Embed presentation
Download to read offline

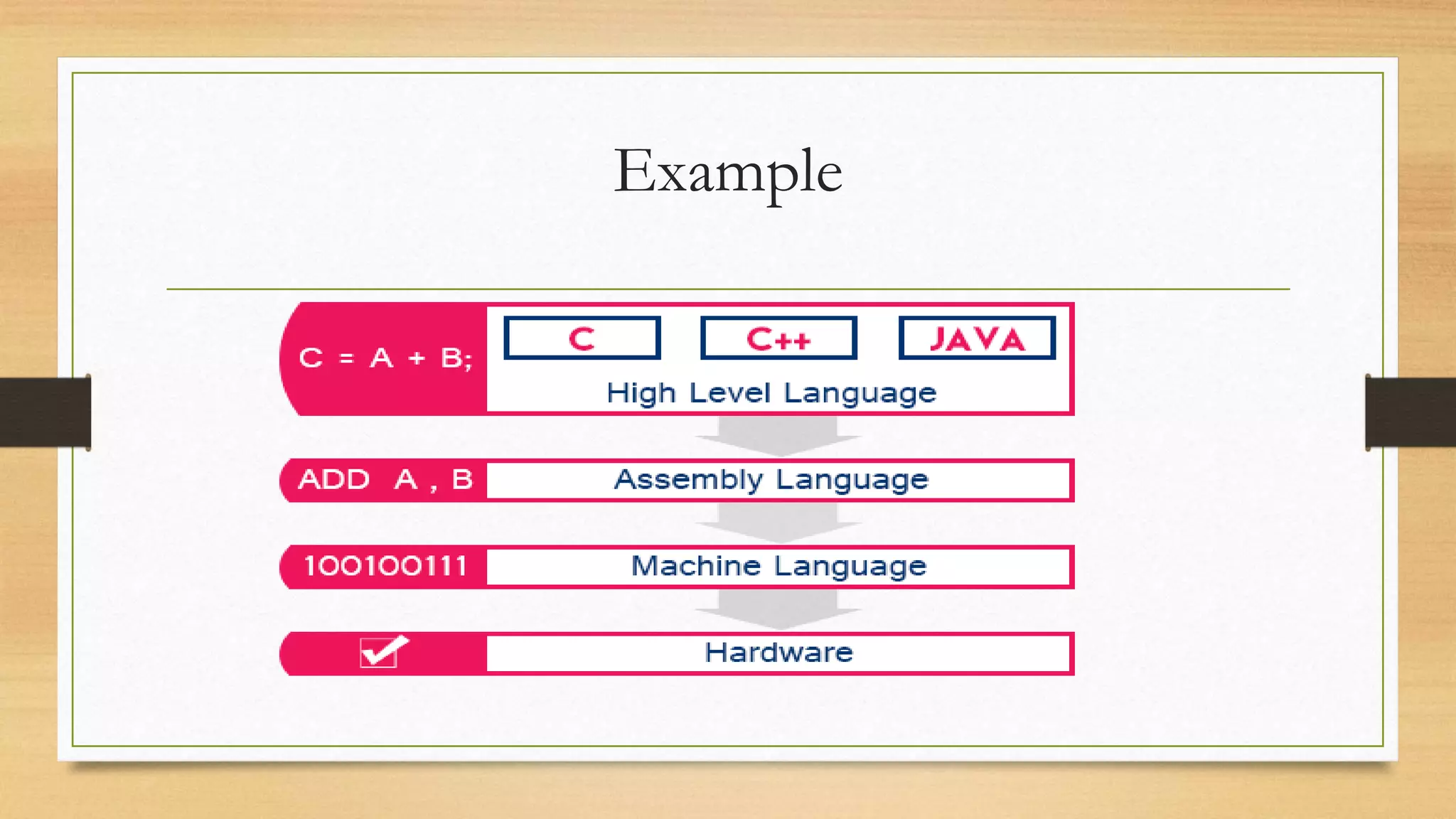

