage ⚫ more complex software in a receiver, more buffer needed at the receiver
- 18. Classical TCP Improvements – Transaction –oriented TCP 18 ⚫ Example TCP connection setup overhead
- 19. Transaction –oriented TCP 19 ⚫ TCP phases ⚫ Connection setup, data transmission, connection release ⚫ Using 3-way-handshake needs 3 packets for setup and release, respectively ⚫ Thus, even short messages need a minimum of 7 packets! ⚫ Transaction oriented TCP ⚫ RFC1644, T-TCP, describes a TCP version to avoid this overhead ⚫ Connection setup, data transfer and connection release can be combined ⚫ Thus, only 2 or 3 packets are needed ⚫ Advantage ⚫ More efficient ⚫ Disadvantage ⚫ Requires changed TCP ⚫ Mobility not longer transparent