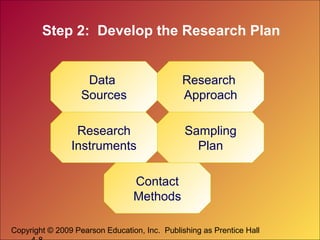
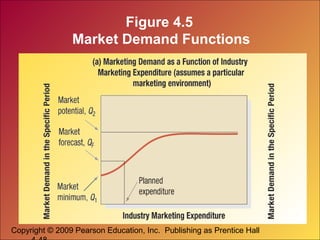
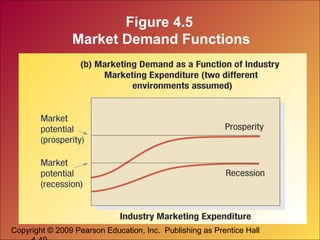
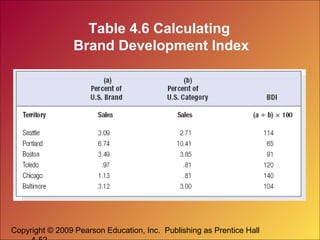
This document discusses marketing research and demand forecasting. It defines marketing research as the systematic process of designing, collecting, analyzing and reporting data to help solve specific marketing problems. The key steps in the marketing research process are defining the problem, developing a research plan, collecting information, analyzing the findings and making decisions. Different research methods are discussed, including surveys, experiments and focus groups. Good marketing metrics and marketing-mix modeling can help companies quantify and understand the impact of their marketing activities.