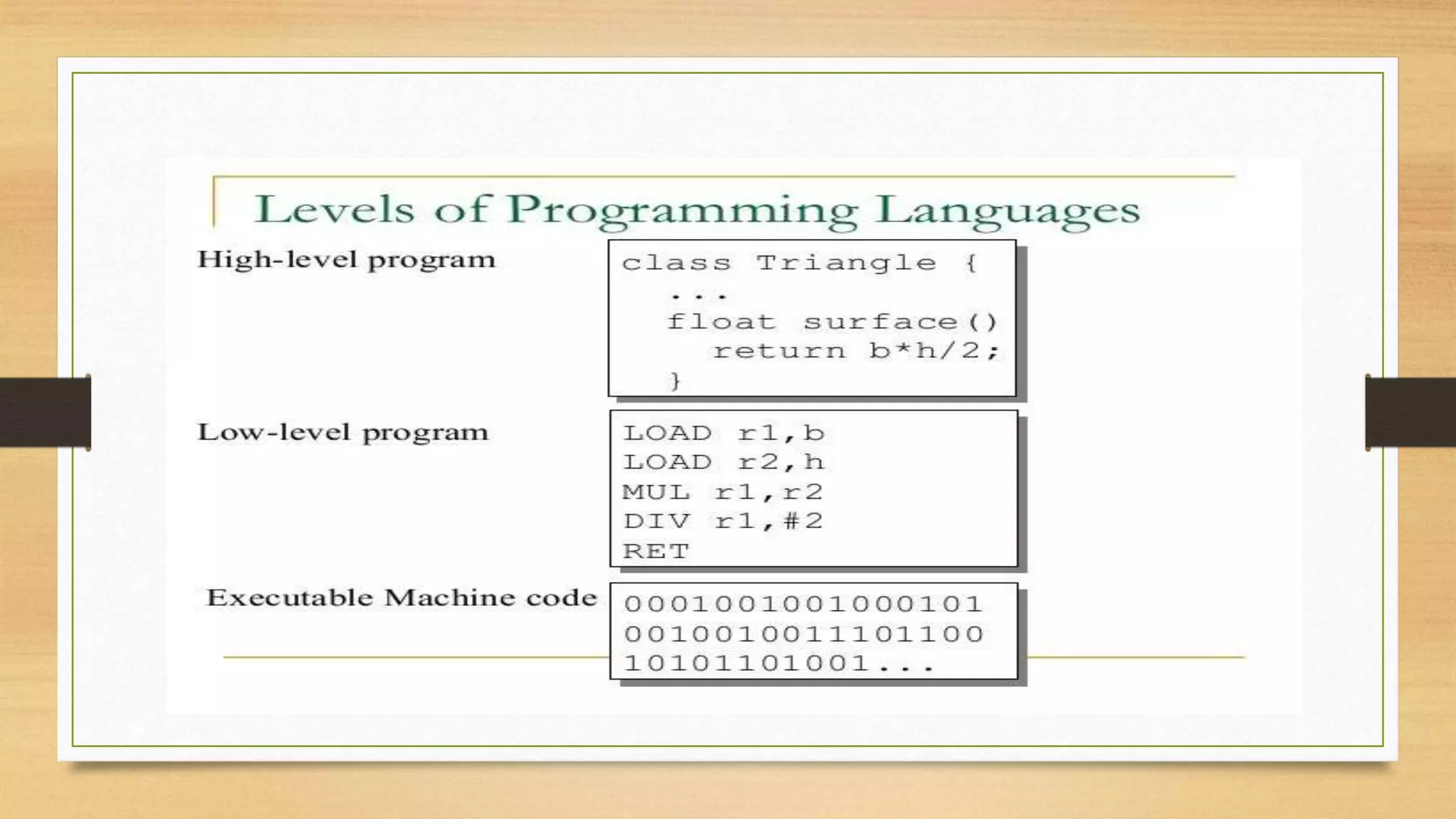


![Programing process :
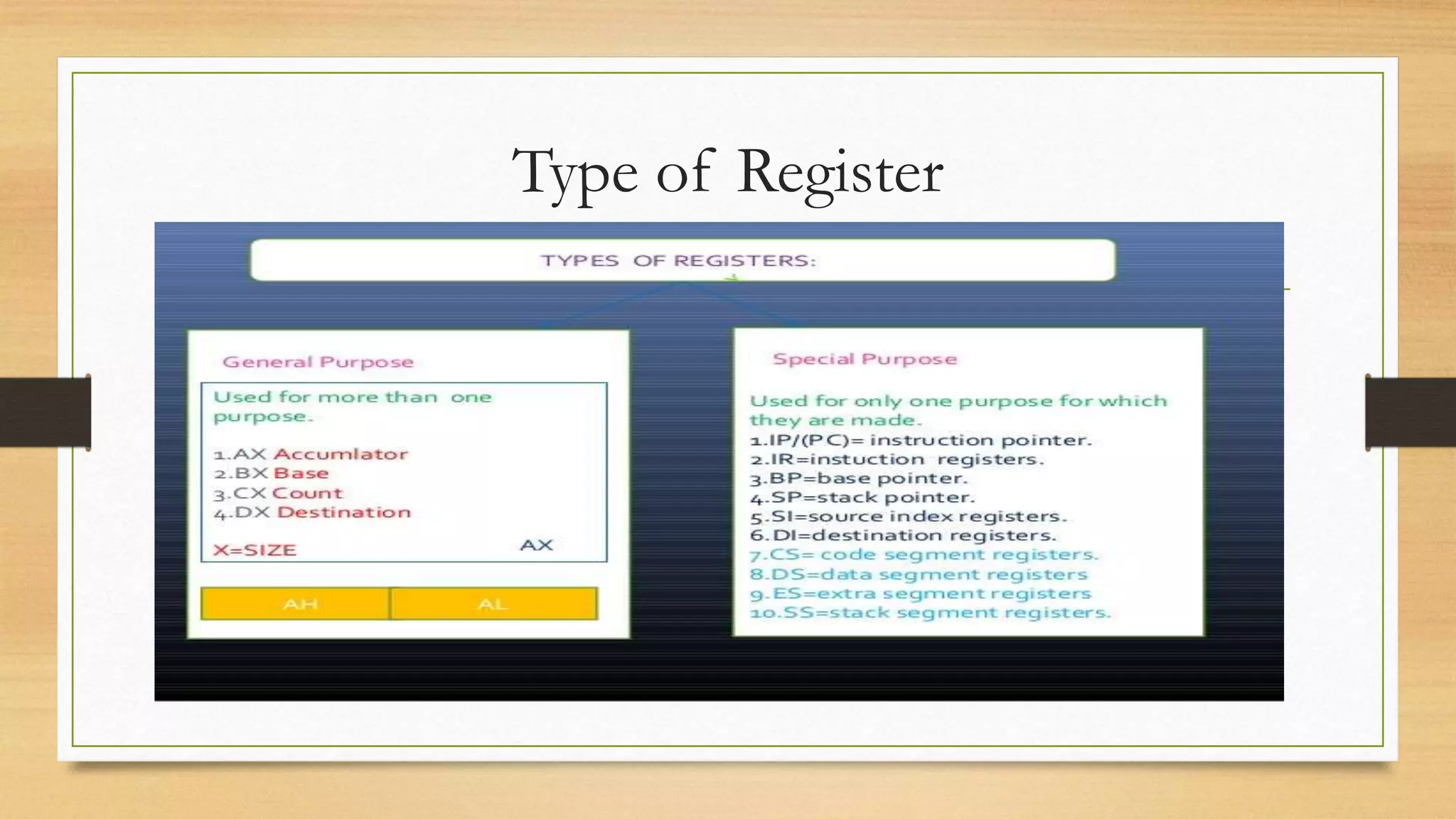
• Register Address: Both Operands are register like as : Reg, Reg.
