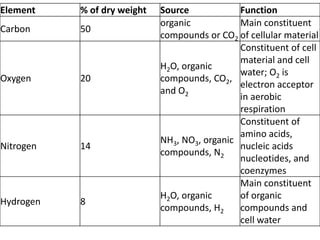
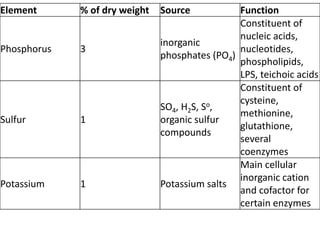
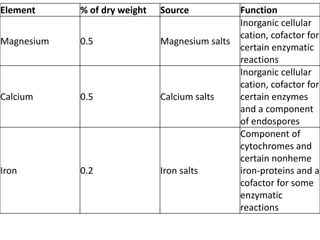
Microbial nutrient requirements refers to the chemicals and elements utilized by bacteria for growth, called nutrients. Bacteria require macroelements like carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and iron which make up over 95% of bacterial cell dry weight. They also require micronutrients like manganese, zinc, cobalt, molybdenum, nickel, and copper in smaller amounts. A balanced mixture of all required nutrients is necessary for bacterial growth, as a shortage of any essential nutrient will limit growth.





![Besides the common macroelements and trace
elements, microorganisms may have particular
requirements that reflect the special nature of their
morphology or environment.
Diatoms need silicic acid (H4SiO4) to construct their
beautiful cell walls of silica [(SiO2)n]. Although most
bacteria do not require large amounts of sodium, many
bacteria growing in saline lakes and oceans depend on
the presence of high concentrations of sodium ion (Na).
It must be emphasized that microorganisms require a
balanced mixture of nutrients. If an essential nutrient is
in short supply, microbial growth will be limited
regardless of the concentrations of other nutrients.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1-1-230121135228-9abfc7e1/85/Microbial-nutrient-requirements-8-320.jpg)