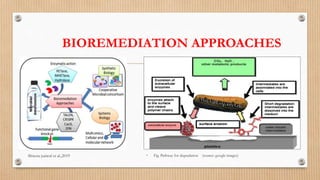
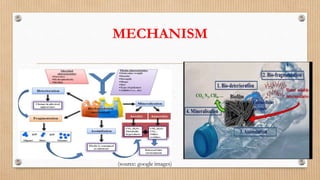
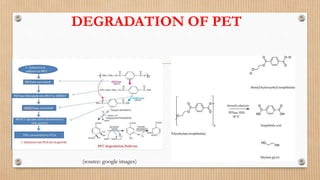
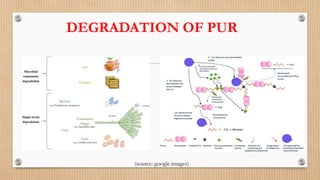
The document discusses microbial degradation of plastics, highlighting various types of plastics and the microorganisms, particularly bacteria and fungi, that can break them down into simpler molecules. It concludes that microbial degradation is a more environmentally friendly option compared to chemical processes, but warns that the diversity of degrading microbes is still limited. Future research should focus on identifying and modifying microbes to enhance their ability to degrade synthetic plastics.