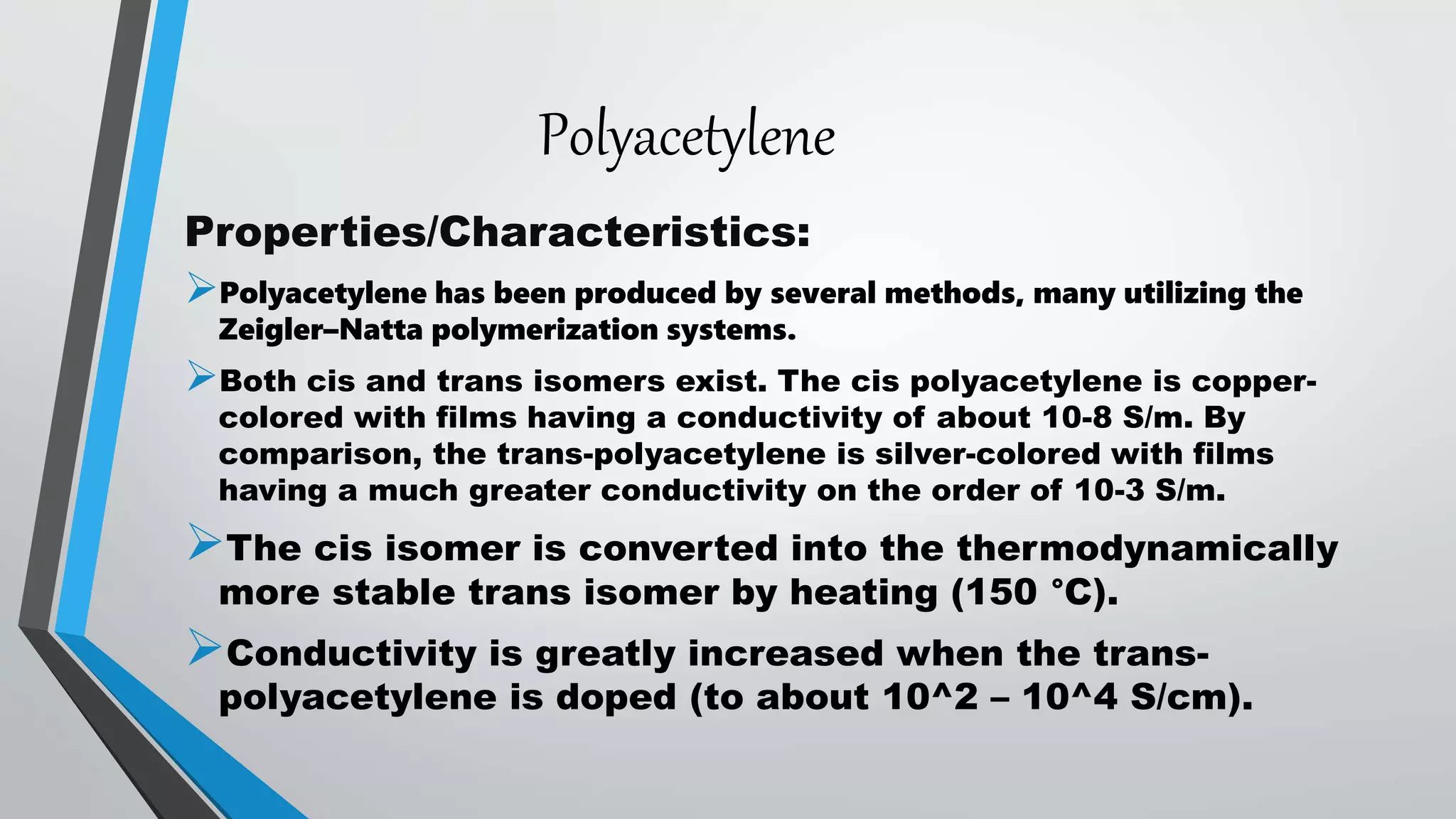
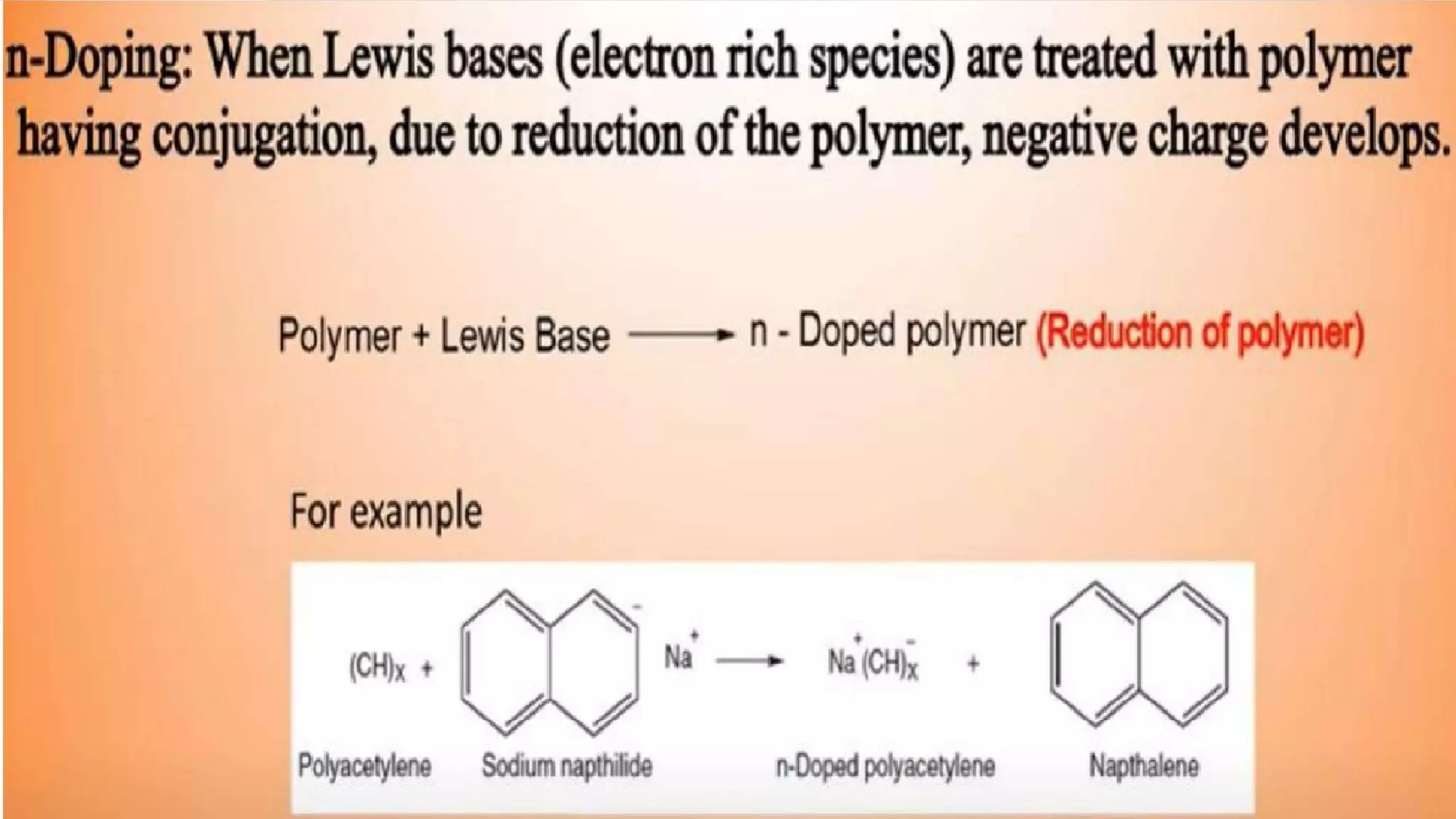
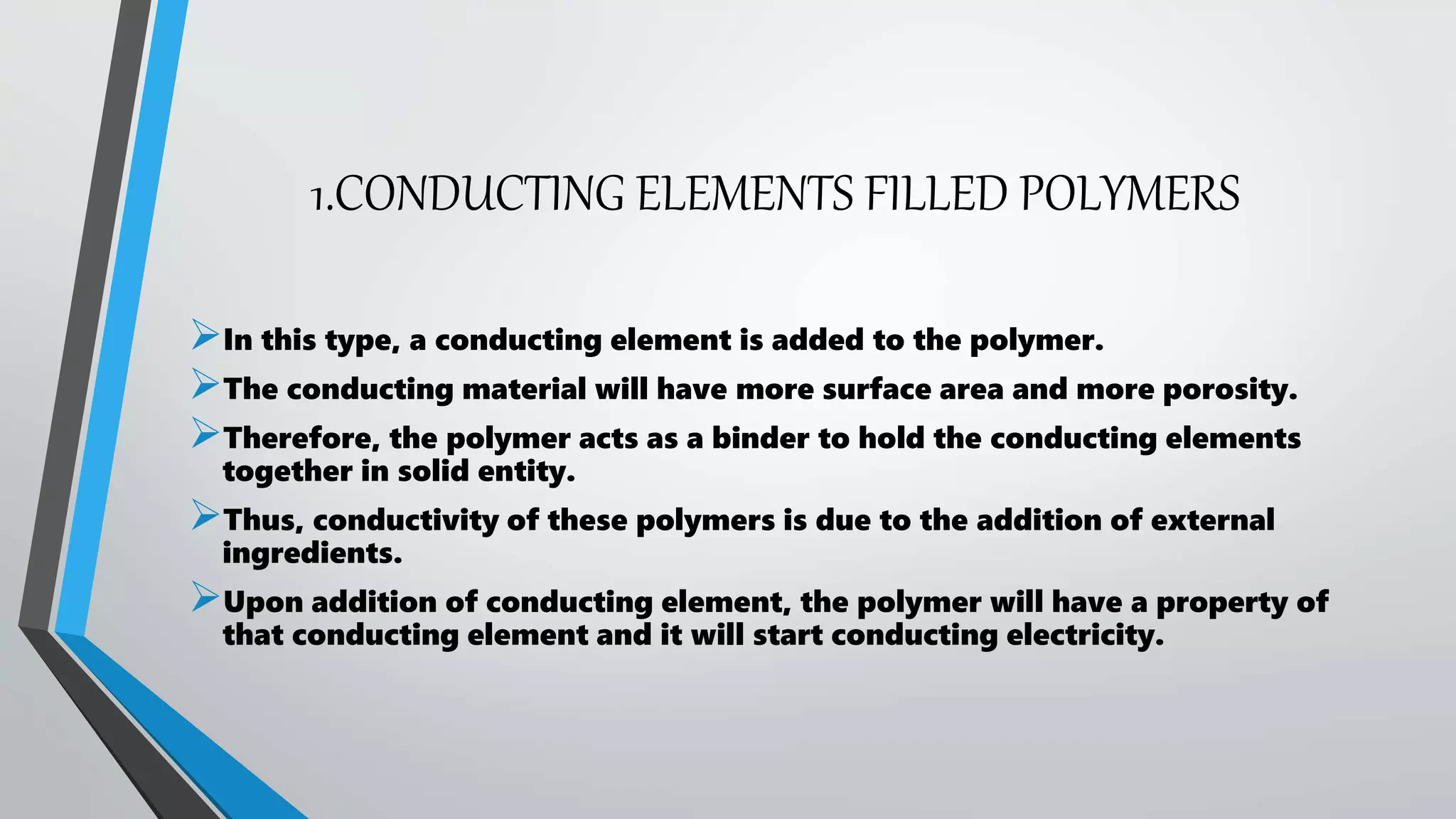
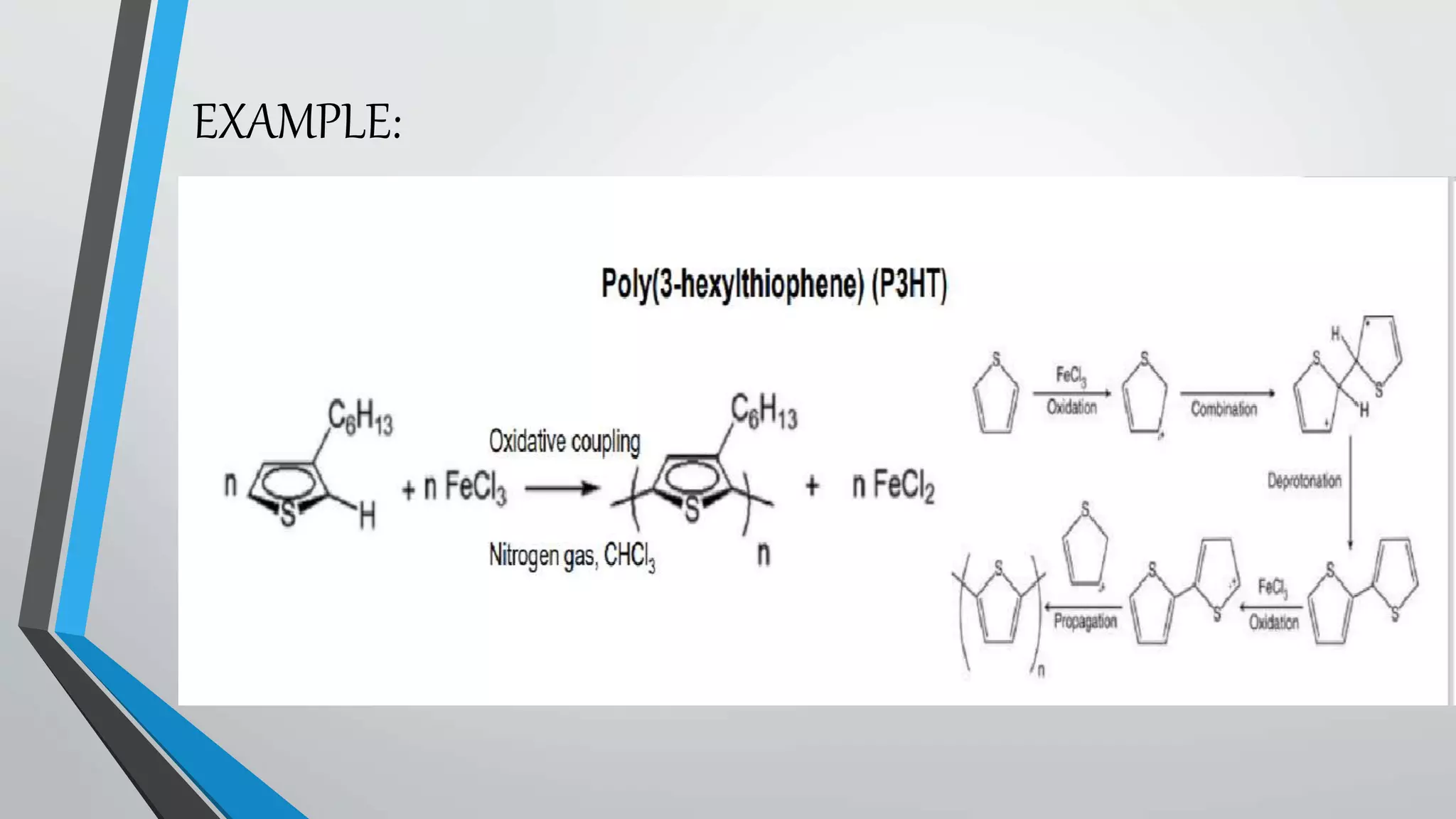
