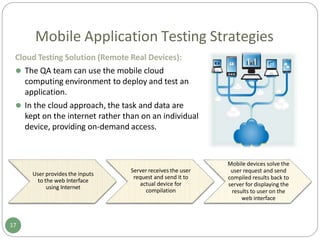
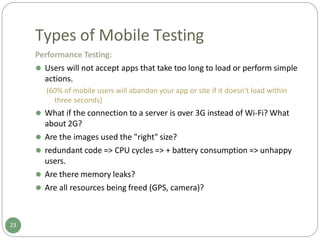
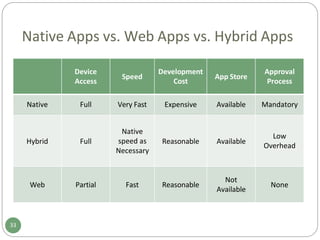
The document provides an overview of mobile application testing. It discusses the rapid growth in mobile app downloads and usage across various industries. It then covers some of the key challenges in mobile app testing, including the large number of device variations, limitations of current mobile testing tools, and lack of industry standards. The document also presents different mobile app testing strategies such as using real devices, emulators, and cloud-based testing. It defines various types of mobile app testing like interface, usability, performance, security, service, and localization testing. Finally, it compares native apps, web apps, and hybrid apps in terms of how they are developed and deployed and what features they support.