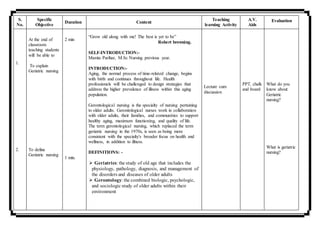
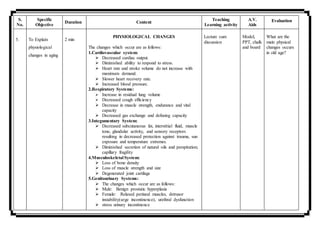
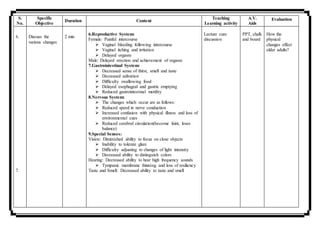
Mamta Parihar presented a 10 minute microteaching session on changes in aging to nursing students. She began with introducing herself and the topic. She defined geriatric nursing and listed factors that influence aging such as heredity, nutrition, and environment. Mamta then described normal age-related physiological changes like decreased cardiac output and lung function. She also discussed psychological changes like social isolation and cognitive changes including delirium and dementia. The session aimed to provide students with knowledge of geriatric nursing and the changes associated with aging.