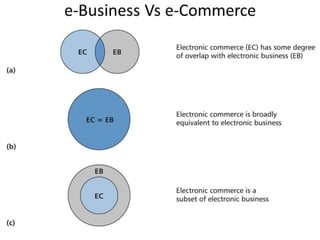
This document presents information on e-commerce. It defines e-commerce as the purchase and sale of goods and services using electronic systems like the Internet. The document outlines different types of e-commerce models including B2B, B2C, C2C, B2G, and M-commerce. It also lists opportunities like global markets and reduced costs, as well as challenges such as security issues. In conclusion, e-commerce allows businesses to create new offerings and improve existing products using electronic technologies.