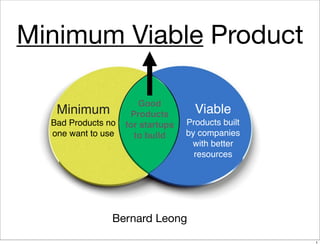
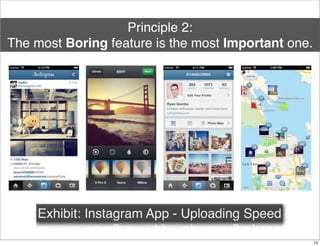
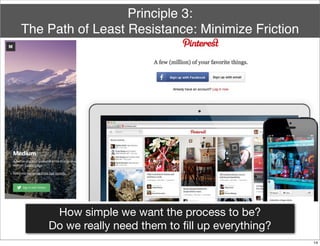
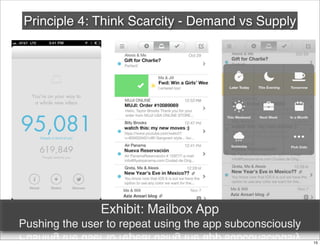
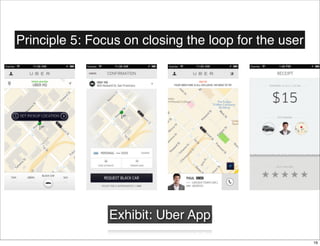
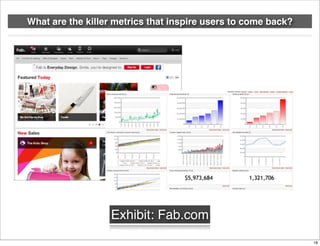
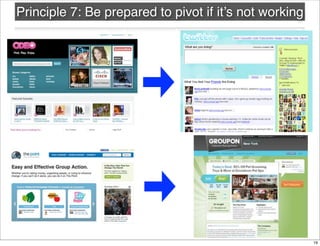
The document discusses the concept of Minimum Viable Product (MVP) in a lean startup context, emphasizing its importance for validating business hypotheses with minimal resources. It outlines key principles for MVP development, including the need for simplicity, user feedback, and the iterative process. The document also includes practical exercises for product managers to identify essential features and metrics needed to build and deploy various types of products within three months.