i.e. Mov bx,dx
• Immediate Register: one Operands and constant term: i.e mov ax, value
• Memory Addressing: access static data directly . i.e reg, [30h]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/micro-lec-03-200729174339/75/Micro-lec-03-12-2048.jpg)

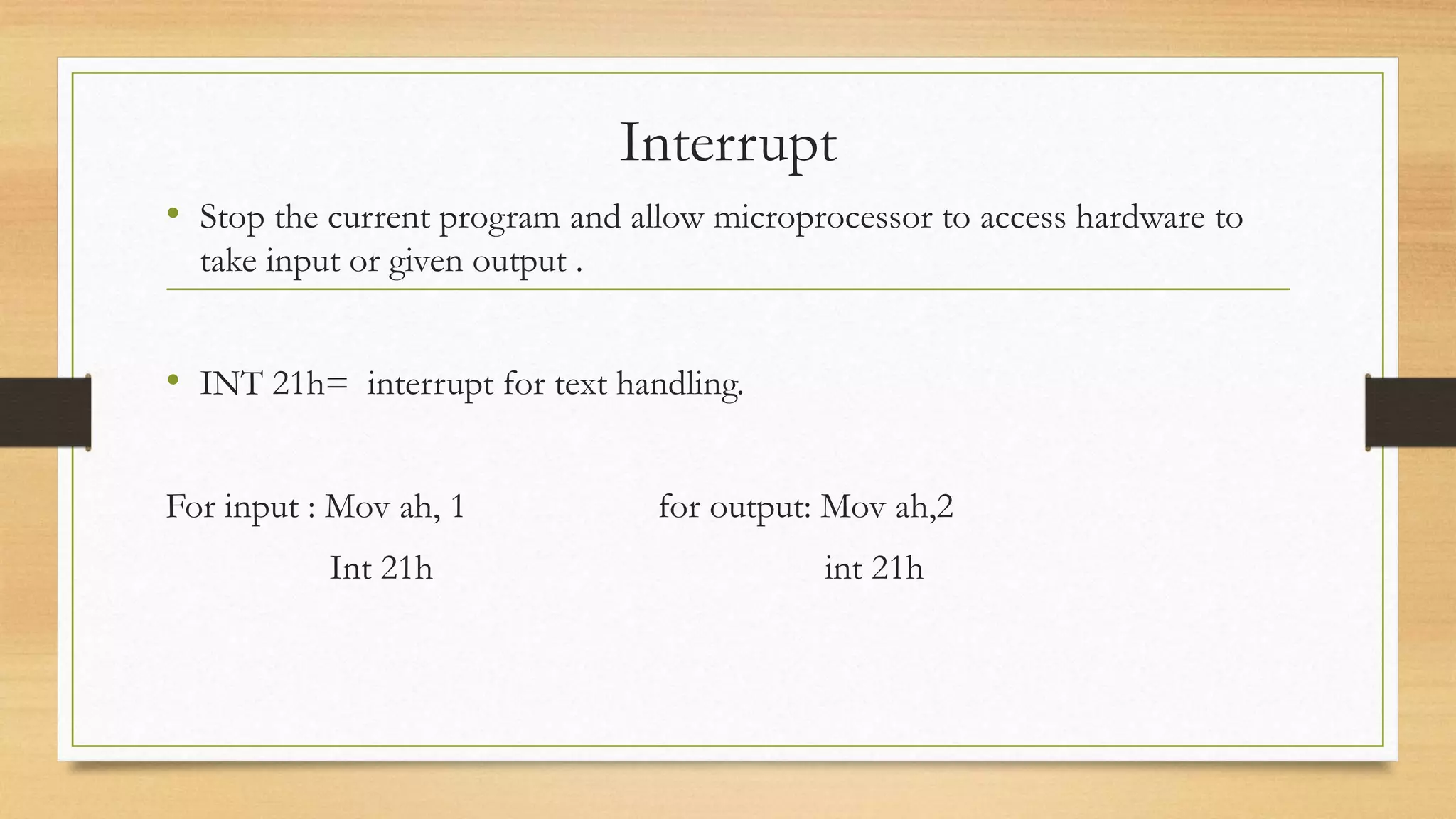


