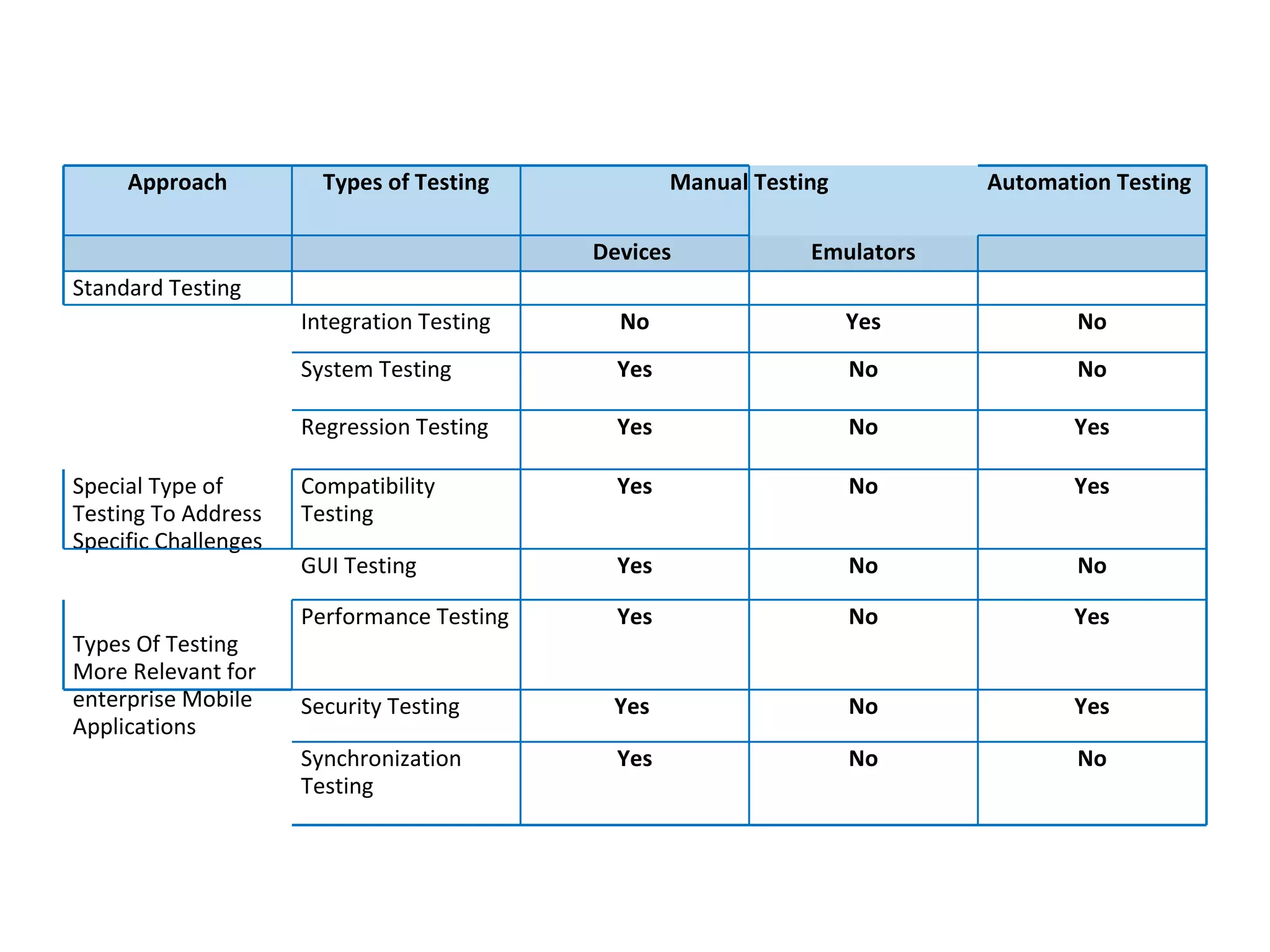
The document outlines the challenges and strategies in mobile app quality assurance (QA) across various platforms, including iOS, Android, and BlackBerry, highlighting the complexities of testing across multiple devices and OS versions. It details a comprehensive mobile testing approach that includes manual and automated testing, usability, compatibility, performance, and security testing. The conclusion emphasizes the need for a well-defined scope, assessment of requirements, and investment in specialized expertise and tools.