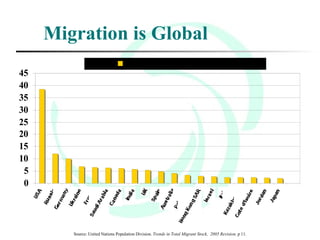
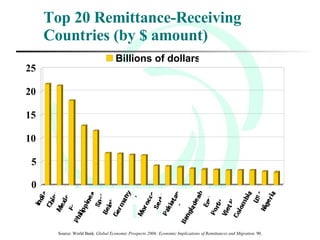
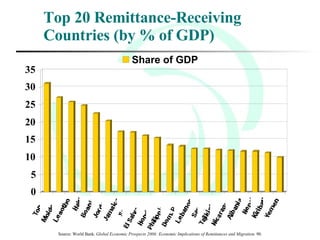
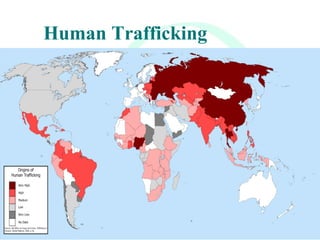
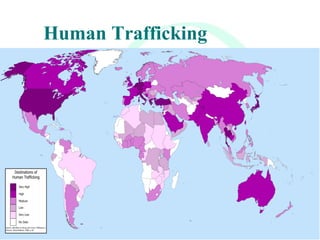
This document provides an overview of global migration trends and the causes and effects of human migration. It notes that 191 million people lived outside their country of birth in 2005, which is double the number since World War II. The main causes of migration discussed are economic factors like employment opportunities, political factors like war or persecution, and social factors like family reunification. The effects outlined include impacts on immigrants, host countries, home countries, and multi-national issues.