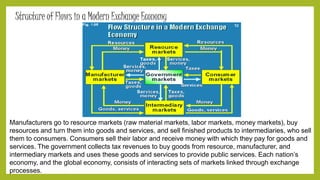
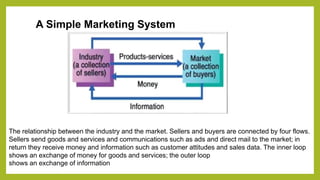
1. The document discusses the importance and role of marketing in business. It explains that marketing is the process of creating, communicating, and delivering value to customers in a way that benefits both the customer and the organization.
2. Marketers manage demand for a variety of products and services. They seek to influence different aspects of demand.
3. Marketing must be integrated across the entire organization and affect all customer touchpoints. Both the marketing department and other departments must work together to create great customer experiences.