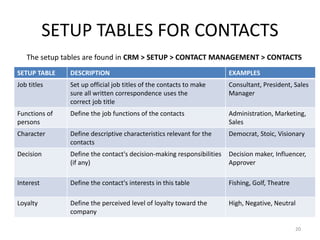
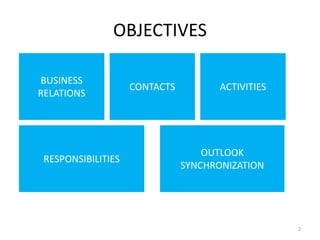
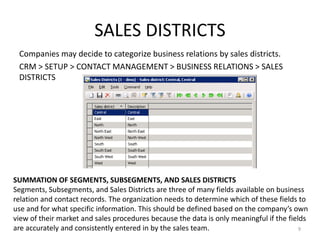
This document provides an introduction to the CRM module in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2009. It discusses setting up and using various CRM features like business relations, contacts, activities, responsibilities, and quotations. The objectives are to define business relations and understand their significance, set up default fields and categorizations for business relations, create and maintain business relations, convert them to customers and vendors, and know the available reports. It also covers creating and maintaining contacts connected to business relations, and creating activities, responsibilities, and quotations in the CRM module.













![DOCUMENTS
You can view documents related to a business
relations by clicking on :
CRM > Business Relations > select the
Document icon on a Business Relation record
[Activity]
link a document to business relation record
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/crmtrainingintroduction-140918110659-phpapp02/85/Microsoft-Dynamics-AX-2009-CRM-training-16-320.jpg)