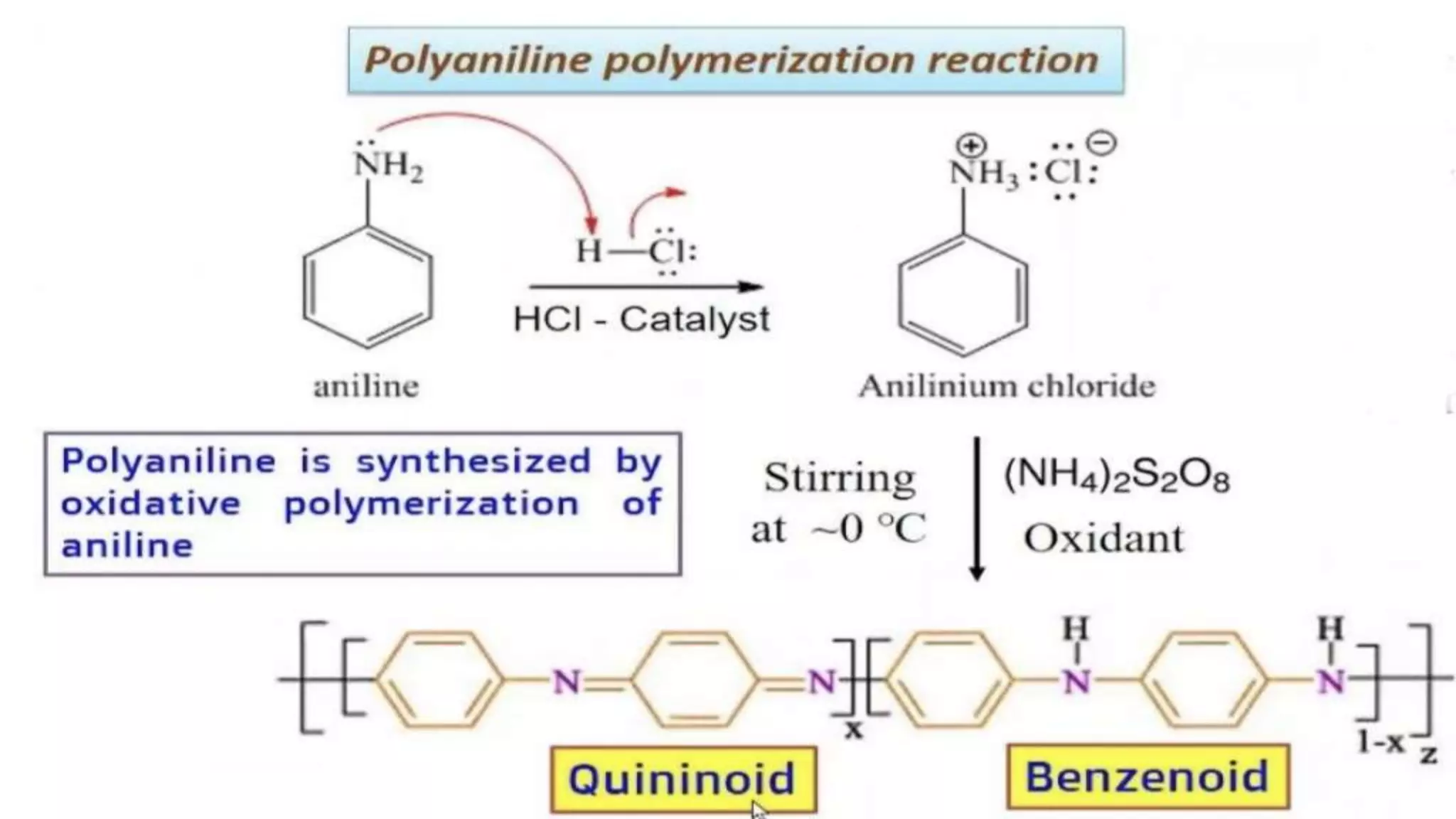
This document discusses conductive polymers and their properties. It notes that conductive polymers are organic polymers that conduct electricity unlike insulating polymers. Polyacetylene was one of the first conductive polymers discovered, with the trans isomer conducting much better than the cis isomer. Doping polyacetylene can increase its conductivity significantly. Conjugated conductive polymers have delocalized pi electrons that allow for electron movement. Extrinsic conductive polymers derive their conductivity from externally added components like conductive fillers or blending with other conductive polymers. Examples of conductive polymers discussed include poly(3-hexylthiophene).