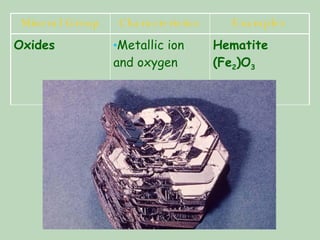
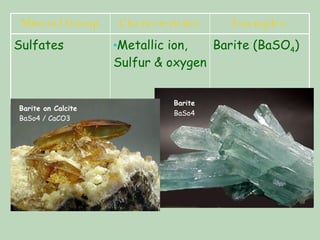
The document discusses minerals, their properties, and how they are classified. It defines minerals as naturally occurring solid substances with a crystal structure. All minerals share common characteristics - they form through natural processes, are not living, have a definite shape and volume, and are made of elements or compounds arranged in repeating crystal patterns. Minerals are grouped based on their chemical composition, with the most abundant group being silicates like quartz and mica. Physical properties like color, luster, hardness, cleavage/fracture, and specific gravity can be used to identify different minerals.