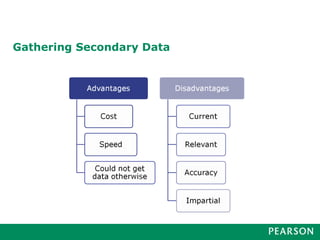
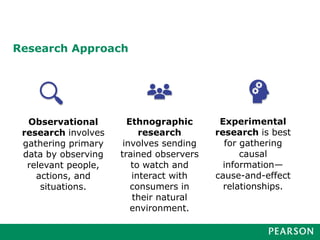
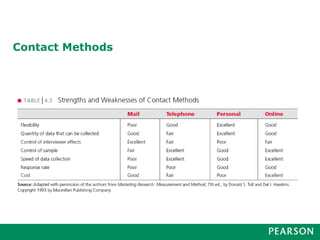
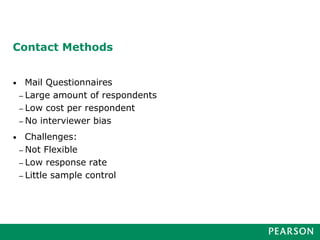
Marketing research involves a 6-step process: 1) defining the problem, 2) developing a research plan, 3) collecting information, 4) analyzing the information, 5) presenting findings, and 6) making a decision. Good marketing research is objective, relevant, accurate, reliable, timely, and accessible. It follows this process and utilizes various research methods and tools to gather and interpret meaningful data to inform business decisions.