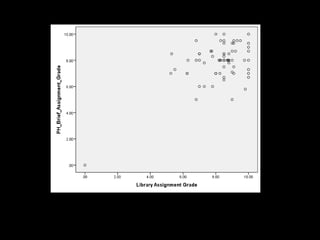
This document summarizes research investigating the impact of library instruction sessions on student assignment grades in a public health course. The research found that attendance at both optional library instruction sessions was significantly associated with higher grades on the library research assignment and another individual assignment. Several characteristics of better assignments, such as identifying a literature review and having clear search criteria, were also significantly associated with instruction session attendance. However, the research had limitations and did not prove the instruction caused improved grades. Future work could explore assignments without search strategies and fully online instruction.
















![RESULTS
• Assignment characteristics significantly
associated with instruction session
attendance:
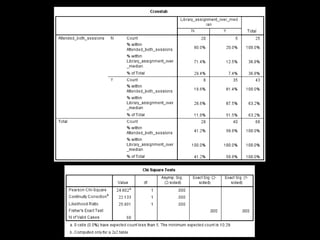
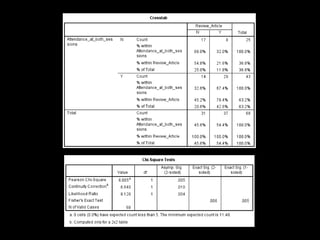
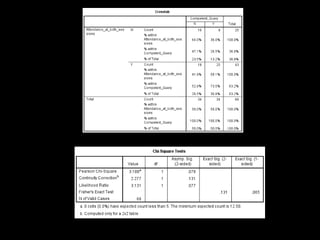
+ Correct identification of a literature review
[67.4% (n = 29/14) of students attending
both sessions (p = 0.005)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mla-presentation-slides-150518140741-lva1-app6892/85/Library-Instruction-Attendance-Correlates-with-Better-Assignment-Grades-Better-Assignment-Quality-17-320.jpg)
![RESULTS
• Assignment characteristics significantly
associated with instruction session
attendance:
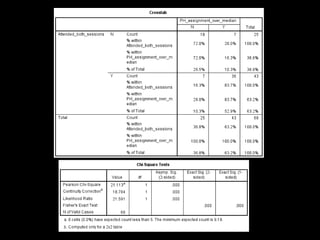
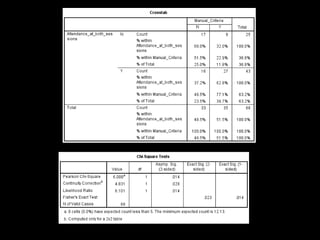
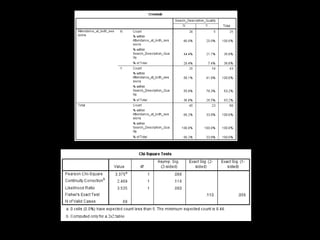
+ Clear statements of inclusion and exclusion
criteria that don’t confuse manual and
automated search processes [62.8%
(n=27/16) of students attending both
sessions (p = 0.01)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mla-presentation-slides-150518140741-lva1-app6892/85/Library-Instruction-Attendance-Correlates-with-Better-Assignment-Grades-Better-Assignment-Quality-18-320.jpg)
![RESULTS
• Assignment characteristics significantly
associated with instruction session
attendance:
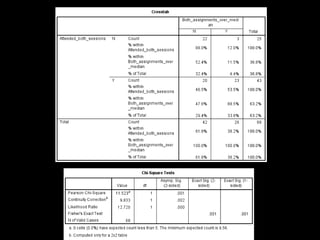
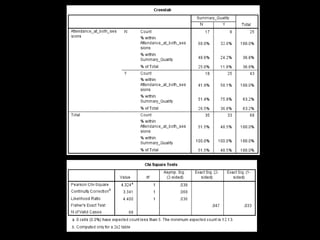
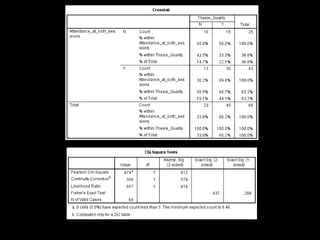
+ Accurate summary of primary sources and
correct use of AMA citation style [58.1%
(n=25/18) of students attending both
sessions (p = 0.03)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mla-presentation-slides-150518140741-lva1-app6892/85/Library-Instruction-Attendance-Correlates-with-Better-Assignment-Grades-Better-Assignment-Quality-19-320.jpg)
![RESULTS
• Assignment characteristics associated
with instruction session attendance:
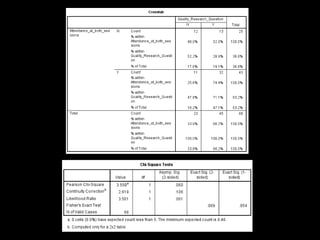
+ Better, PICOT structured research
questions [74.4% (n=32/11) of students
attending both sessions (p = 0.06)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mla-presentation-slides-150518140741-lva1-app6892/85/Library-Instruction-Attendance-Correlates-with-Better-Assignment-Grades-Better-Assignment-Quality-20-320.jpg)
![RESULTS
• Assignment characteristics associated
with instruction session attendance:
+ Use of controlled vocabulary and Boolean
logic [58.1% (n = 25/18) of students
attending both sessions, compare to 36% (n
= 9/16) of students who missed a session (p
= 0.07)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mla-presentation-slides-150518140741-lva1-app6892/85/Library-Instruction-Attendance-Correlates-with-Better-Assignment-Grades-Better-Assignment-Quality-21-320.jpg)
![RESULTS
• Assignment characteristics associated
with instruction session attendance:
+ Coherent description of search strategy
[41.9% (n = 18/25) of students attending
both sessions, compare to 20% (n = 5/20 of
students who missed a session (p = 0.06)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mla-presentation-slides-150518140741-lva1-app6892/85/Library-Instruction-Attendance-Correlates-with-Better-Assignment-Grades-Better-Assignment-Quality-22-320.jpg)