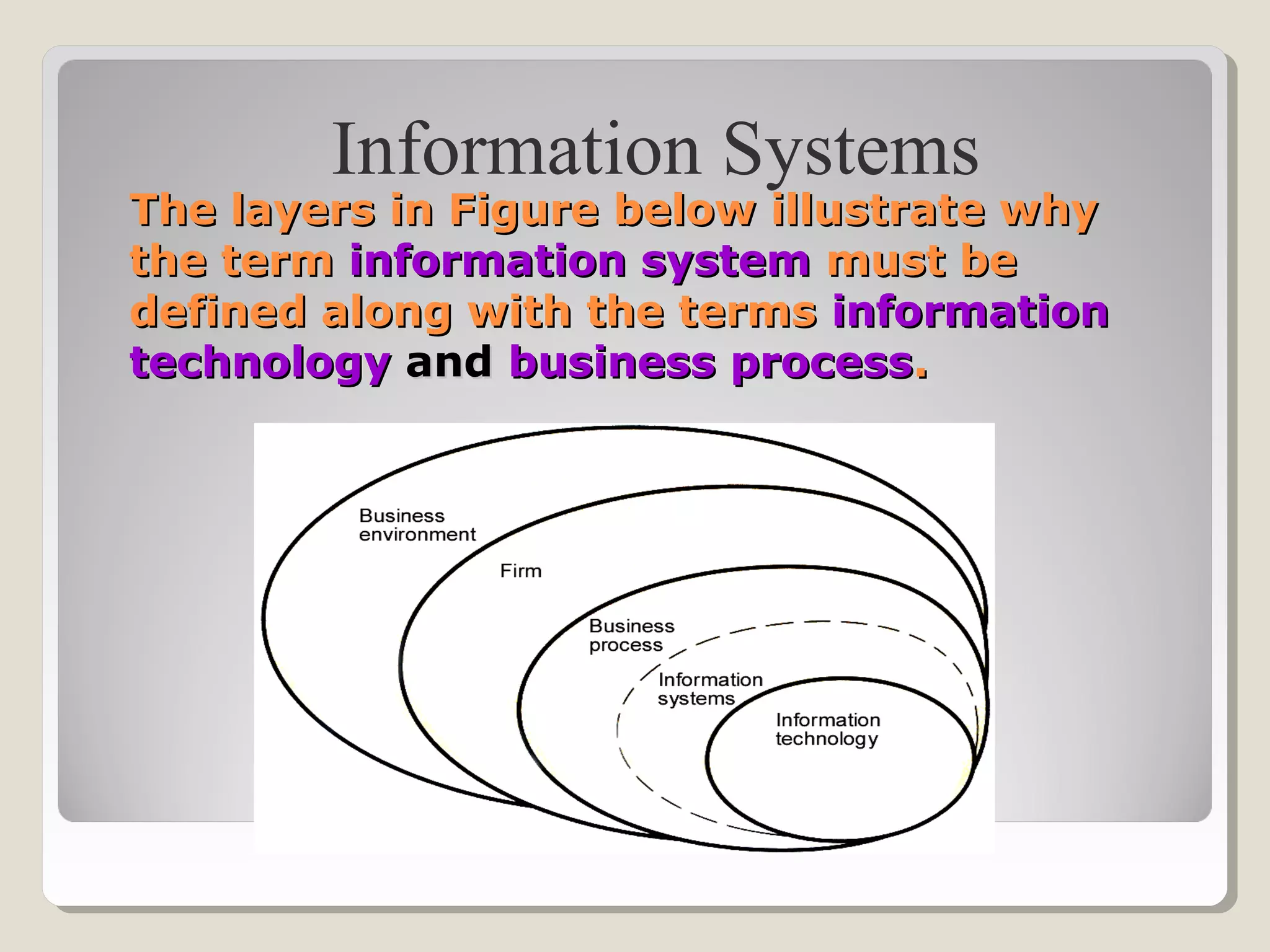
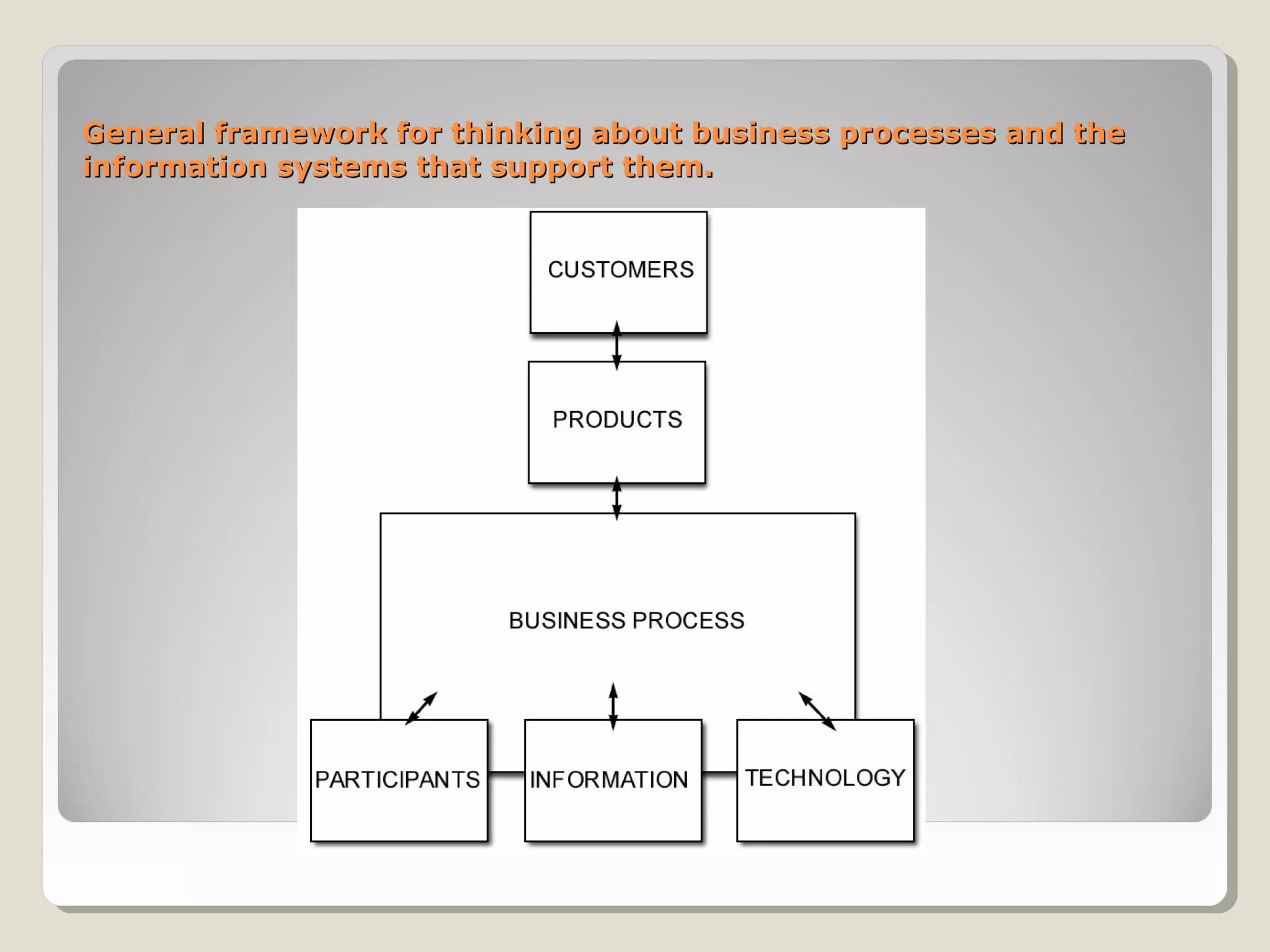
Information technology (IT) focuses on selecting, integrating, and deploying computing technology, while information systems (IS) focus on applying computing technology to business processes. IT deals with the technical side, providing hardware and software, while IS deals with the business side, using information technology to capture, store, and process information for business processes and decision making. Some key advantages of IT and IS include increased productivity, efficiency, communication, and profitability, while disadvantages include costs, security issues, unemployment, and information overload.