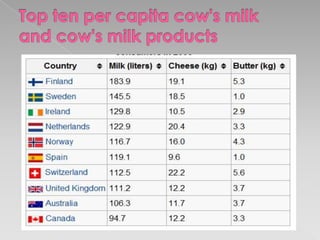
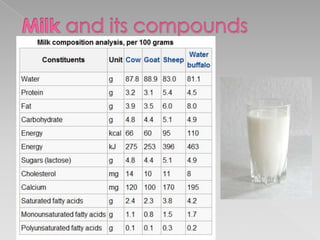
This document discusses the composition of milk and the process of separating its main components - protein, fats, carbohydrates, and phosphate. Milk is a colloidal solution of these compounds. Proteins fold into complex 3D structures to remain soluble in water. Fats are composed of glycerol and fatty acid chains. A separation process involves adding acid to separate the protein and fats, then adding acetone to extract the fats, leaving the protein behind.