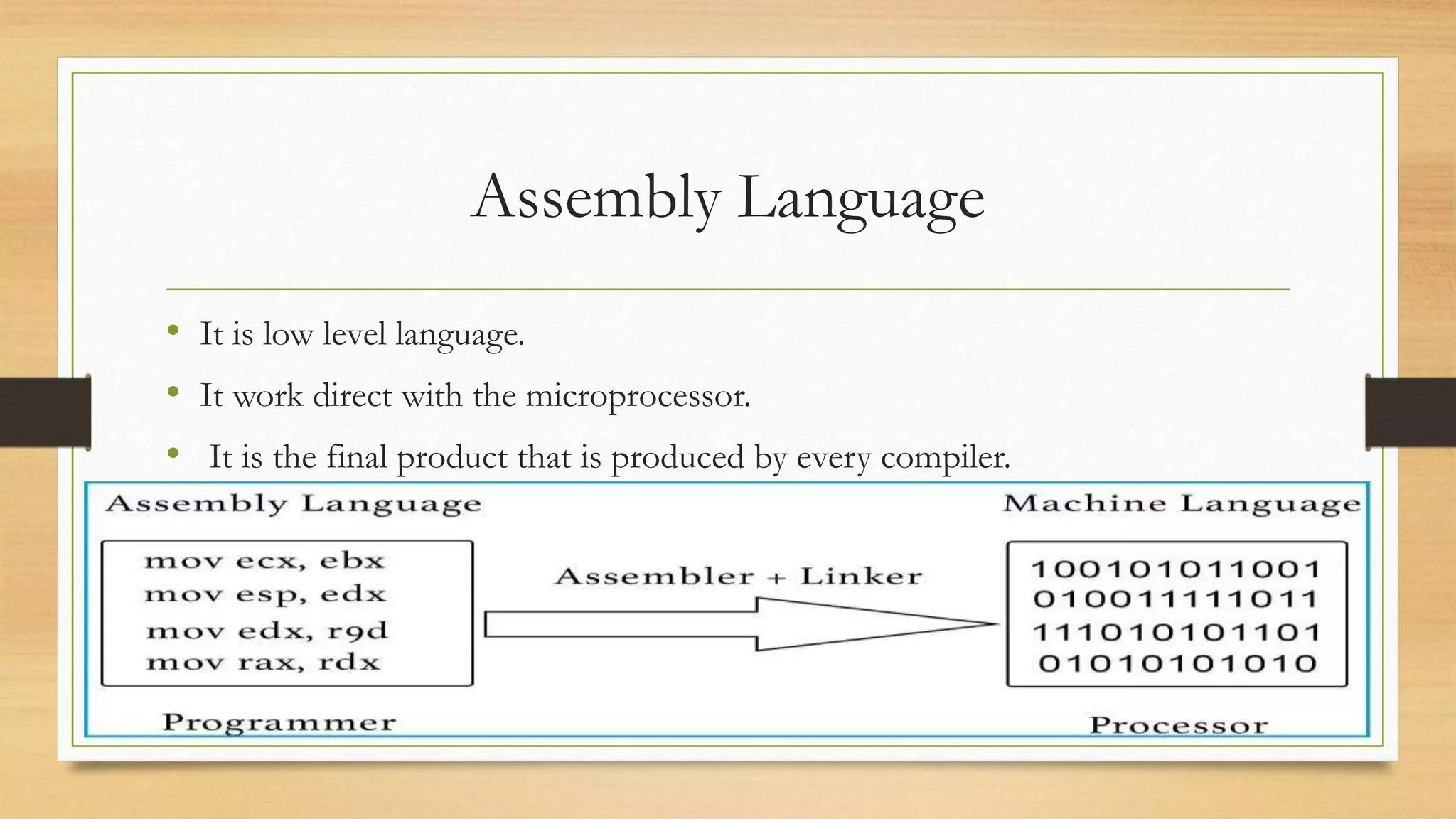
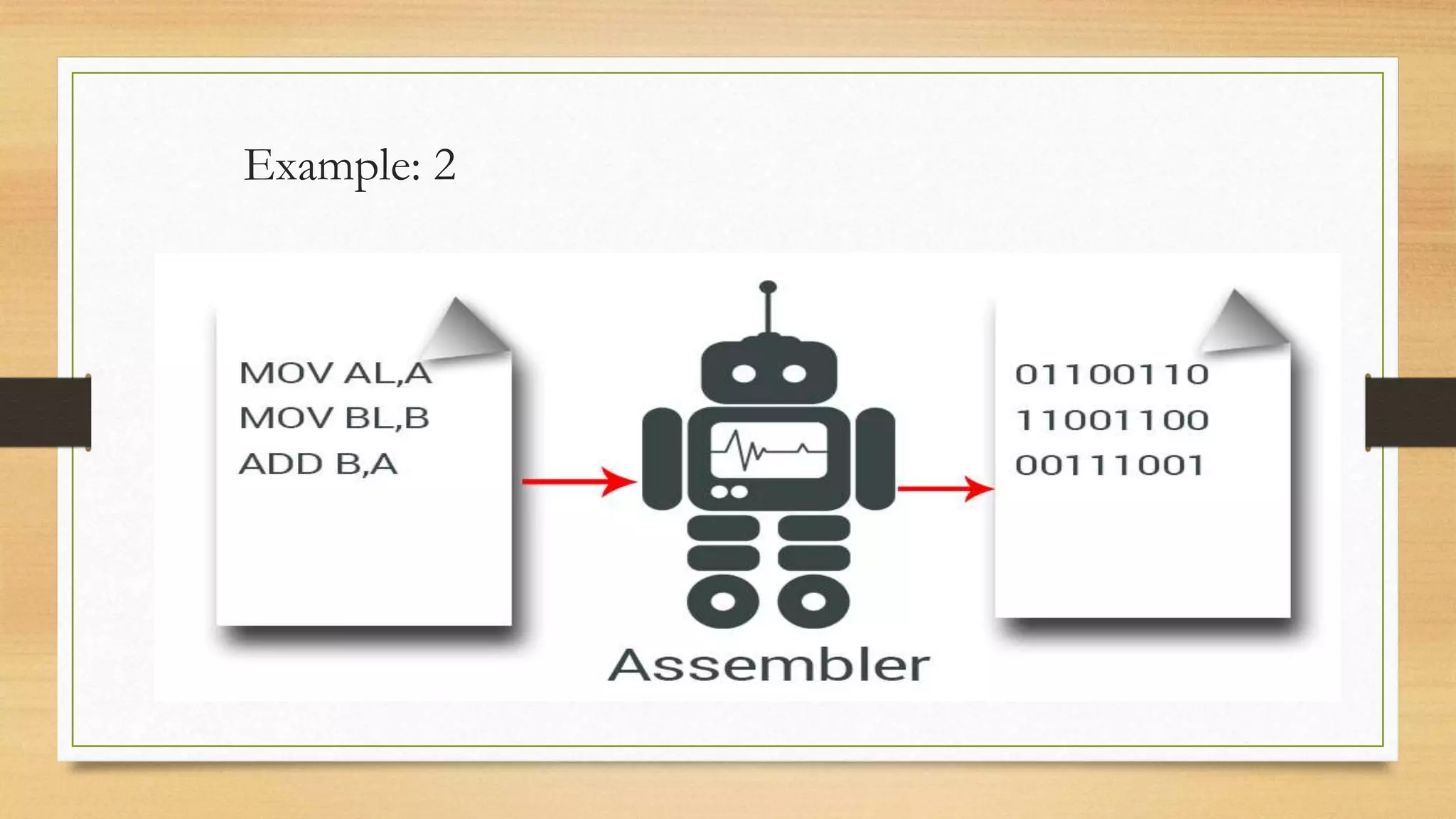
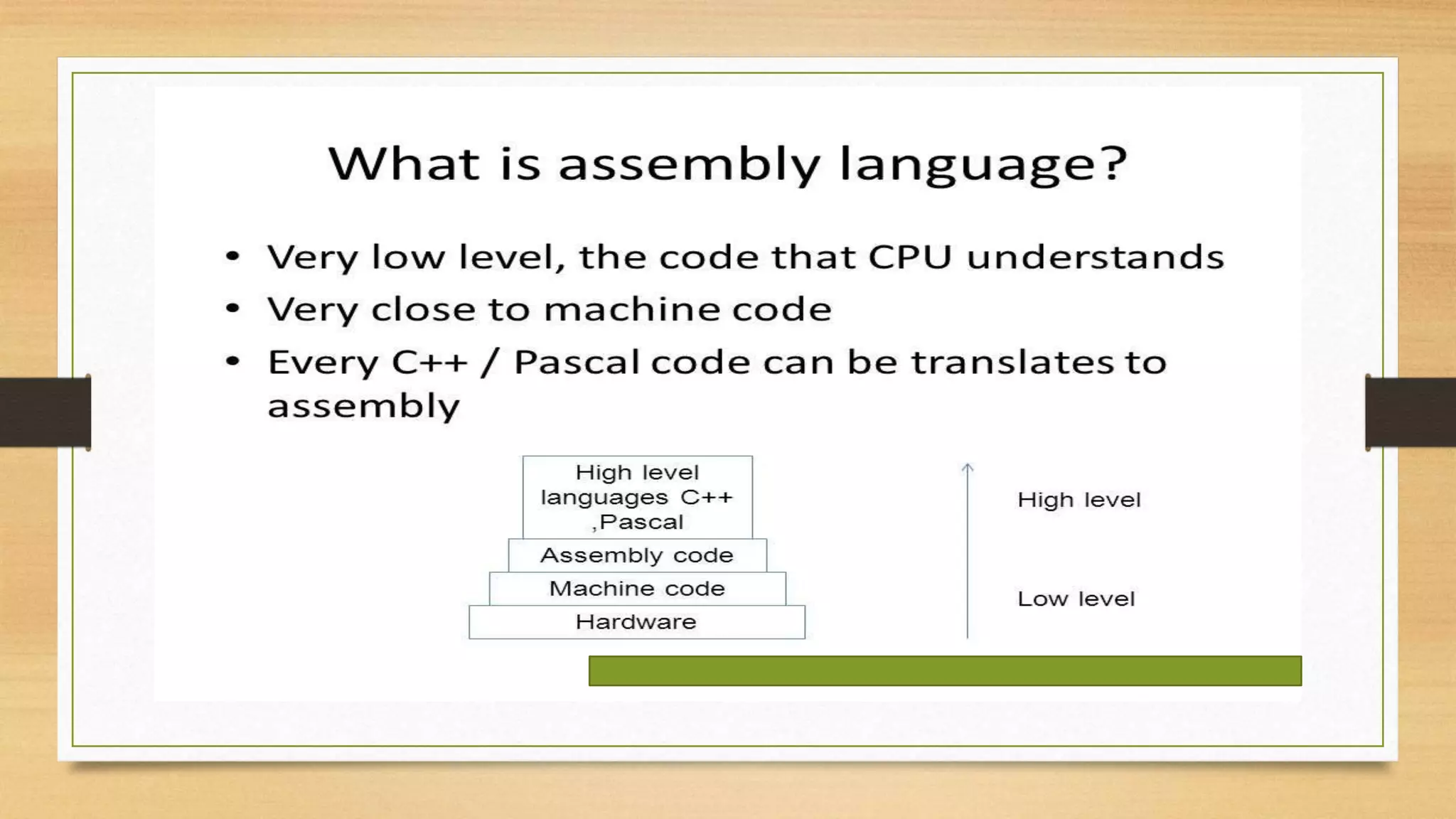
This document discusses assembly language and its relationship to microprocessors. It notes that assembly language works directly with microprocessors, is a low-level language, and is the final product of compiler translations from high-level languages. It provides examples of assembly language programming processes like register addressing and memory addressing. Important concepts like interrupts and input/output functions are also summarized.











![Programing process :
• Register Address: Both Operands are register like as : Reg, Reg.
i.e. Mov bx,dx
• Immediate Register: one Operands and constant term: i.e mov ax, value
• Memory Addressing: access static data directly . i.e reg, [30h]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/micro-lec-03-200729174339/75/Micro-lec-03-12-2048.jpg)


