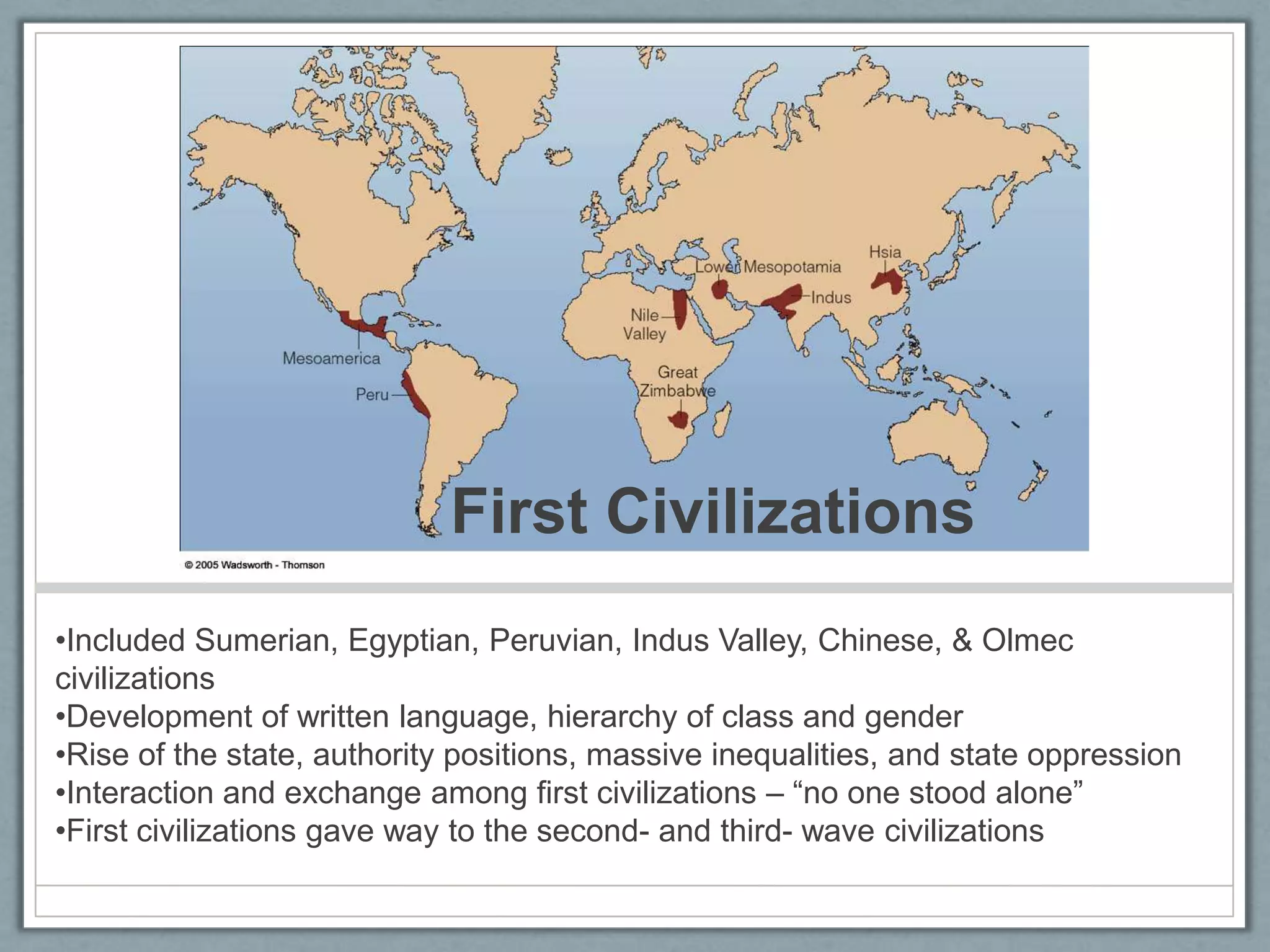
This document summarizes Jennifer Yung's mid-term PowerPoint report on World History from the Paleolithic era to the Classical era. It covers the first migrations of Homo sapiens out of Africa, hunter-gatherer societies like the Hadza and San, the Agricultural Revolution, early civilizations in places like Sumer and Egypt, the rise of empires in places like Rome and China, and the development of major world religions from 500 BCE to 500 CE. The Classical era saw the exchange of ideas, cultures, and values between second-wave civilizations and empires.